Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-196
Massive Pulmonary Embolism Mimicking Acute Coronary Syndrome in a Young Man
By Mohd Asyiq Al-Fard Bin Mohd Raffali, Boon Cong Beh, Noor Diyana Binti Mohamad Farouk, Shawal Faizal Mohamad, Hamat Hamdi Che Hassan
Presenter
Mohd Asyiq Al-Fard Bin Mohd Raffali
Authors
Mohd Asyiq Al-Fard Bin Mohd Raffali1, Boon Cong Beh1, Noor Diyana Binti Mohamad Farouk1, Shawal Faizal Mohamad1, Hamat Hamdi Che Hassan1
Affiliation
Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz UKM, Malaysia1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-196
STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE - Pulmonary Intervention: CTEPH, PHTN
Massive Pulmonary Embolism Mimicking Acute Coronary Syndrome in a Young Man
Mohd Asyiq Al-Fard Bin Mohd Raffali1, Boon Cong Beh1, Noor Diyana Binti Mohamad Farouk1, Shawal Faizal Mohamad1, Hamat Hamdi Che Hassan1
Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz UKM, Malaysia1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
MA
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
We present a 25 year old man with no known medical illness, who presented with chest discomfort and shortness of breath for the past 3 days. He was a heavy smoker, with family history of ischemic heart disease. Upon arrival to the emergency department, he was tachypneic with respiratory rate of 24 breaths per minute. His blood pressure was 105/60 mm Hg, with pulse rate of 95 beats per minute. On examination, his lungs were clear and CVS examination was unremarkable.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Initial ECG showed subtle ST elevation over inferior leads. However bedside echocardiography showed dilated right ventricle with D-shaped LV suspicious of acute pulmonary hypertension. Laboratory investigation showed elevated troponin of 139.5 pg/ml. Initial chest x-ray showed prominent pulmonary trunk with borderline cardiomegaly. Patient was subsequently treated for acute coronary syndrome with dual antiplatelet and parenteral anticoagulant.
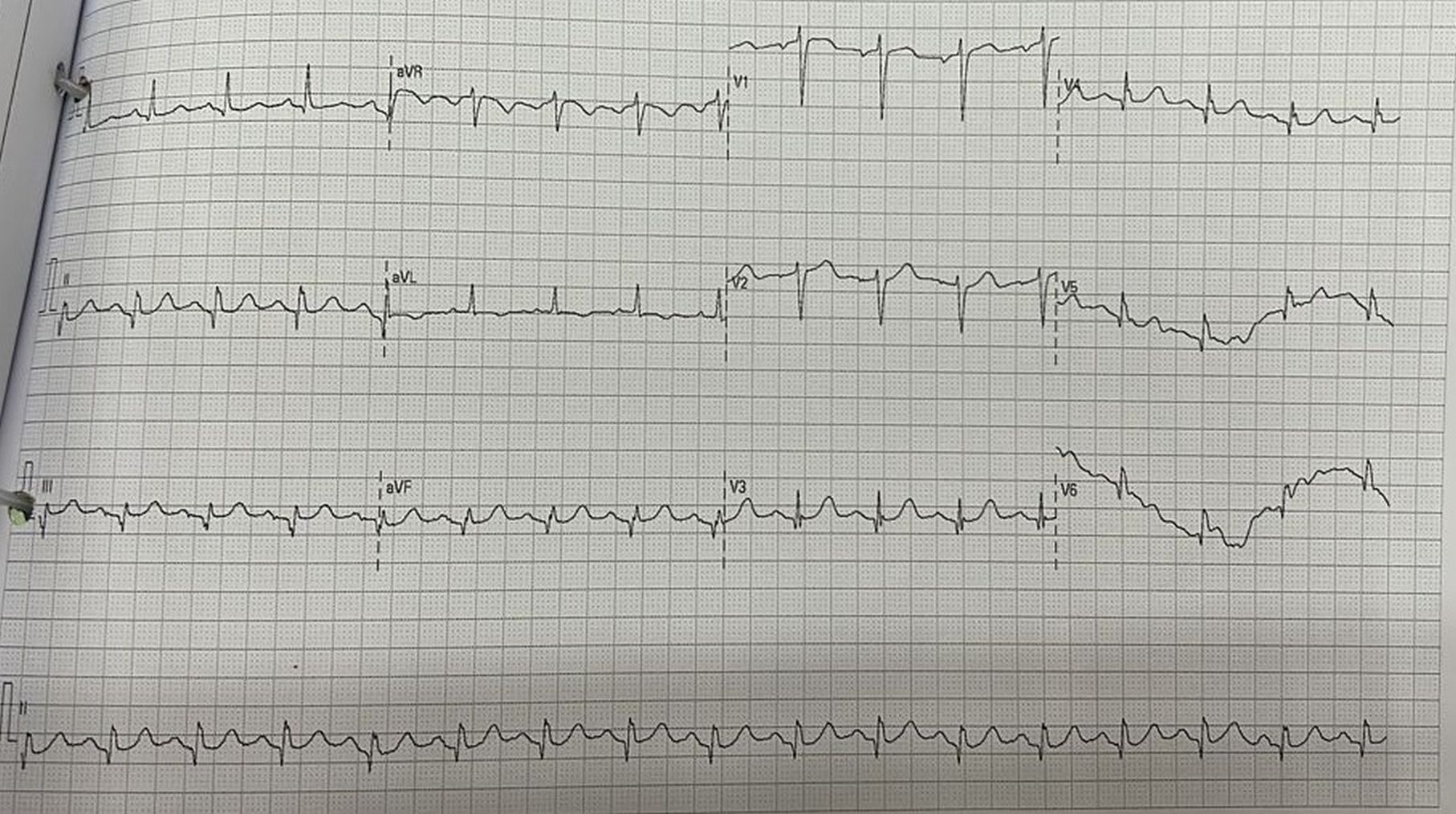

Relevant Catheterization Findings
However, he soon developed hypotension and was intubated for impending respiratory collapse. CT pulmonary angiography showed extensive bilateral pulmonary embolism, with multiple hilar lymphadenopathy. As he was hemodynamically unstable, decision for percutaneous pulmonary intervention was made.
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Vascular access was done over right femoral vein with an 8F sheath. Diagnostic pulmonary angiography with a pigtail catheter confirmed bilateral PE with left worse than right, with PA mean pressure of 45 mm Hg. Catheter aspiration with PENUMBRA device was done over 3 runs over the left PA. A total of 1 liter blood loss was recorded. However patient remained hemodynamically stable. About 60 cc of blood clot was evacuated. Post procedure left pulmonary angiography showed improved pulmonary perfusion. Final mean PA pressure of 30 mm Hg was documented at the end of procedure. Patient then transferred to the coronary care unit for further observation with intravenous heparin infusion.
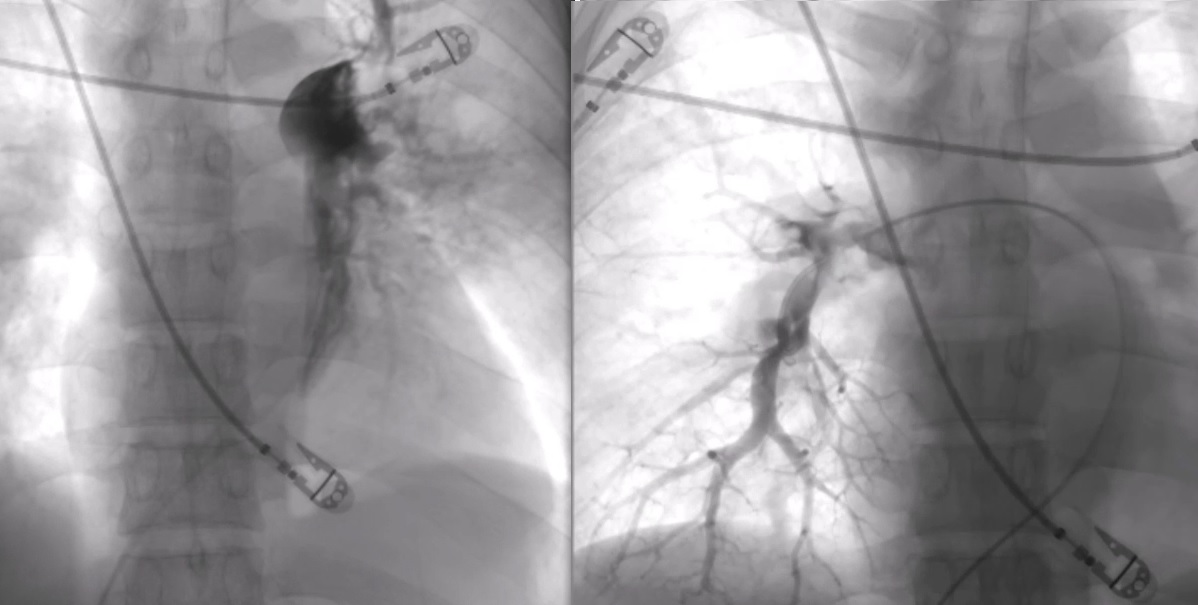
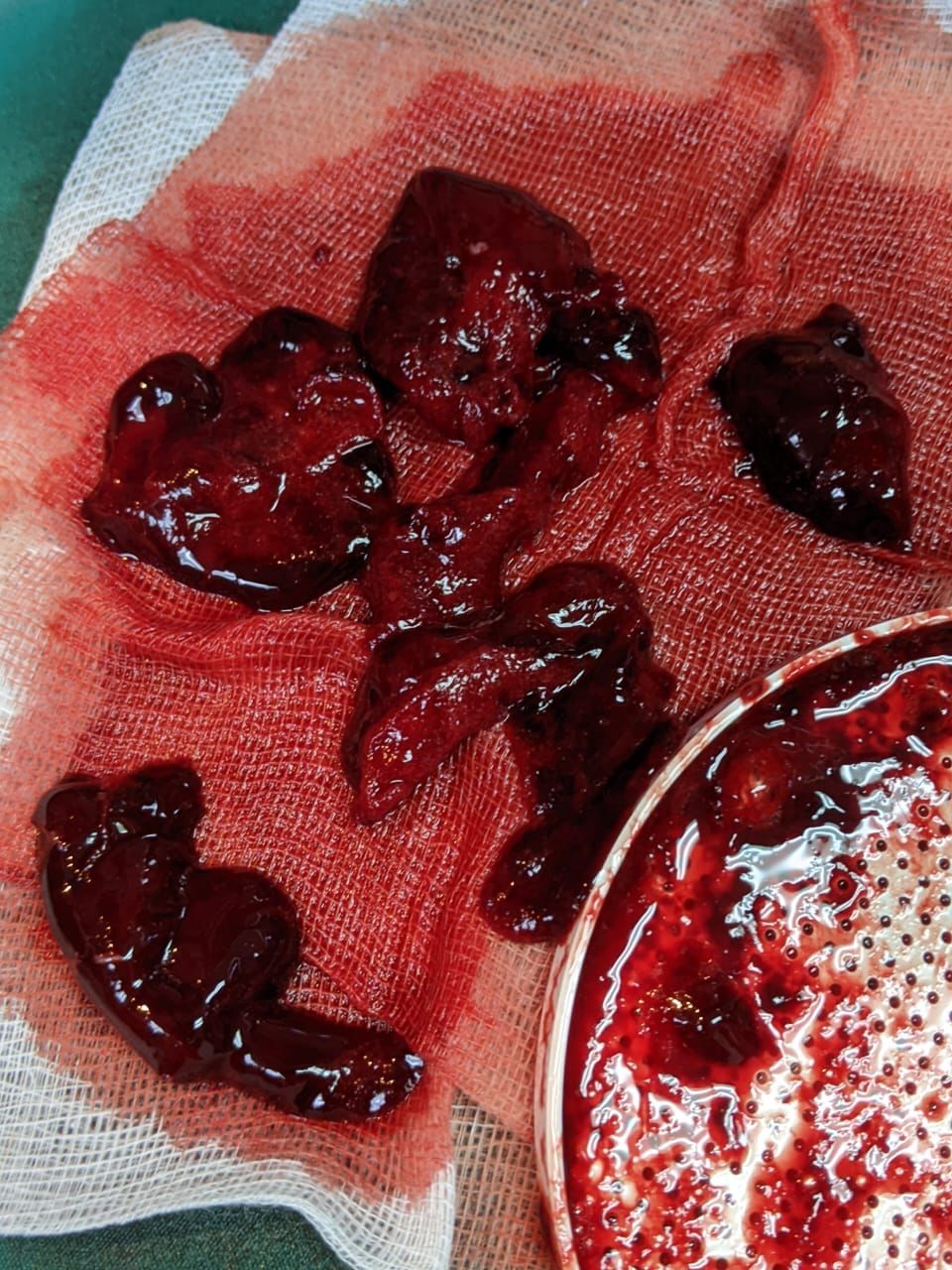


Case Summary
The next day, patient was extubated with good oxygen saturation. On further laboratory testing, his B-HCG was elevated, and he was diagnosed as non-seminoma germ cell tumor by the oncology team, and was started on chemotherapy. He was discharged after 2 weeks post intervention, and was seen at our clinic a month after in which he was given direct oral anticoagulant for at least 3 months. Repeated echocardiography showed normal cardiac chambers with no features of pulmonary hypertension.This case showed how acute pulmonary embolism may mimic acute coronary syndrome especially from the ECG and cardiac enzymes parameters. Percutaneous intervention helped to save the patient.


