Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-113
Iatrogenic Aortocoronary Dissection During Emergency Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in a 47-Year-Old STEMI Patient
By John Joel Javier
Presenter
John Joel Hernandez Javier
Authors
John Joel Javier1
Affiliation
Philippine Heart Center, Philippines1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-113
CORONARY - Complications (Coronary)
Iatrogenic Aortocoronary Dissection During Emergency Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in a 47-Year-Old STEMI Patient
John Joel Javier1
Philippine Heart Center, Philippines1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
NA
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 47-year-old woman sought medical care at a private hospital due to severe substernal chest pain for 6 hours. The patient was aware of being hypertensive. Her electrocardiogram showed STEMI of the Inferior Wall. She was advised primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and was transferred to our institution. Physical examination at the emergency room was BP: 139/80 mmHg and HR: 78 beats per minute, with vesicular breath sounds and no murmurs was noted.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
12-Lead electrocardiogram revealed ST-segment elevation in leads II, III, aVF. There are no posterior and right ventricular involvement . Her high sensitivity Troponin I was 329 which was 11 times elevated and her serum creatinine was 50 umol/L.
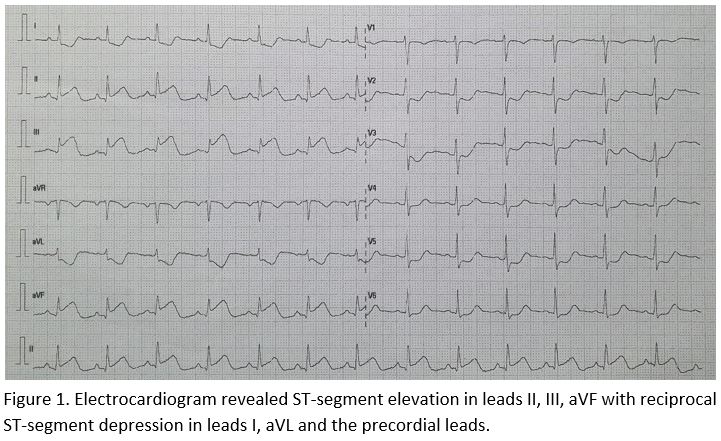

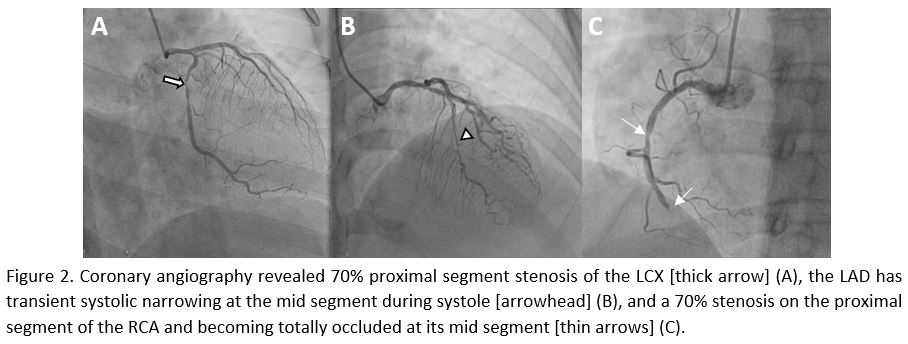
Relevant Catheterization Findings
After insertion of a 7-F right radial sheath, the left main coronary artery (LMCA) and right coronary artery (RCA) were engaged with a 5 French TIG diagnostic catheter (Optitorque, Terumo, Japan) which showed transient systolic narrowing at the mid LAD during systole, there was a 70% proximal segment stenosis of the LCX and a 70% stenosis on the proximal RCA and becoming totally occluded at its mid segment.

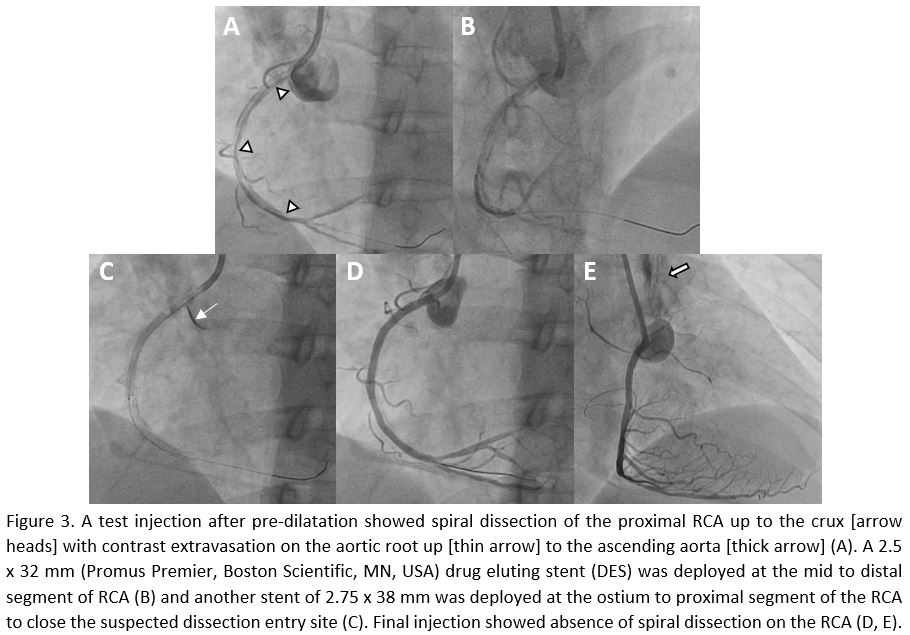
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
A 7-F Judkins Right (Mach-1, Boston Scientific, Boston, USA) was selected on the basis of the lesion. Sion Blue (Asahi Intecc, Tokyo, Japan) wire was passed to the mid RCA to allow ballooning of the lesion. The lesion was pre-dilated with 2.0 x 20 mm semicompliant balloon. A test injection after pre-dilatation showed spiral dissection of the proximal RCA up to the crux with contrast extravasation on the aortic root up to the ascending aorta. First, a 2.5 x 32 mm (Promus Premier, Boston Scientific, MN, USA) drug eluting stent (DES) was deployed at the mid to distal segment of RCA and another stent of 2.75 x 38 mm (Promus Premier, Boston Scientific, MN, USA) was deployed at the ostium to proximal segment of the RCA to close the suspected dissection entry site.
An urgent CT aortogram was done to decide if surgical intervention was necessary. The CT scan showed presence of contrast extravasation in the pericardium and mediastinum surrounding the ascending aorta, the proximal segment of the transverse aorta, as well as the pulmonary arteries. The patient was observed in the coronary care unit, and she showed no signs of chest pain. A follow-up CT aortogram was taken 2 days after the procedure and revealed clearing of the previously noted contrast material in the pericardium, superior mediastinum surrounding the ascending aorta, the proximal segment of the transverse aorta, and pulmonary arteries.
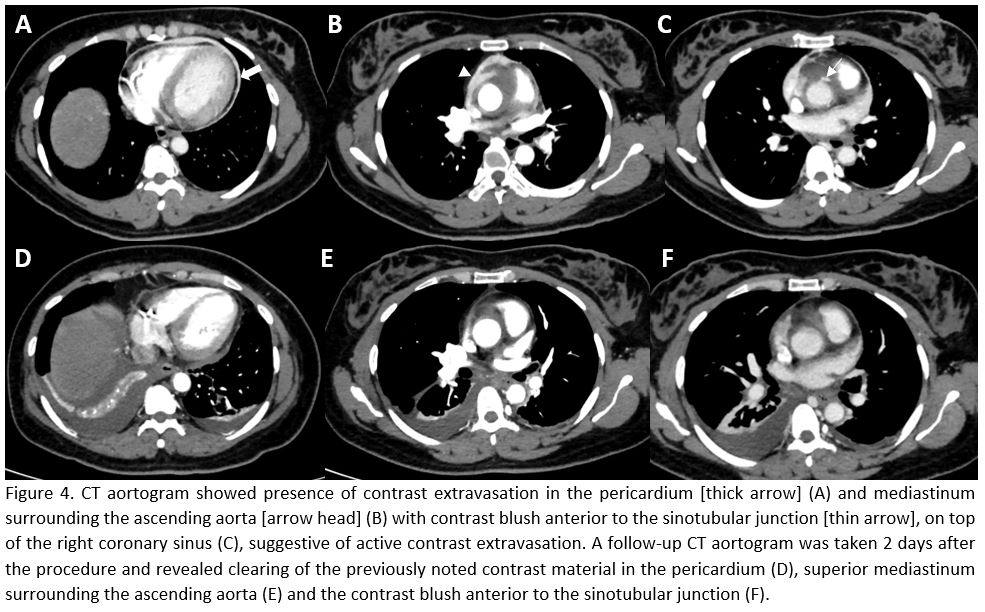
An urgent CT aortogram was done to decide if surgical intervention was necessary. The CT scan showed presence of contrast extravasation in the pericardium and mediastinum surrounding the ascending aorta, the proximal segment of the transverse aorta, as well as the pulmonary arteries. The patient was observed in the coronary care unit, and she showed no signs of chest pain. A follow-up CT aortogram was taken 2 days after the procedure and revealed clearing of the previously noted contrast material in the pericardium, superior mediastinum surrounding the ascending aorta, the proximal segment of the transverse aorta, and pulmonary arteries.


Case Summary
Iatrogenic guide catheter aortocoronary dissection is a known complication of percutaneous coronary intervention. It is usually managed by immediate stent implantation followed by imaging of the ascending aorta, to determine whether cardiac surgery or a conservative strategy is more appropriate.


