Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-074
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection Sequlae
By Norhaliza Am Haris
Presenter
Norhaliza Am Haris
Authors
Norhaliza Am Haris1
Affiliation
National Heart Institute, Malaysia1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-074
CORONARY - Chronic Total Occlusion
Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection Sequlae
Norhaliza Am Haris1
National Heart Institute, Malaysia1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
MJ
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
MJ, a 59 years old lady with a known case of spontaneous coronary artery dissection of proximal left anterior descending artery in 2016 treated with coronary angioplasty, presented with recurrent chest pain and exertional dyspnea. Vital signs were stable and physical examinations revealed an obese lady with normal physical findings. She underwent coronary angioplasty of the proximal LAD spontaneous dissection with drug-eluting stent however complicated with mild perforation, discharged well.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
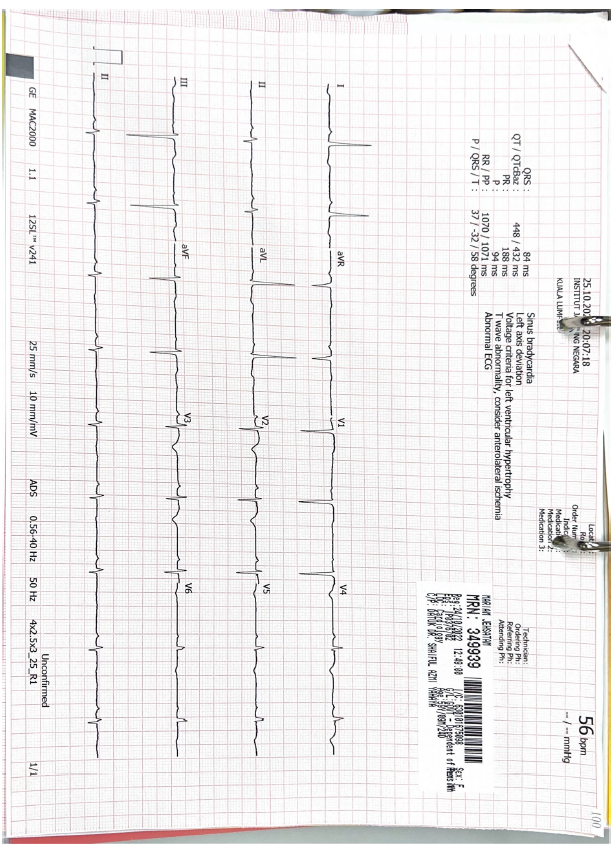
ECG: Sinus rhythm with new T wave inversion anterior leads
CTA Coronary: Severe peri-stent stenosis at ostial LAD with possible significant ISR within the proximal LAD stent. Normal LCX and RCA.
Echocardiogram: Mildly dilated LV with reduced LV function LVEF 39%, hypokinesia at LAD territory. No significant valves abnormality.
FBC normal. Hb 13.1g/dl, platelet 194x10^9Renal profile normal. Creatinine 67, eGFR>60Troponin T 10 pg/mlHbA1c 5.4%LDL-C 1.7mmol/L
 ECHO.avi
ECHO.avi
 ECHO2.avi
ECHO2.avi
CTA Coronary: Severe peri-stent stenosis at ostial LAD with possible significant ISR within the proximal LAD stent. Normal LCX and RCA.
Echocardiogram: Mildly dilated LV with reduced LV function LVEF 39%, hypokinesia at LAD territory. No significant valves abnormality.
FBC normal. Hb 13.1g/dl, platelet 194x10^9Renal profile normal. Creatinine 67, eGFR>60Troponin T 10 pg/mlHbA1c 5.4%LDL-C 1.7mmol/L

Relevant Catheterization Findings
LMS: short, normalLAD: severe disease ostial segment with CTO ISR proximal LAD stentLCX: normalRCA: mild disease, collaterals to septal LAD
Impression: Severe single vessel disease with CTO ISR proximal LAD stent
 pre1.avi
pre1.avi
 pre2.avi
pre2.avi
Impression: Severe single vessel disease with CTO ISR proximal LAD stent
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Hybrid approach/dual injections techniqueEBU 3.0 6Fr, attempted to cross the lesion with Fielder XT then Gaia second with Caravel microcatheter. Lesion crossed.Predilated with RYUREI 1.25x10mm, EMERGE MONORAIL 2.0x20mm. Wire changed to run-through floppy.IVUS done noted distal wire at the false lumen of previous dissection plane from the the distal stent edge of proximal LAD; non-flow limiting. Stents well opposed with neointimal proliferation and minimal calcification.Predilated further with WEDGE NC 3.0x15mm @10atm. DCB from distal to proximal LAD with SEQUENT PLEASE NEO 2.0x30mm overlapped with 2.75x30mm, 3.0x30mm proximally. Noted non flow limiting dissection distally, TIMI 3 flow. Asymptomatic.Overlapped stent up to ostial LAD with XIENCE SIERRA 3.5x18mm, post dilated with NC EMERGE 3.5x15mm@ 18atm.. IVUS noted minimal ostial LAD stent strut went into the distal LM, post dilated further with POT balloon 4.0x6mm@12atm. Final IVUS good results, stent well opposed. TIMI 3 flow distally. No immediate complications. Patient had no angina.
 post1.avi
post1.avi
 post2.avi
post2.avi
Case Summary
This is a case of CTO of ISR in a patient who had stent implantation following spontaneous coronary artery dissection of proximal LAD six years ago. IVUS run this time after the operator able to cross the CTO lesion, the distal LAD was actually recanalized at the false lumen starting from the distal stent edge of proximal LAD to distally. It is therefore important to have imaging as a guidance for the case of coronary artery dissection. IVUS not only useful in detecting the dissection but also helpful to guide us on introducing guidewire to the true lumen. Since the flow of the recanalized false lumen had good flow distally but diffusely diseased, we decided to treat the lesions with DCB.


