Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-147
An Interesting Case Report: Delayed Presentation of Presumed Right Infected Groin Hematoma Originating From Right Common Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm
By Khor Leet Ming, Yee Sin Tey, Norhaliza Am Haris, Kogulakrishnan Kaniappan, Kumara Gurupparan Ganesan, Shaiful Azmi Yahaya
Presenter
Khor Leet Ming
Authors
Khor Leet Ming1, Yee Sin Tey2, Norhaliza Am Haris2, Kogulakrishnan Kaniappan2, Kumara Gurupparan Ganesan2, Shaiful Azmi Yahaya2
Affiliation
Hospital Pulau Pinang, Malaysia1, National Heart Institute, Malaysia2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-147
ENDOVASCULAR - Complications (Endovascular)
An Interesting Case Report: Delayed Presentation of Presumed Right Infected Groin Hematoma Originating From Right Common Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm
Khor Leet Ming1, Yee Sin Tey2, Norhaliza Am Haris2, Kogulakrishnan Kaniappan2, Kumara Gurupparan Ganesan2, Shaiful Azmi Yahaya2
Hospital Pulau Pinang, Malaysia1, National Heart Institute, Malaysia2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
K.V
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
55 year old gentleman, underlying diabetes mellitus, hypertension and coronary artery disease with history of recent angioplasty to right coronary artery done via right femoral artery, presented two weeks later with painful right groin swelling for one week with pus discharge but no fever. He took a course of antibiotics but the swelling was increasing in size. He was admitted, started on intravenous antibiotics and treated as infected right groin hematoma to rule out pseudoaneurysm or abscess.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Ultrasound right groin: Right groin hematoma with subcutaneous edema and focal deep vein thrombosis of right common femoral vein, no pseudoaneurysm
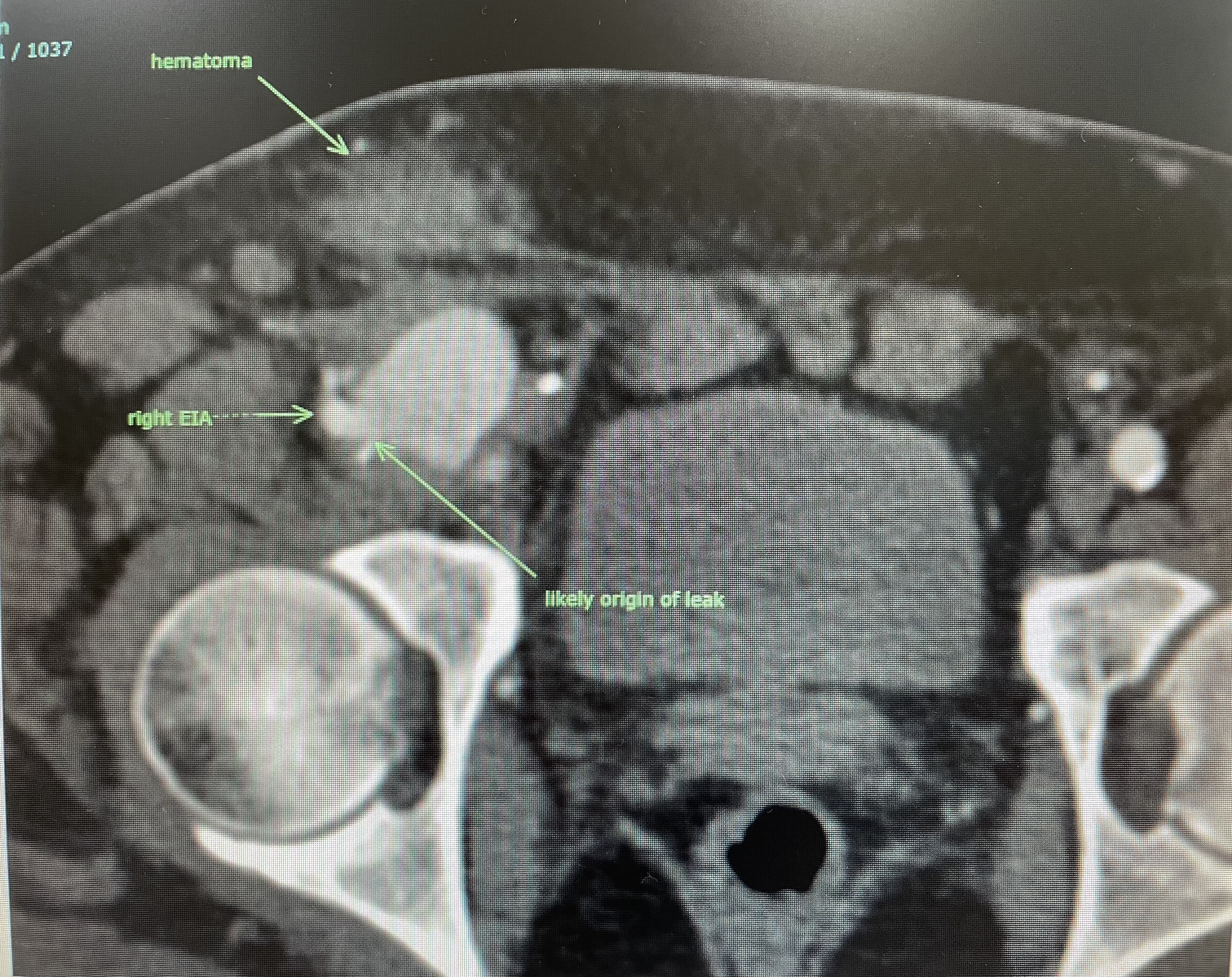
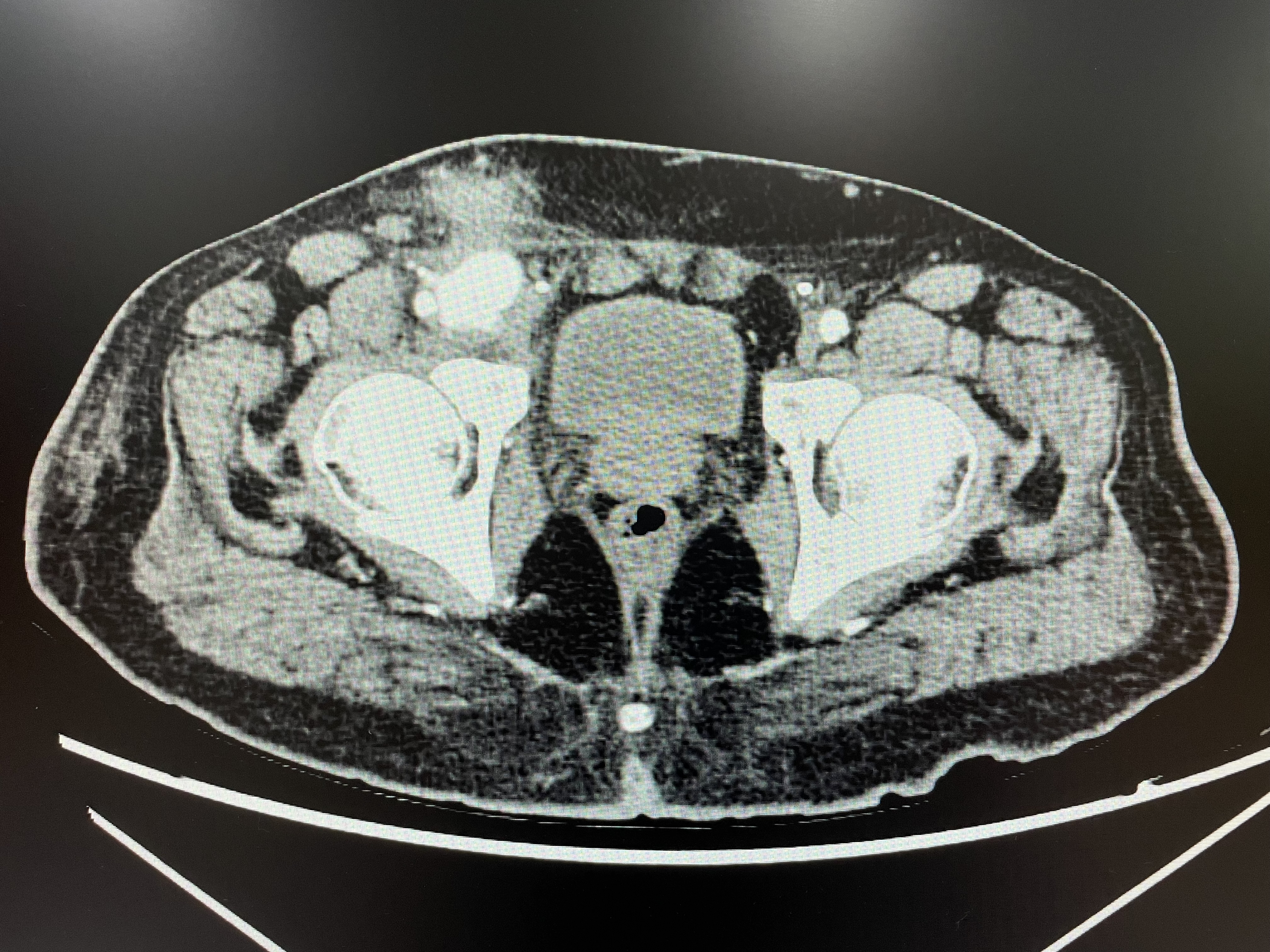
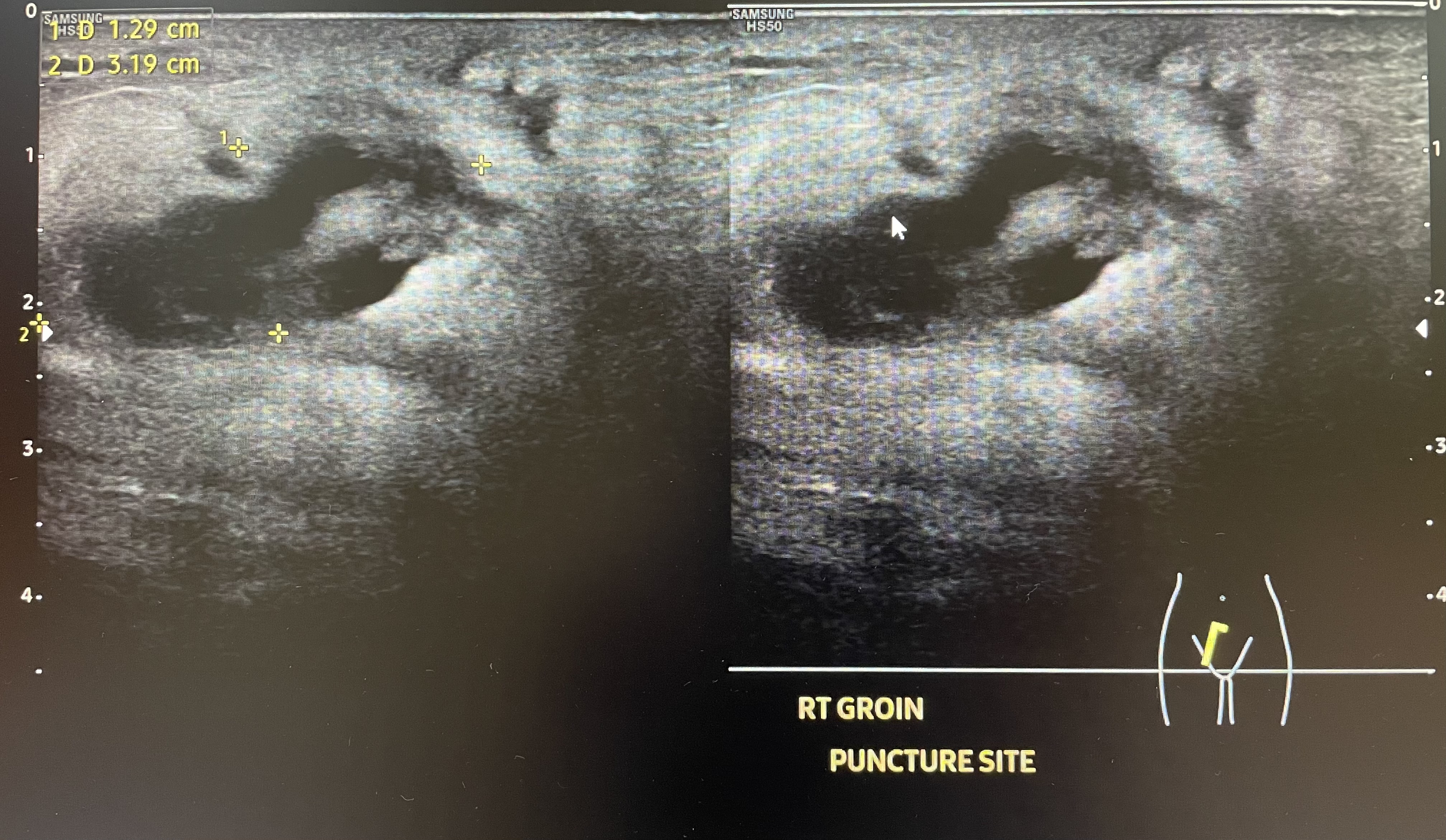



Relevant Catheterization Findings
Contrast leak from the distal right external iliac artery/proximal right common femoral artery forming a focal area of collection in connection with main artery likely a pseudoaneurysm
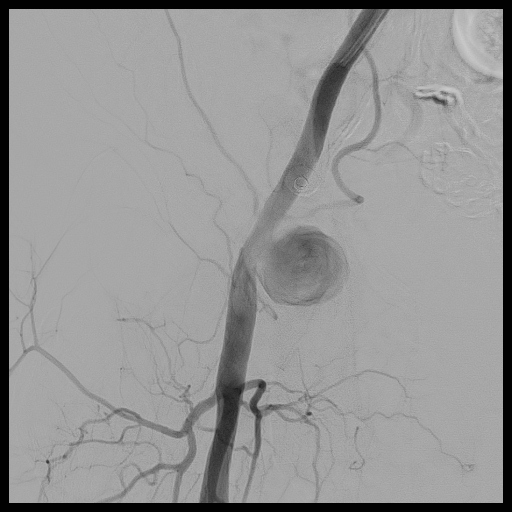
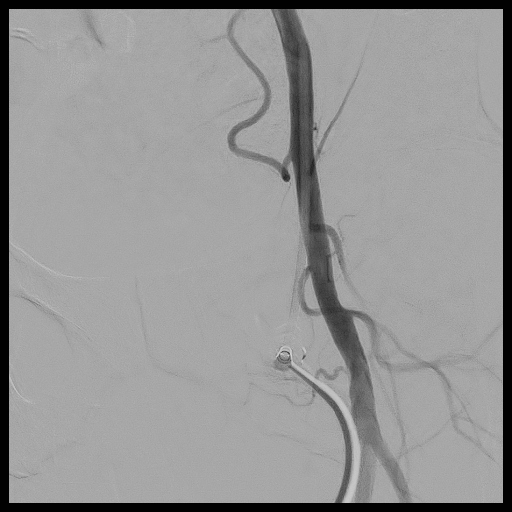


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) of right common femoral artery pseudoaneurysm
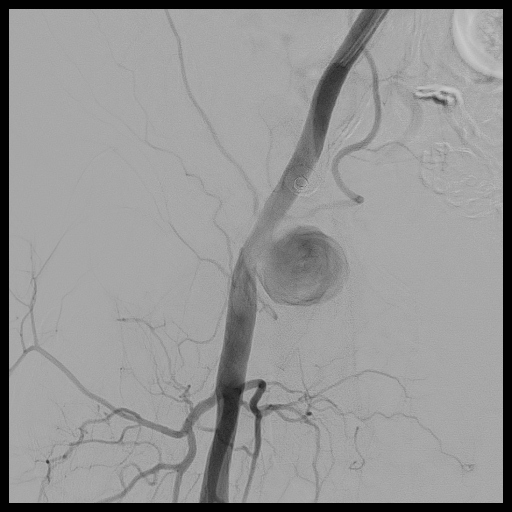
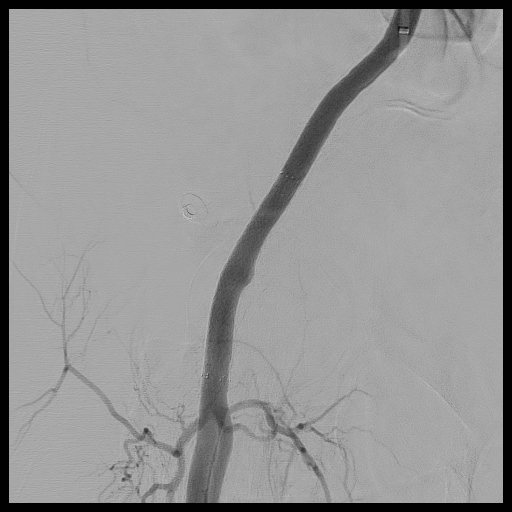
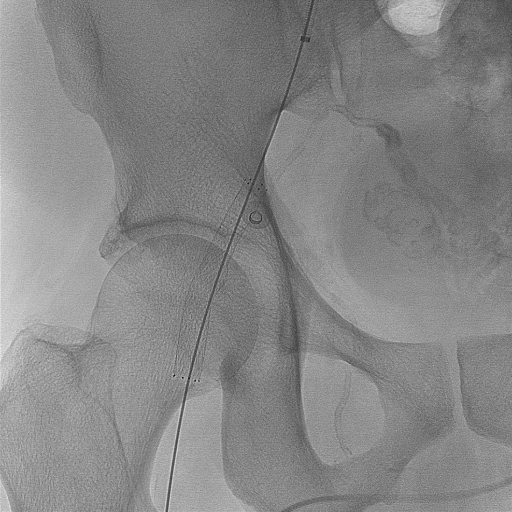



Case Summary
This case illustrates the need for high index suspicion of pseudoaneurysm in the setting of persistent groin hematoma post-catheterization despite delayed appearance of hematoma. There is limitation in the sensitivity of ultrasound doppler in detecting pseudoaneurysm in some cases. The incidental finding of focal common femoral vein DVT may be due to the compression effect of the superficial hematoma over the vein (provoked DVT). Several treatment options for pseudoaneurysm have been utilized to avoid the risks of open surgery. Percutaneous endovascular treatment using a covered stent maybe a safe and feasible method for the treatment of pseudoaneurysm.


