Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-168
Post PCI FFR 0.64, Additional Procedure? Or Termination?
By Sungjoon Park, Bon-Kwon Koo
Presenter
Sungjoon Park
Authors
Sungjoon Park1, Bon-Kwon Koo1
Affiliation
Seoul National University Hospital, Korea (Republic of)1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-168
IMAGING AND PHYSIOLOGIC LESION ASSESSMENT - Physiologic Lesion Assessment
Post PCI FFR 0.64, Additional Procedure? Or Termination?
Sungjoon Park1, Bon-Kwon Koo1
Seoul National University Hospital, Korea (Republic of)1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
KYS
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
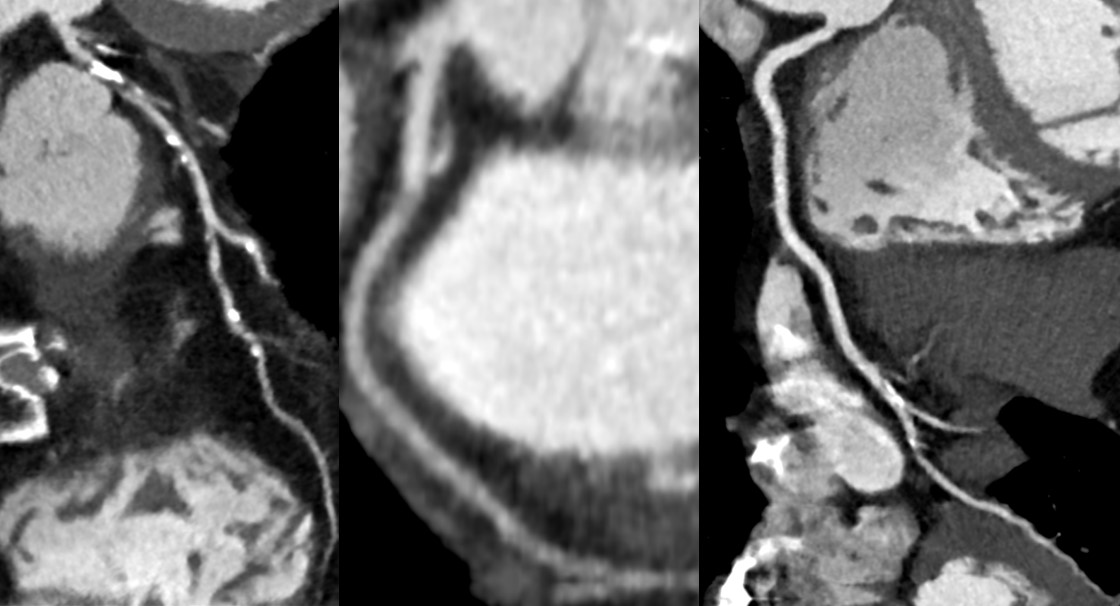
A 66-year-old man was admitted to the hospital for coronary artery evaluation with angina on exertion. He visited local clinic for the first hand and went through coronary CT angiography(CCTA).

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
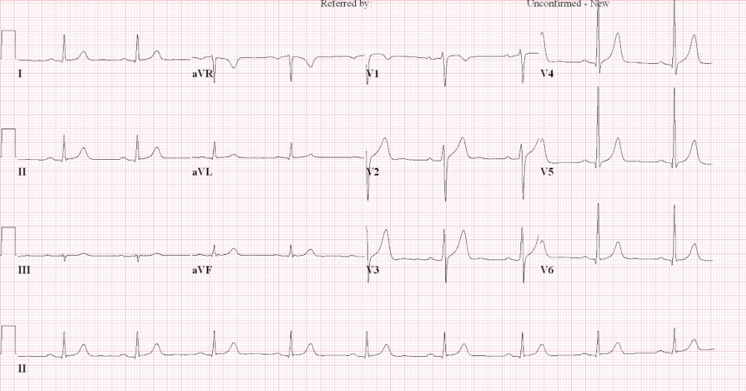
Electrocardiogram showed moderate left ventricular hypertrophy with sinus bradycardia 55 bpm.From the CCTA, left anterior descending(LAD) artery had proximal segmental upto 70% stenosis with mixed plaque, and mid to distal upto 50% multifocal stenosis with mixed plaque. Left circumflex artery was intact and right coronary artery had distal upto 50% stenotic lesion with mixed plaque.

Relevant Catheterization Findings
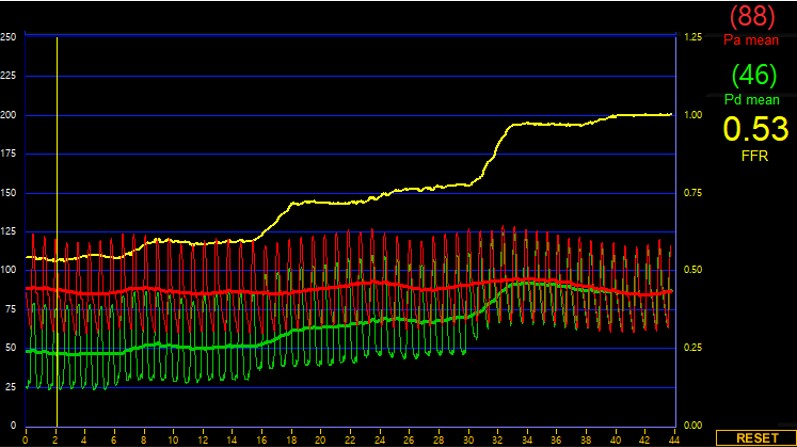
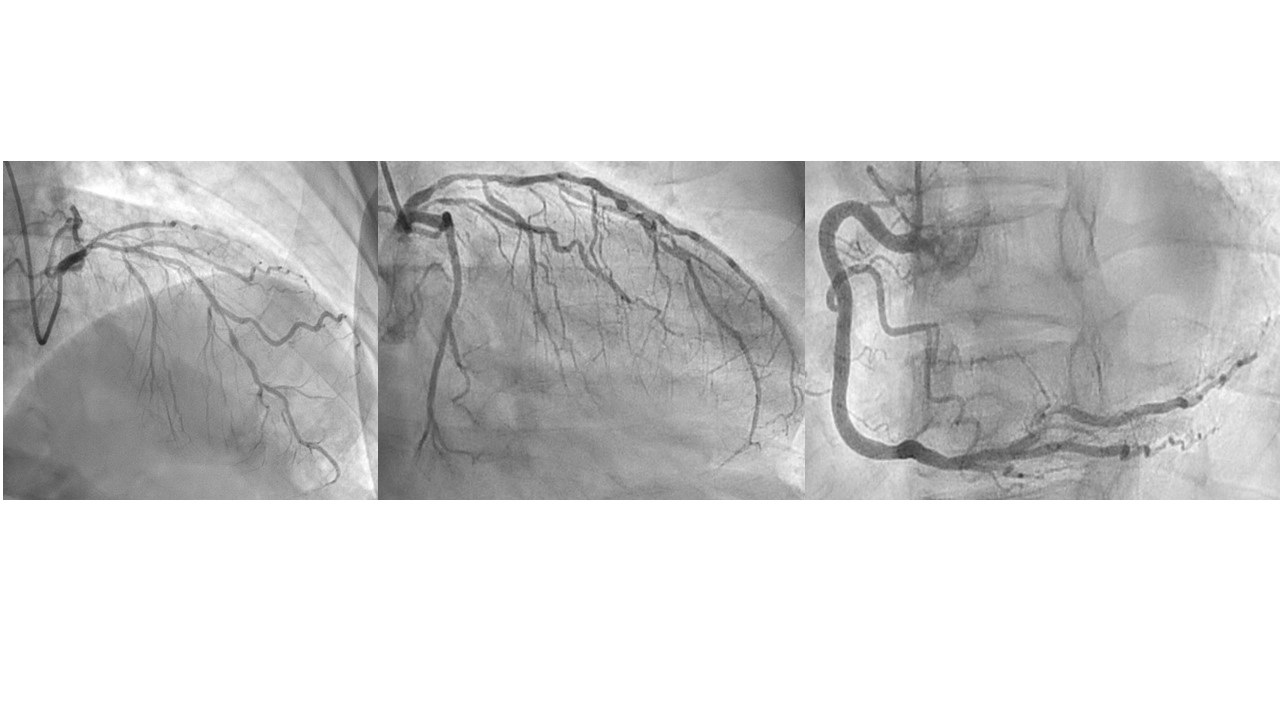
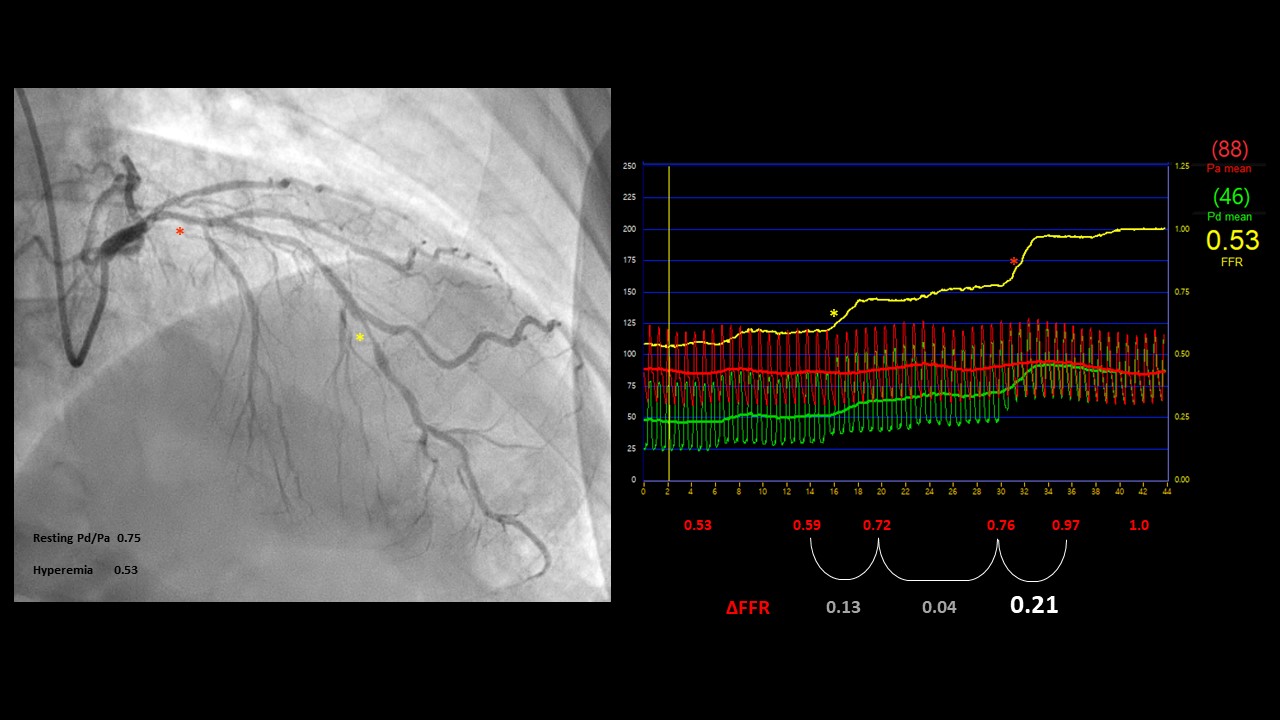
Coronary angiography demonstrated that left anterior descending artery (LAD) had a multiple stenosis of intermediate severity. Visually, proximal to mid LAD had diffuse lesions approximately 70%, distal LAD showed tubular up to 90% luminal narrowing. For LAD diffuse lesion, initial Pd/Pa was 0.75 and FFR 0.53.


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
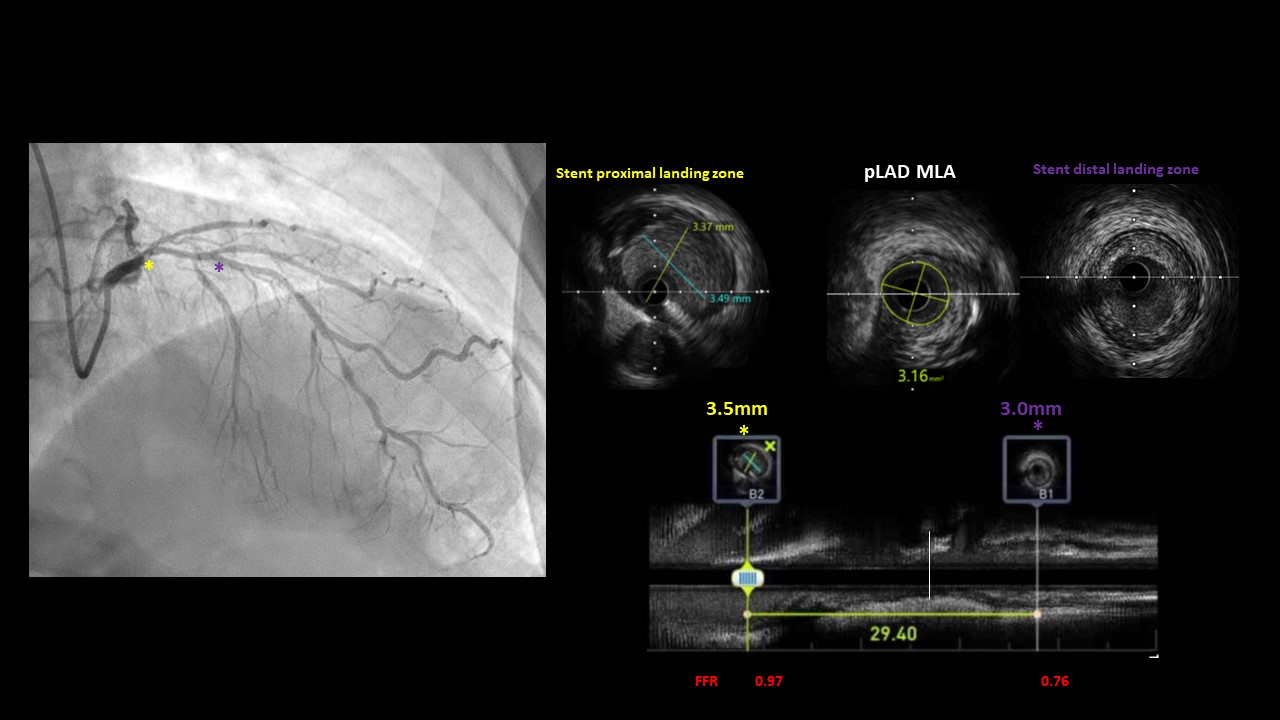
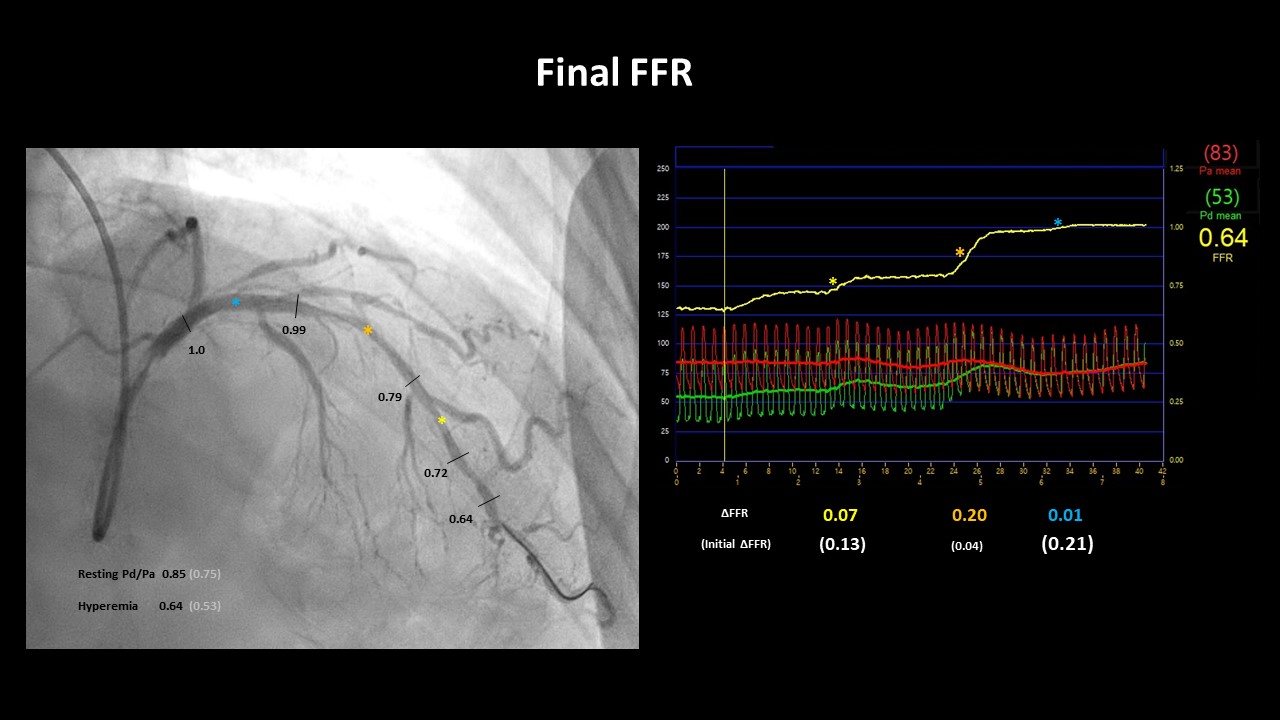
To measure sophisticated lesion severity, initial fractional flow reserve (FFR), intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) was done.Proximal LAD FFR result showed delta of 0.21 (distal end of proximal lesion 0.76, proximal end of proximal lesion 0.97), and distal LAD lesion has delta of 0.13 (distal end of lesion 0.59, proximal end of lesion 0.72). Unexpectedly, proximal LAD lesion was hemodynamically most significant than distal LAD lesion which thought to be visually worse. We decided to stent proximal LAD with 3.0 x 26mm sirolimus DES. Post DES implantation FFR delta value improved from 0.21 to 0.15 (distal end of proximal lesion 0.81,proximal end of proximal lesion 0.96), but FFR still remained Resting value Pd/Pa of 0.85 due to m-distal LAD untreated tandem lesions.



Case Summary
For Single vessel with whole diffuse denovo tandem irregular lesions including small vessels, optimal intervention approach can be examined with multiple imaging modalities. FFR is defined as a ratio of myocardial flow in the stenotic territory to normal myocardial flow in hyperemia. However, myocardial ischemia and symptoms depend on the absolute amount of blood flow passing through the lesion. Therefore, in this specific case, myocardial flow of baseline and stenotic territory would be both sufficient enough, resulting in FFR value less than the cutoff, 0.75. Final FFR 0.64 is associated with diffuse mid LAD lesion, post procedural mild distal dissection, and reactive hyperemia.


