Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-150
Combined Thrombectomy and Stent Placement for Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Due to Invasive Thymoma
By Hsin Yi Huang, Chung-Ho Hsu
Presenter
Hsin-Yi Huang
Authors
Hsin Yi Huang1, Chung-Ho Hsu1
Affiliation
China Medical University Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-150
ENDOVASCULAR - Peripheral Vascular Disease and Intervention
Combined Thrombectomy and Stent Placement for Superior Vena Cava Syndrome Due to Invasive Thymoma
Hsin Yi Huang1, Chung-Ho Hsu1
China Medical University Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
17085196
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
The 69-year-old woman with history of hypertension, Sjogrens syndrome under plaquenil, acute fulminant hepatitis, HBV related s/p liver transplantation, B3 Thymoma with thyroid and lung metastasis s/p Radiotherapy for 10 times, s/p bilateral total thyroidectomy and right central compartment lymph node dissection , thoracoscopic RLL wedge resection on 2022/1/13, suffered from face and left arm swelling for one week. Physical examination revealed engorged external jugular veins.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Echography revealed DVT, right internal jugular vein with partial recanalization. Neck CT revealed thyomoma s/p radiotherapy with metastasis to right lower lobe of lung, s/p thoracoscopic wedge resection. It showed residual tumor invasion into anterior mediastinum and invasion into the SVC. Thrombus of right internal jugular vein was found. No pulmonary embolism was detected.
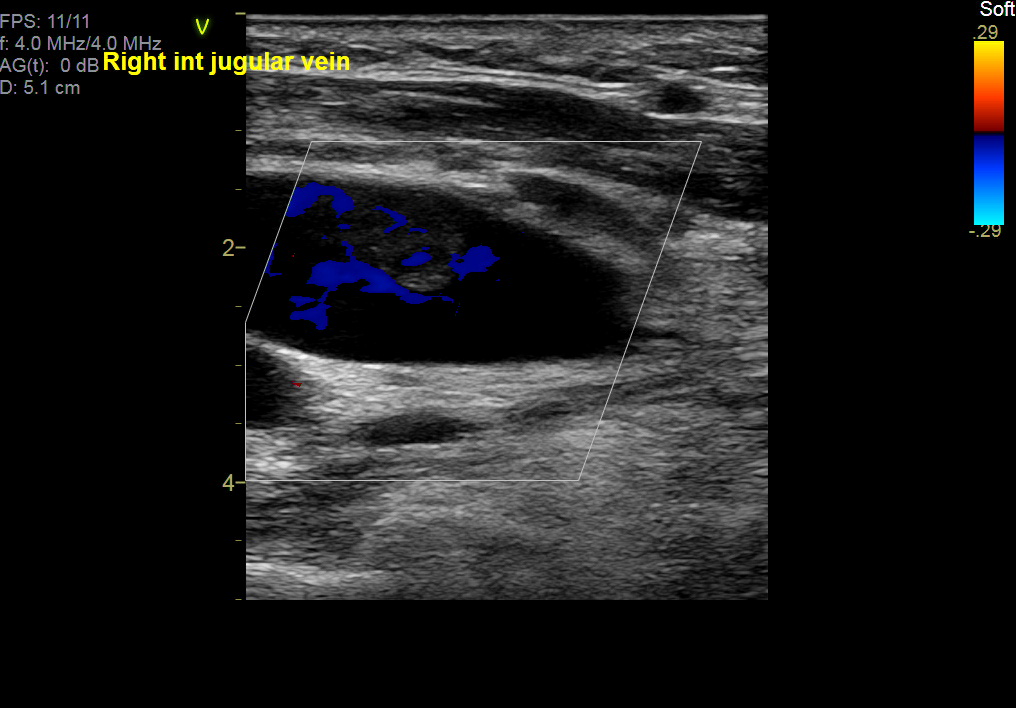
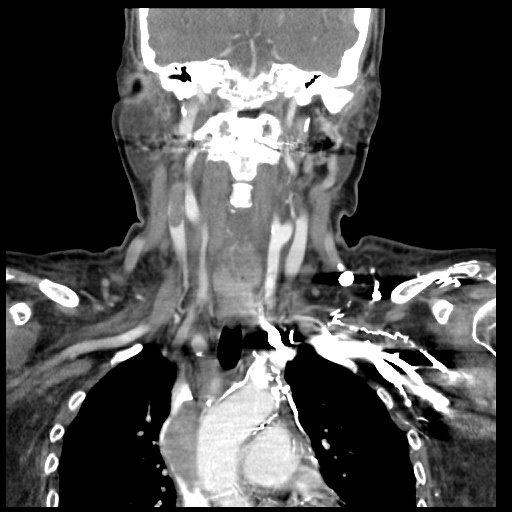
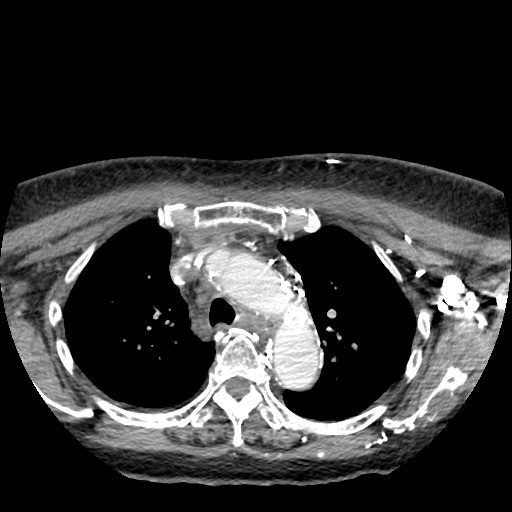



Relevant Catheterization Findings
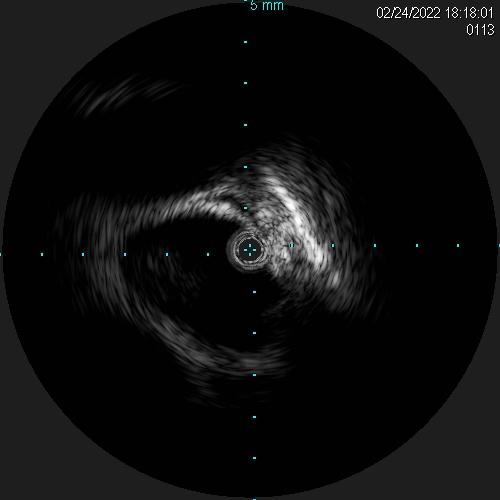
Thrombus over right internal jugular vein, near occluded SVC (IVUS 15-16 mm), proximal left subclavian vein stenosis with thrombus (IVUS 12 mm). Vital sign before intervention: 151/67 mmHg, 80 BPM. The pathology report of sampling after thrombectomy revealed epithelioid tumor cells. The immunohistochemical study reveals the tumor cells are CK19(+), p40(+), and CD117(-). Combineed with clinical information and previous pathologic report, the above picture is compatible with type B3 thymoma.
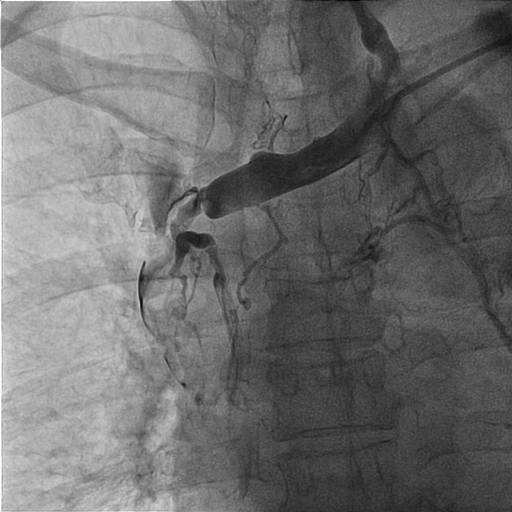
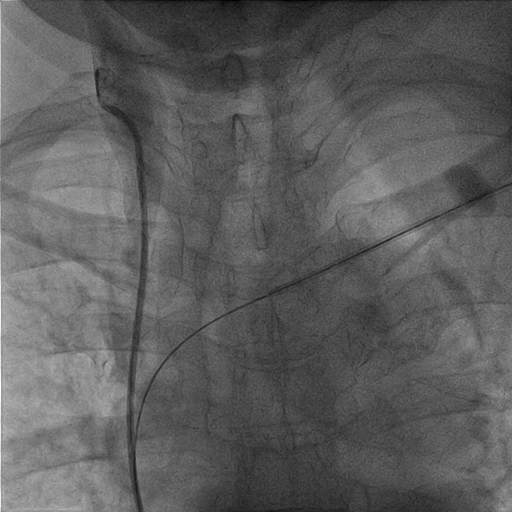



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
A 8/9/11 Fr sheath was inserted via RCFV under echo-guidance, micropuncture, V18, 4Fr sheath. A 8/9 Fr sheath was inserted to LCFV. Two 6Fr sheaths were inserted to right basilic vein/left cephalic vein. Two 0.035" Terumo wires were externalized with Snares (Left cephalic to LCFV; Right basilic to RCFV). CDT with heparin 5000 U, UK 120000 U was given via Fountain to SVC/Right jugular vein. Left subclavian/innominate vein was dilated with 6.0/80, 10.0/40 mm Admiral at 10 atm. PMT with 8Fr CAT was performed over right int jugular vein, SVC to aspirate thrombus with blood loss 960 ml noted. Kissing stents were performed (SVC: 13/50 mm V3H(Viabahn) x 2; SVC-innominate-Left subclavian 11.0/100 mm V3H x 1, kissing with two 10.0/40 mm Admiral at 10 atm). Good antegrade flow without residual stenosis was noted. IVUS showed adequate apposition of stents.
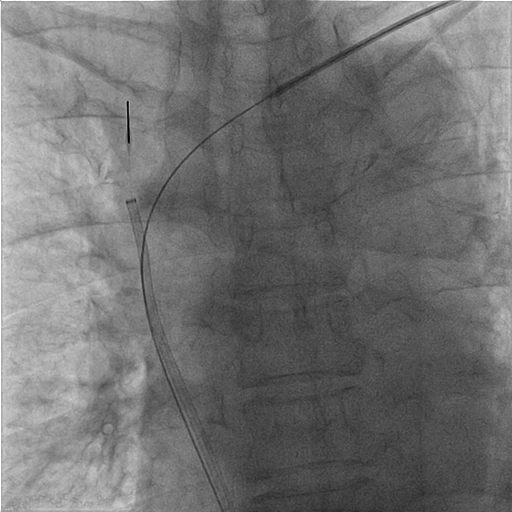
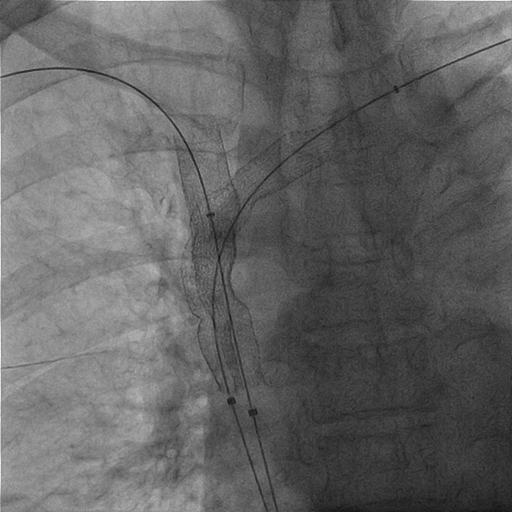
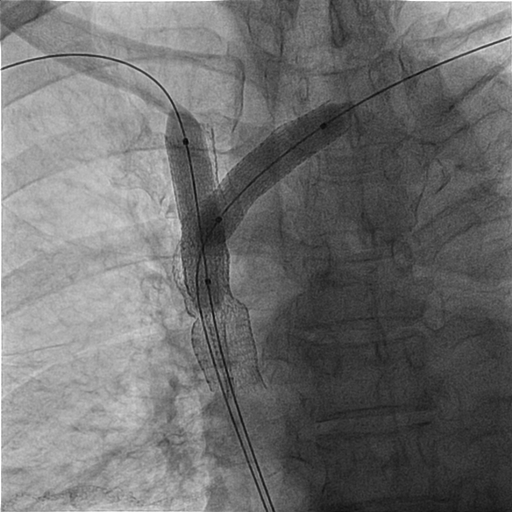



Case Summary
For SVC syndrome associated with thrombus, CDT/PMT/stenting is feasible. Endovascular thrombectomy has been emerging as first-line therapy for SVC syndrome due to thrombus and tumor with the advanced device. Operation should be also considered for the thymoma but tumor has been status post radiotherapy with invasion of vessels. For cases with contraindication for thrombolysis, aspiration thrombectomy can be considered (Angiojet, Aspirex, Indigo..etc in Taiwan) Risk of pulmonary embolism should be evaluated after operation.


