Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-078
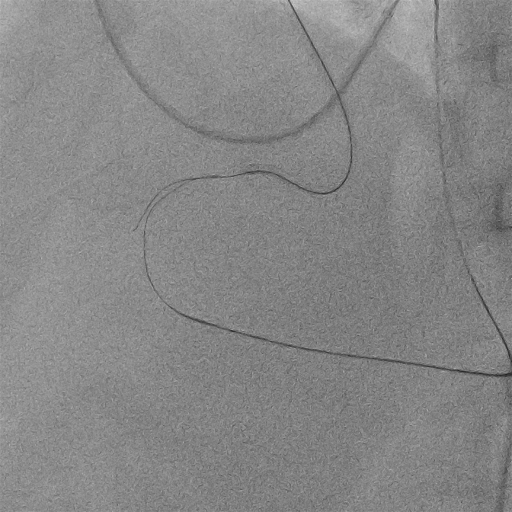
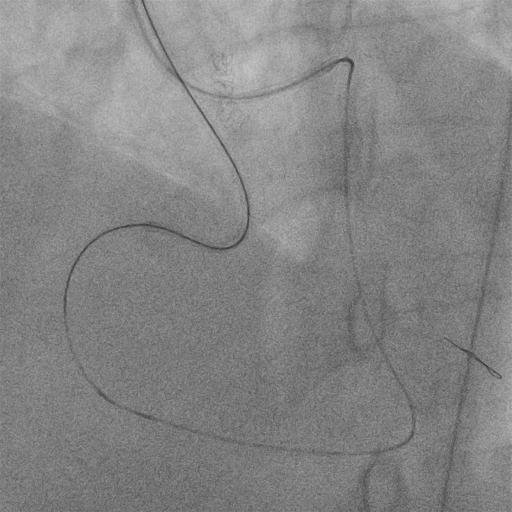
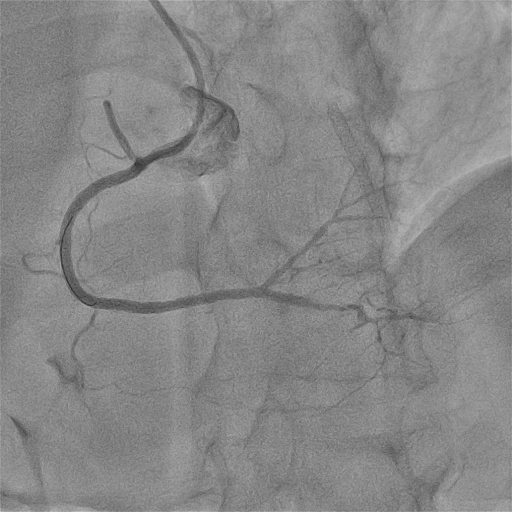
Retrograde Recanalization of Chronic Occlusion of the Right Coronary Artery by Tip-in Technique
By Liudmila Ulyanova, Emelianov Pavel, Alexey Sozykin, Alexandr Shlykov, Natalya Novikova, Evgeniy Averin
Presenter
Authors
Affiliation
Retrograde Recanalization of Chronic Occlusion of the Right Coronary Artery by Tip-in Technique
Liudmila Ulyanova1, Emelianov Pavel2, Alexey Sozykin3, Alexandr Shlykov4, Natalya Novikova3, Evgeniy Averin3
Scientific Clinical Center 2 Petrovsky National Research Center of Surgery, Russian Federation1, Scientific Clinical Center 2 Petrovsky National Research Center of Surgery NRCS, Russian Federation2, Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Russian Federation3, Petrovsky National Research Centre of Surgery, Russian Federation4,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
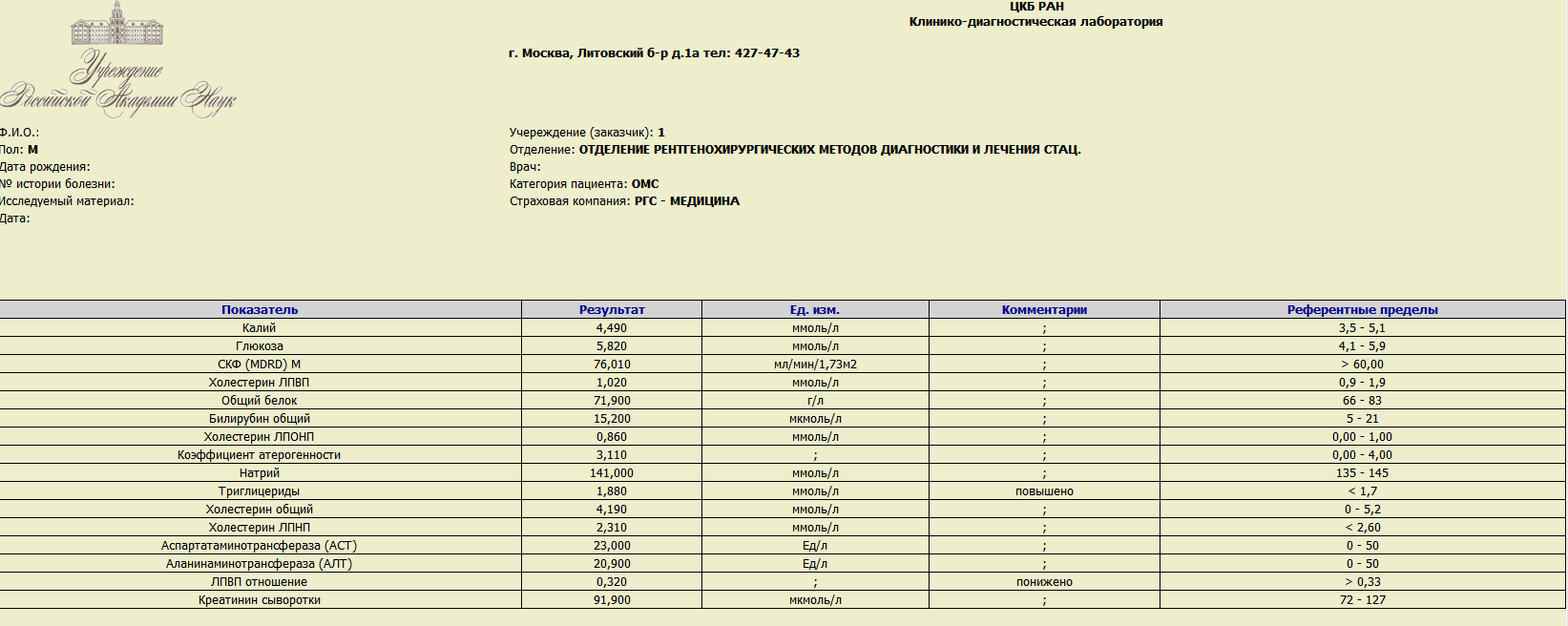
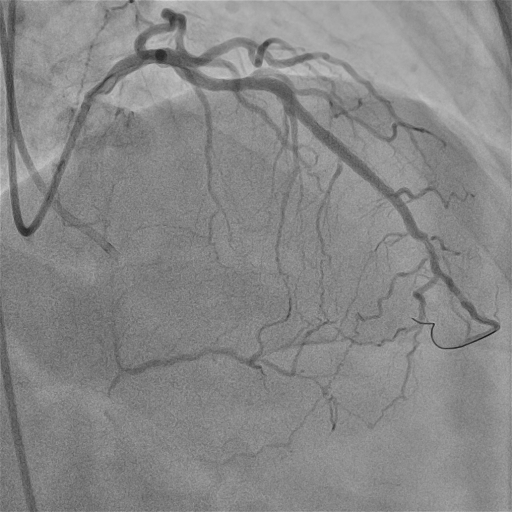
Relevant Catheterization Findings
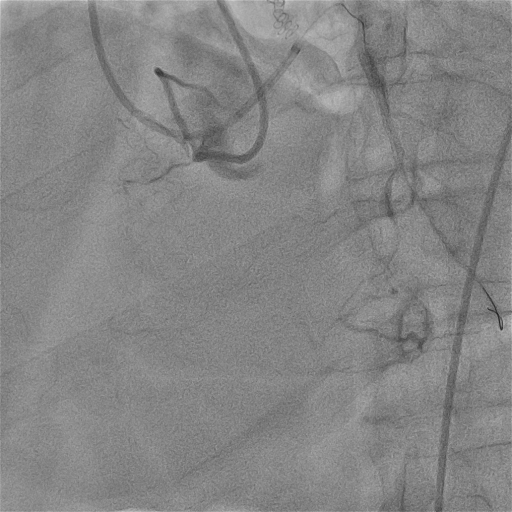
Interventional Management
Procedural Step