Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-049
The Impact of Total Stent Length on All-Cause Mortality Among Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Diabetes Mellitus Patients, a Retrospective Single-Center Study
By You-Ning Chang, Shih-Hsien Sung
Presenter
You-Ning Chang
Authors
You-Ning Chang1, Shih-Hsien Sung1
Affiliation
Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-049
Stents (Bare-metal, Drug-eluting)
The Impact of Total Stent Length on All-Cause Mortality Among Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Diabetes Mellitus Patients, a Retrospective Single-Center Study
You-Ning Chang1, Shih-Hsien Sung1
Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taiwan1
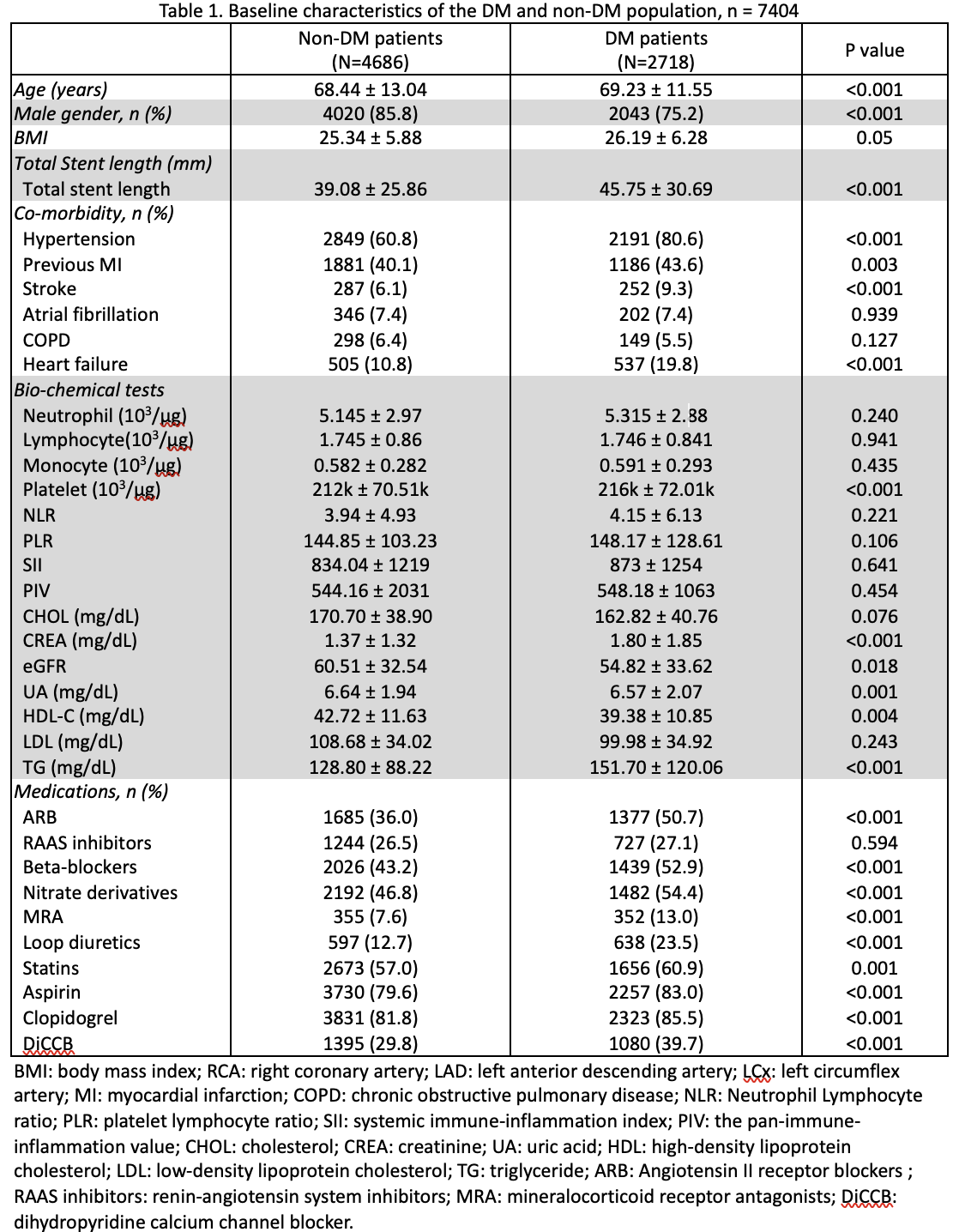
Background
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is the current standard treatment of coronary artery disease (CAD). In the previous studies, the longer stent length was shown to be correlated to adverse outcomes in patients with CAD. Besides, Diabetes Mellitus(DM) is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease and has been associated with 2- to 4- fold higher morality. This study aims at investigating the impact of stent length on mortality among DM and non-DM patients who underwent PCI.

Methods
The patients who underwent PCI between 2003 to 2013 were eligible for the study. Total stent length was defined as the total length of stenting in all three coronary arteries in the first PCI procedure of the patient. The patients were divided into two groups by stent length (< 48 mm, and ≥ 48 mm, according to stent distribution.All-cause mortality up to 10 years after discharge was obtained by linking to the National Death Registry.
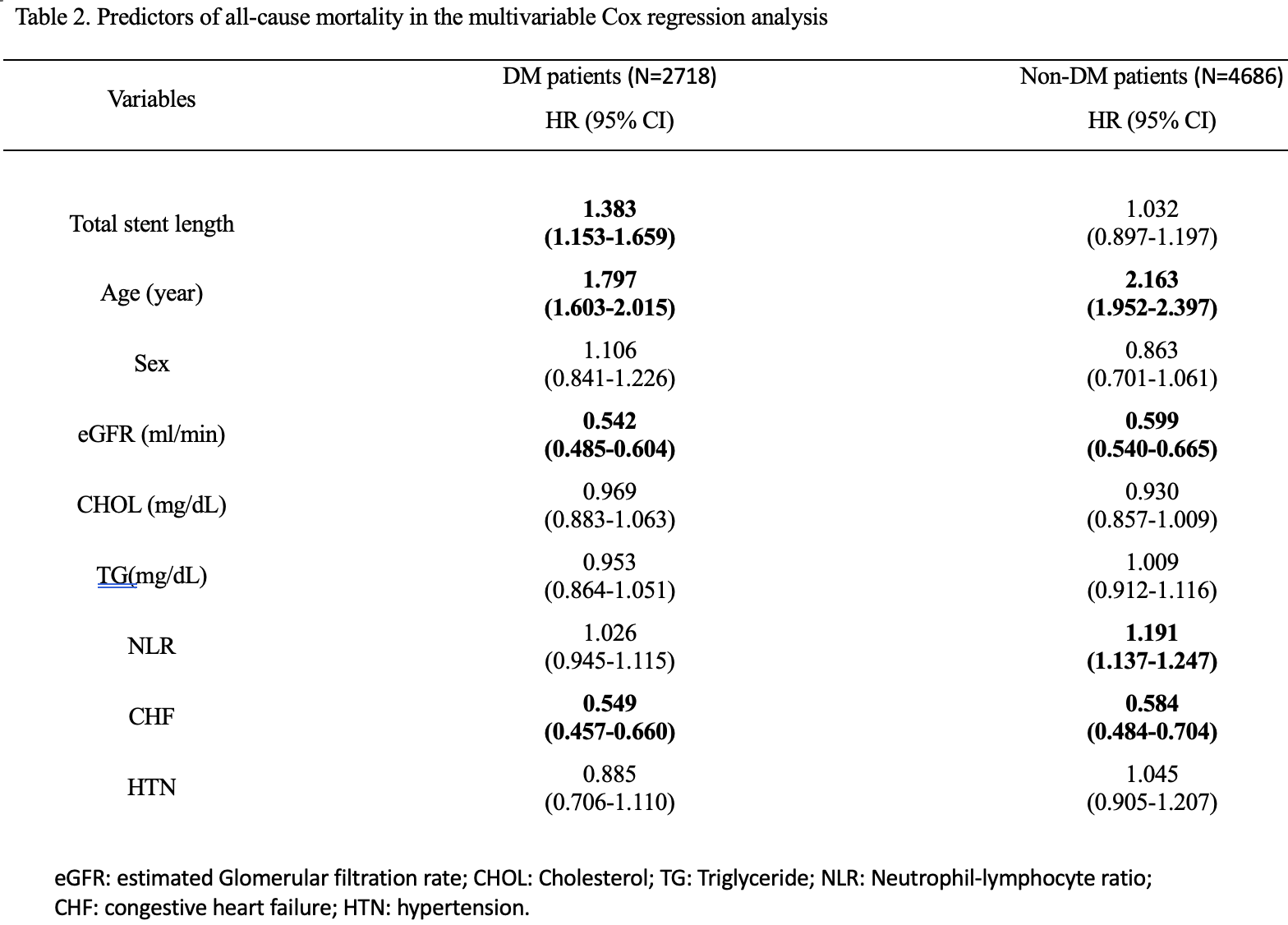
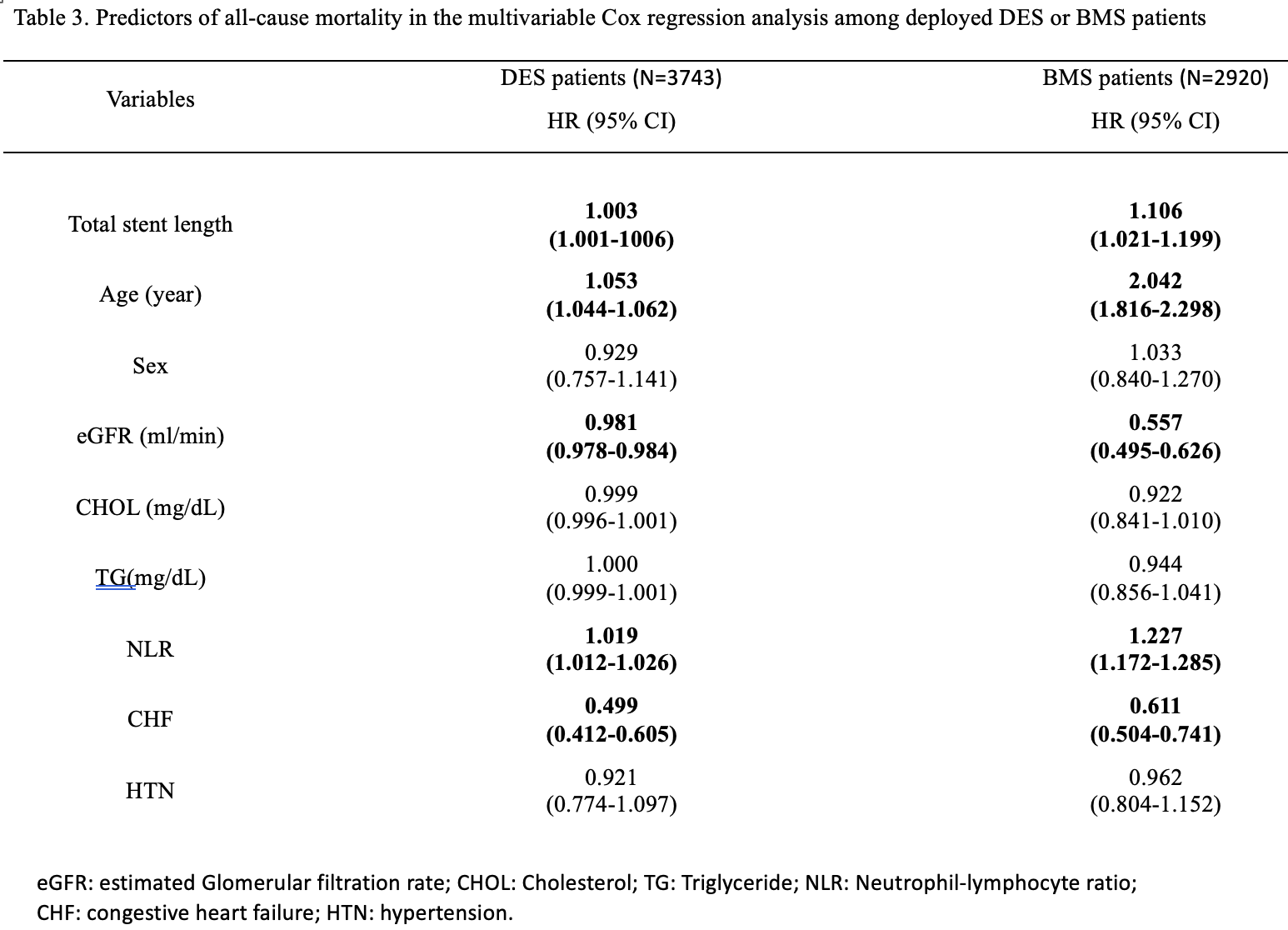


Results
Among a total of 7404 participants (68.73 ± 12.52 years, 81.9% men). There were 4686 (63.2%), and 2718 (36.8%) subjects in non-DM and DM subjects, respectively. The BMI was in randomized distribution. In the Kaplan-Meier analysis, a significantly higher mortality rate was demonstrated among the DM subjects between the group of stent length ≥ 48 mm compared to those <48 mm total stent length (Log-Rank p = 0.003). On the other side, there was no significant difference in mortality among the non-DM subjects between the group of stent length ≥ 48 mm and < 48 mm. (Log-Rank p = 0.303). Multivariate cox models adjusting age, sex, renal function, cholesterol level, triglyceride level, the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), congestive heart failure, hypertension revealed that among the DM subjects comparing with total stent length <48 mm, total stent length over 48mm was significantly associated with all-cause mortality (P<0.001, HR= 1.153-1.659), whereas no significant among the non-DM group. (P=0.659, HR= 0.897-1.187)
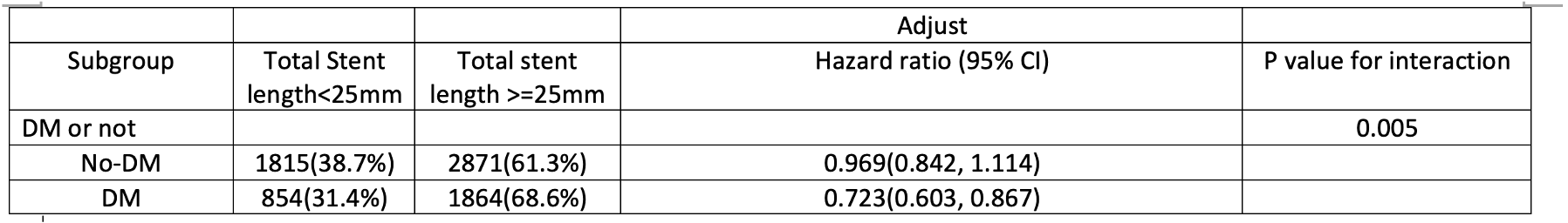
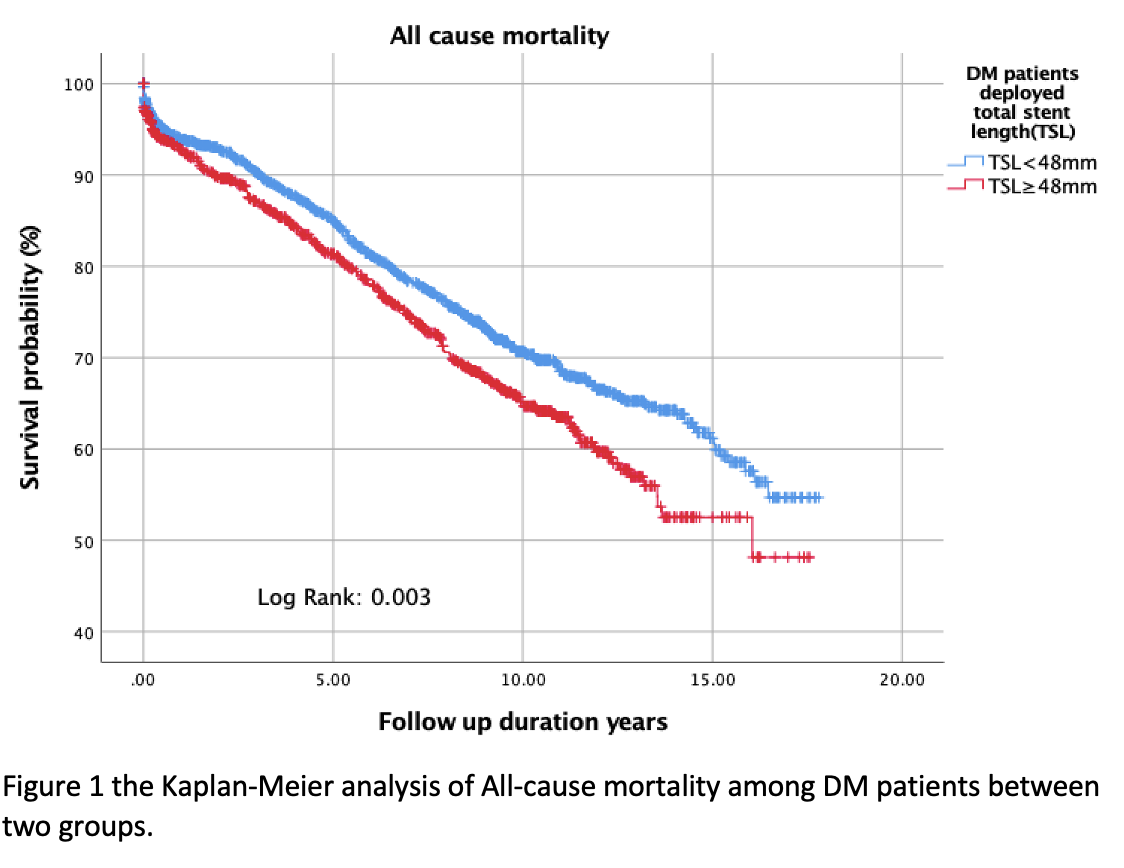
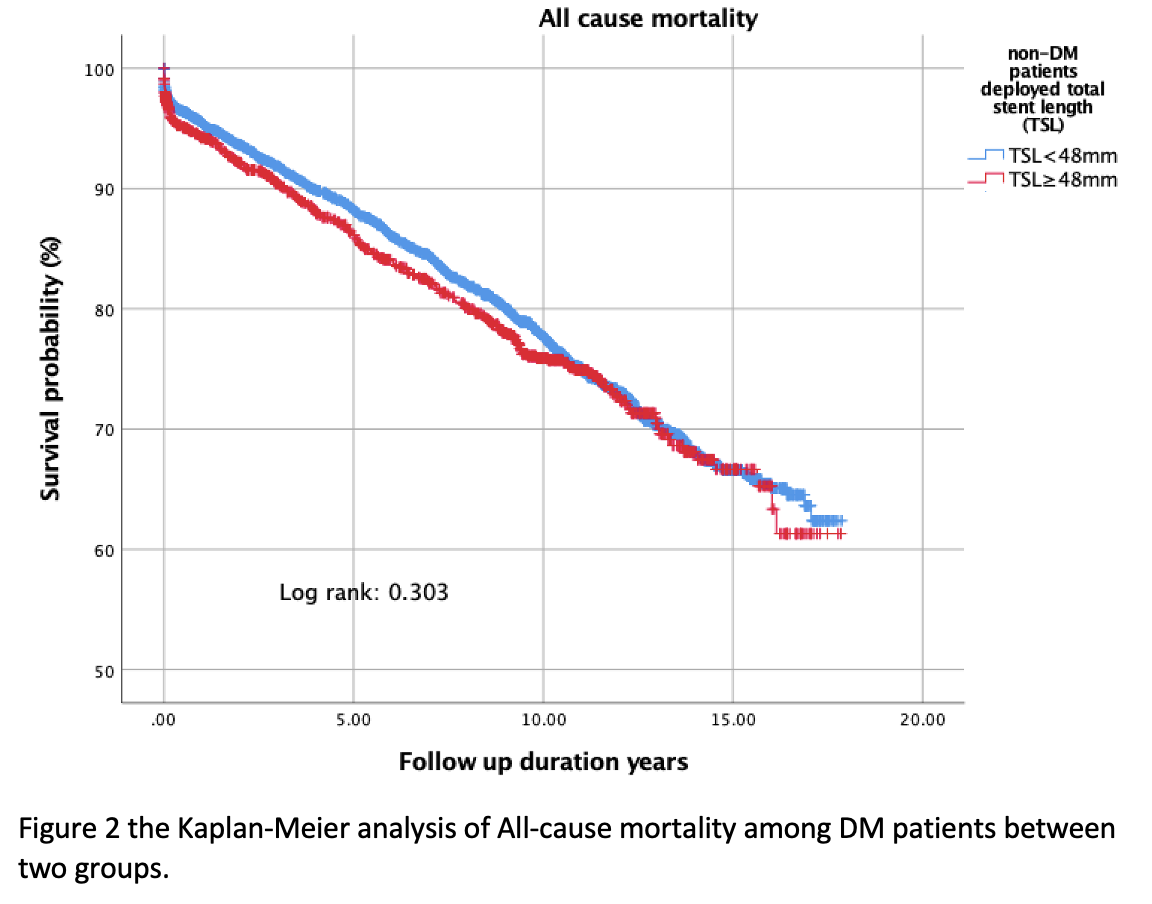



Conclusion
In the present study, we demonstrated that total stent implantation over 48 mm at one time was an independent predictor of long-term mortality among DM patients instead of non-DM patients.


