Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-161
An Unexpected Coronary Haematoma
By Kim Fong Ng, Glendon Seng Lau, Kamaraj Selvaraj, Asri Ranga, Abd Kahar Abd Ghapar
Presenter
Kim Fong Ng
Authors
Kim Fong Ng1, Glendon Seng Lau2, Kamaraj Selvaraj3, Asri Ranga3, Abd Kahar Abd Ghapar3
Affiliation
Sultanah Aminah Hospital, Malaysia1, Hospital Sultan Idris Shah Serdang, Malaysia2, Sultan Idris Shah Serdang Hospital, Malaysia3,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-161
IMAGING AND PHYSIOLOGIC LESION ASSESSMENT - Imaging: Intravascular
An Unexpected Coronary Haematoma
Kim Fong Ng1, Glendon Seng Lau2, Kamaraj Selvaraj3, Asri Ranga3, Abd Kahar Abd Ghapar3
Sultanah Aminah Hospital, Malaysia1, Hospital Sultan Idris Shah Serdang, Malaysia2, Sultan Idris Shah Serdang Hospital, Malaysia3,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Madam S
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 70-year-old lady, non-smoker with background history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension and
end stage renal disease on regular haemodialysis presented with multiple admissions of unstable angina and NSTEMI.
Patient developed hypotension due to poor tolerability with haemodialysis.
Her BP was 110/62 mmHg and pulse rate was 65/min.
Respiratory examination revealed equal breath sound bilaterally.
end stage renal disease on regular haemodialysis presented with multiple admissions of unstable angina and NSTEMI.
Patient developed hypotension due to poor tolerability with haemodialysis.
Her BP was 110/62 mmHg and pulse rate was 65/min.
Respiratory examination revealed equal breath sound bilaterally.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Blood investigations showed Hb of 11.1g/dl, creatinine 512 µmol/L,Troponin T 826.Echocardiography examination revealed reduced left ventricular function with ejection fraction of 45%, dilated left atrial, global hypokinetic and there was no clot or thrombus observed. There was also no pericardial effusion observed.ECG showed LVH pattern and T wave inversion V2 to V6.Chest X ray showed cardiomegaly.
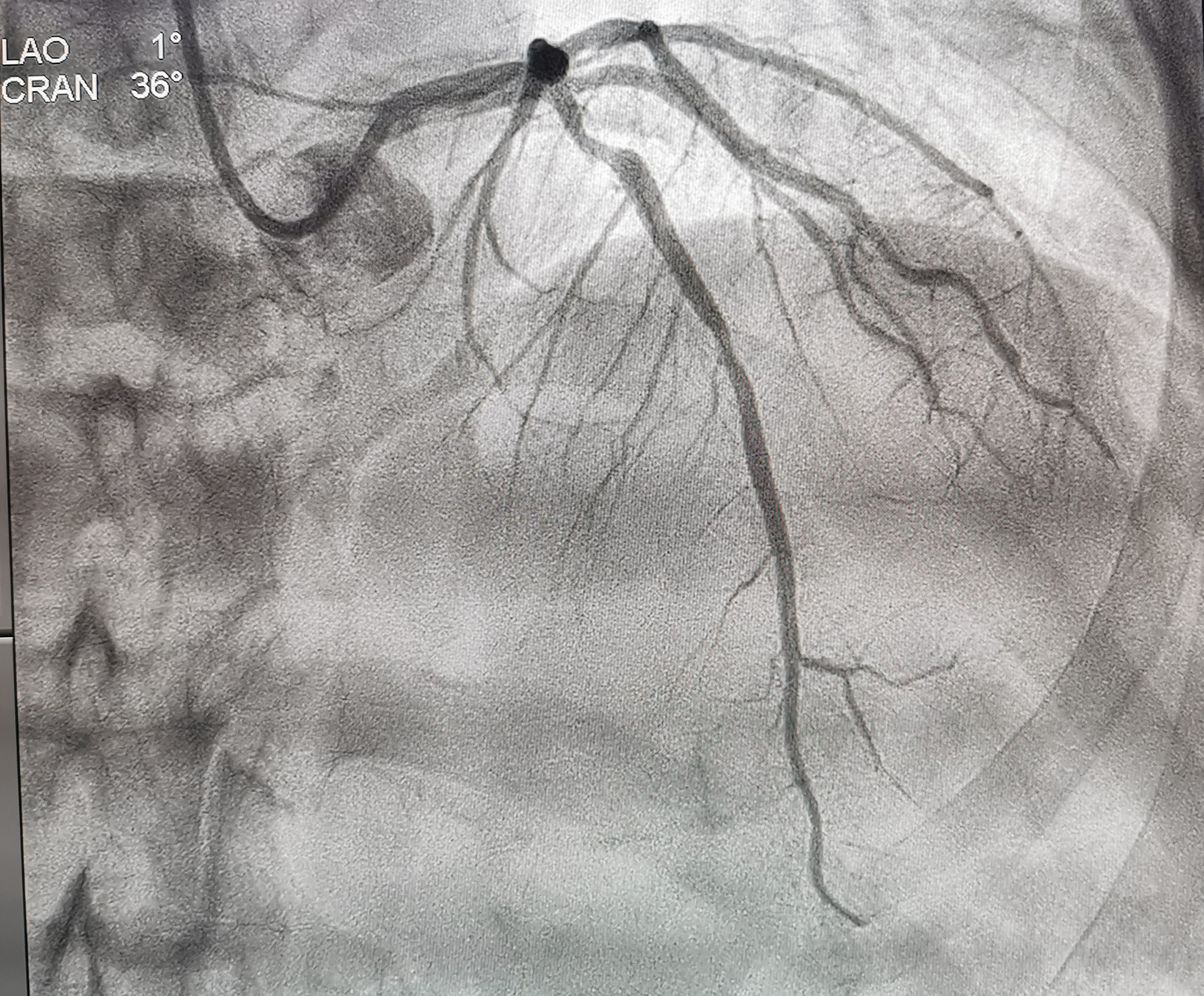
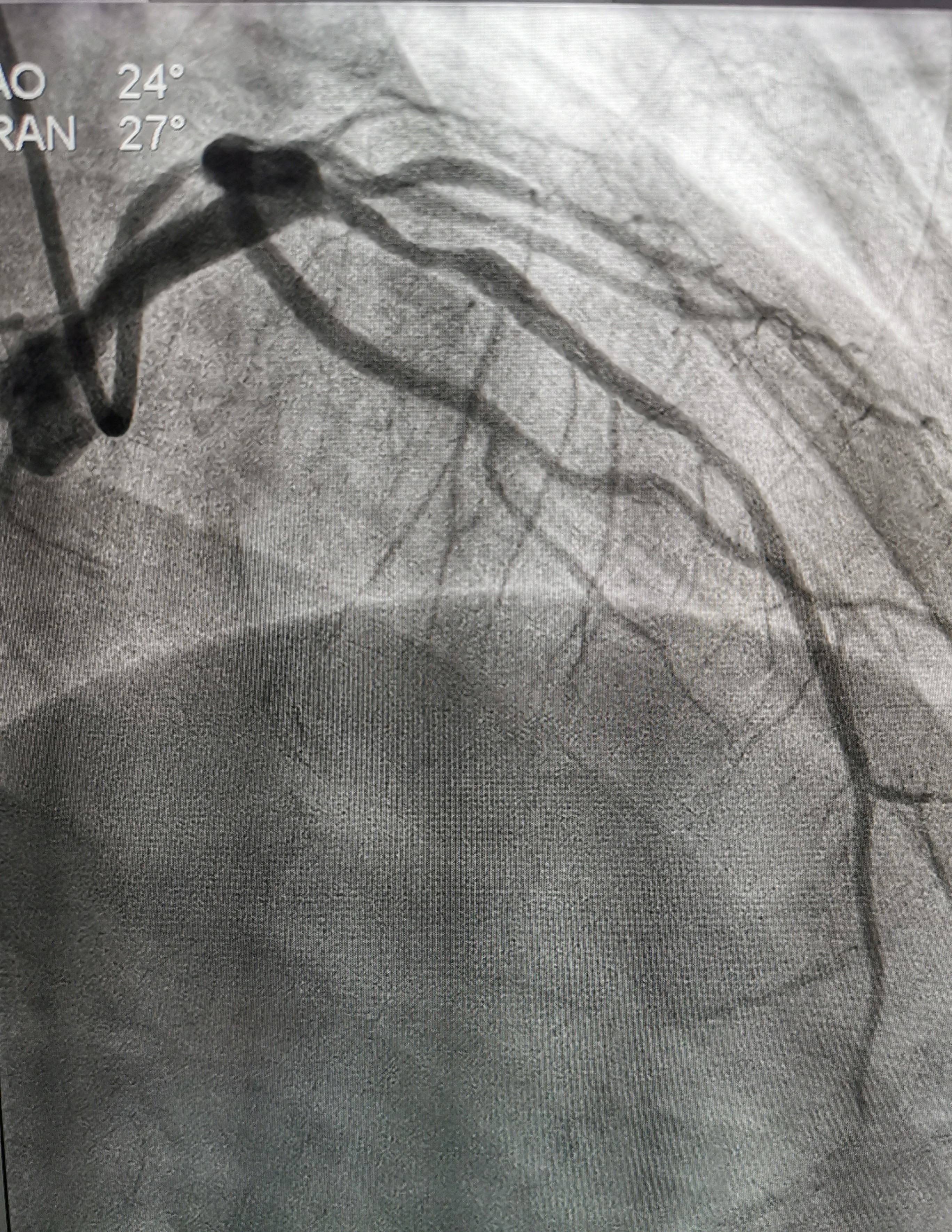


Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiography showed normal LMT , 70% to 80% stenosis at proximal LAD, normal Lcx and RCA.we proceeded with PCI to LAD
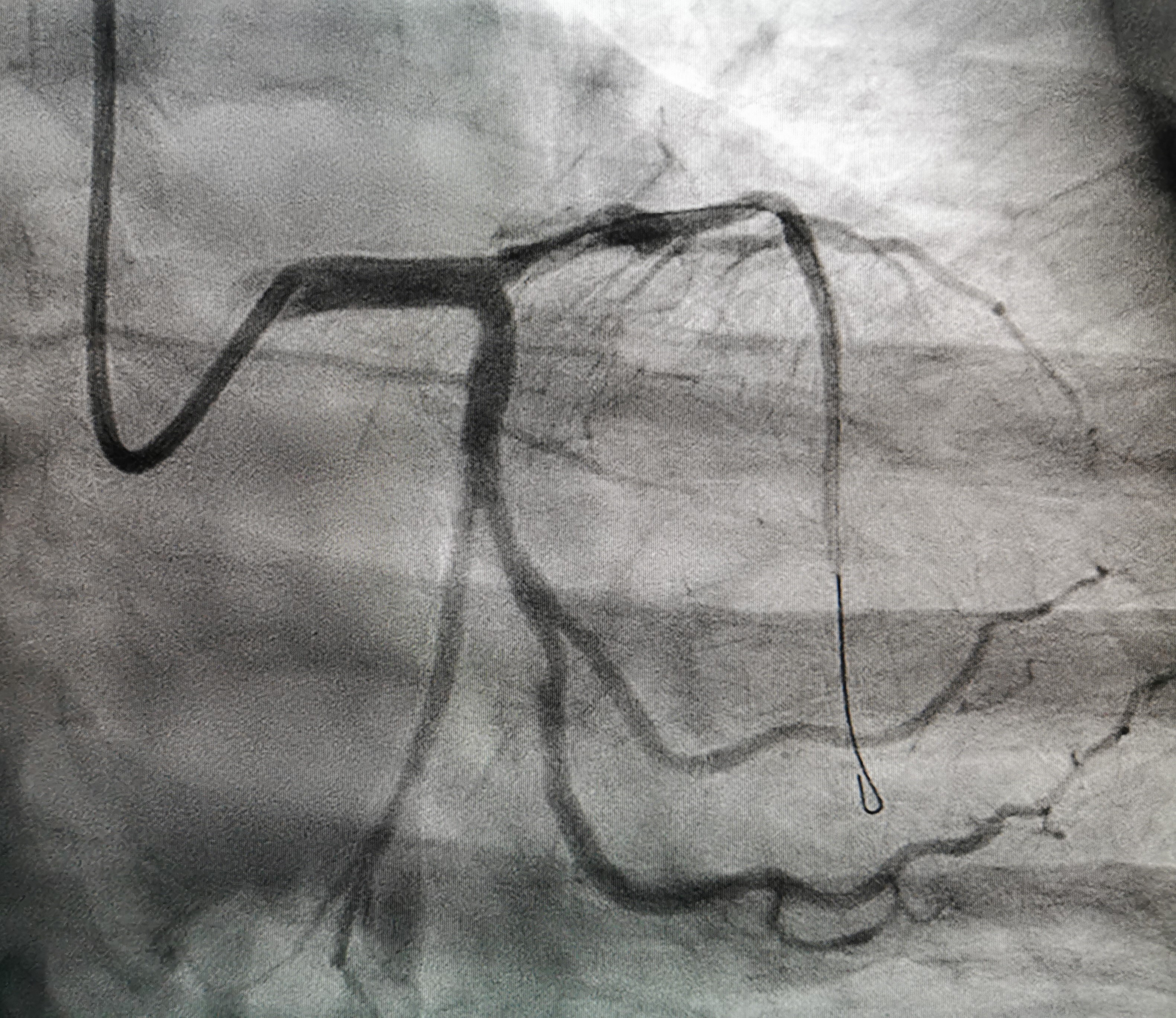



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
The right radial artery (RRA) was punctured.
A 6Fr EBU 3.0 was used to engage LMT with good support.
A sion blue wire was inserted into LAD
The proximal LAD was predilated by NC 2.5x12mm balloon.
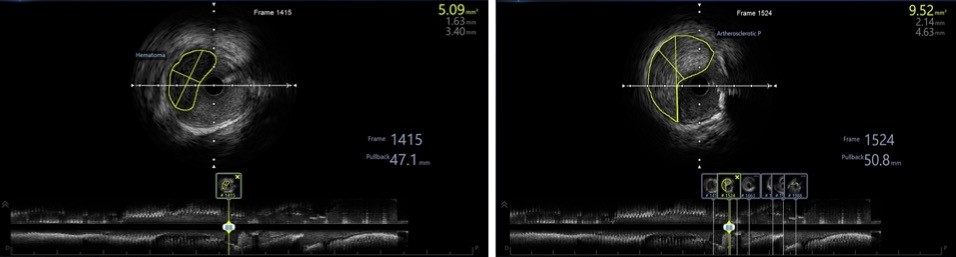
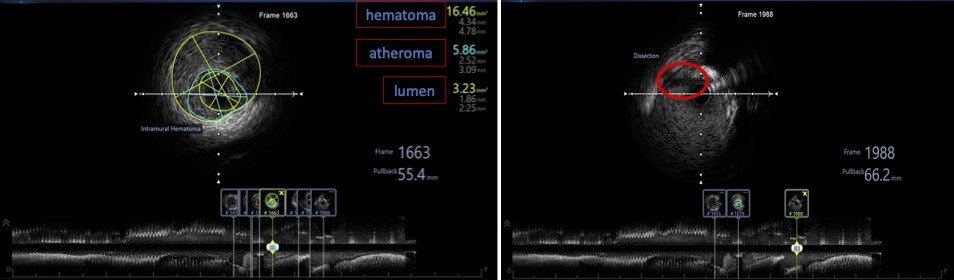
We noted a stained at around proximal LAD. Thus we decided to proceed with IVUS.
IVUS showed intramural haematoma and artherosclerotic plaque at proximal LAD.
LAD lesions was treated with Synergy megatron (4.0x28mm) up to 14 atm.
Postdilated LAD with 4.0x15mm NC balloon at 18 atm.
IVUS was performed again.
Decided postdilate further with 4.5x15mm NC balloon at 14 atm.
Repeated IVUS and showed good result.
Patient undergo heamodialysis well and her functional status improved remarkably after revascularization.
A 6Fr EBU 3.0 was used to engage LMT with good support.
A sion blue wire was inserted into LAD
The proximal LAD was predilated by NC 2.5x12mm balloon.
We noted a stained at around proximal LAD. Thus we decided to proceed with IVUS.
IVUS showed intramural haematoma and artherosclerotic plaque at proximal LAD.
LAD lesions was treated with Synergy megatron (4.0x28mm) up to 14 atm.
Postdilated LAD with 4.0x15mm NC balloon at 18 atm.
IVUS was performed again.
Decided postdilate further with 4.5x15mm NC balloon at 14 atm.
Repeated IVUS and showed good result.
Patient undergo heamodialysis well and her functional status improved remarkably after revascularization.

Case Summary
Following postdilatation with a NC balloon, there was residual contrast staining on angiography. With help of IVUS, it revealed an intramural hematoma.We decided to stent over the hematoma with proper stent’s size with help of IVUS.Final IVUS revealed that the stent was well opposed and the intramural hematoma was covered with no evidence of progression.Eccentric lesions, which compromise approximately 70% of coronary lesions are more likely to develop intramural hematomas.Intramural hematomas can occur even in a simple lesion during PCI. IVUS should be considered the gold standard in the diagnosis of intramural hematoma


