Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-048
Validation of Academic Research Consortium for High Bleeding Risk Definition in East-Asian Patients
By Jinho Lee, Hoyun Kim, Yeonwoo Choi, Do-Yoon Kang, Jung-Min Ahn, Seung-Jung Park, Duk-Woo Park
Presenter
Jinho Lee
Authors
Jinho Lee1, Hoyun Kim2, Yeonwoo Choi3, Do-Yoon Kang4, Jung-Min Ahn4, Seung-Jung Park4, Duk-Woo Park4
Affiliation
Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)1, Bucheon Sejong Hospital, Korea (Republic of)2, Changwon Hanmaeum Hospital, Korea (Republic of)3, Asan Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)4
View Study Report
TCTAP A-048
Pharmacology/Pharmacotherapy
Validation of Academic Research Consortium for High Bleeding Risk Definition in East-Asian Patients
Jinho Lee1, Hoyun Kim2, Yeonwoo Choi3, Do-Yoon Kang4, Jung-Min Ahn4, Seung-Jung Park4, Duk-Woo Park4
Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)1, Bucheon Sejong Hospital, Korea (Republic of)2, Changwon Hanmaeum Hospital, Korea (Republic of)3, Asan Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)4
Background
Clinical applicability of the Academic Research Consortium High Bleeding Risk (ARC-HBR)criteria in East-Asian patients receiving potent antiplatelet therapy for acutecoronary syndromes (ACS) is still undetermined.
Methods
We analyzed data from the TICAKOREA trial, randomly assigned 800 Korean ACS subjects to receive, in a 1:1 ratio, ticagrelor or clopidogrel. Patients were considered HBR if they met at least one major or two minor ARC-HBR criteria. The primary bleeding endpoint was Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) 3 or 5 bleeding and the primary ischemic endpoint was a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE; a composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke) at 12 months.
Results
Among 800 randomized patients, 129 (16.3%) were categorized HBR patients. HBR patients, compared to non-HBR patients, had a higher incidence of BARC 3 or 5 bleeding (10.0% vs. 3.7%; hazard ratio [HR], 2.98; 95%confidence interval [CI], 1.52–5.86; P < 0.001) and MACE (14.3% vs. 6.1%;HR 2.35; 95% CI, 1.35–4.10; P = 0.002). The relative treatment effect of ticagrelor or clopidogrel on primary bleeding and ischemic outcomes were different between each group.
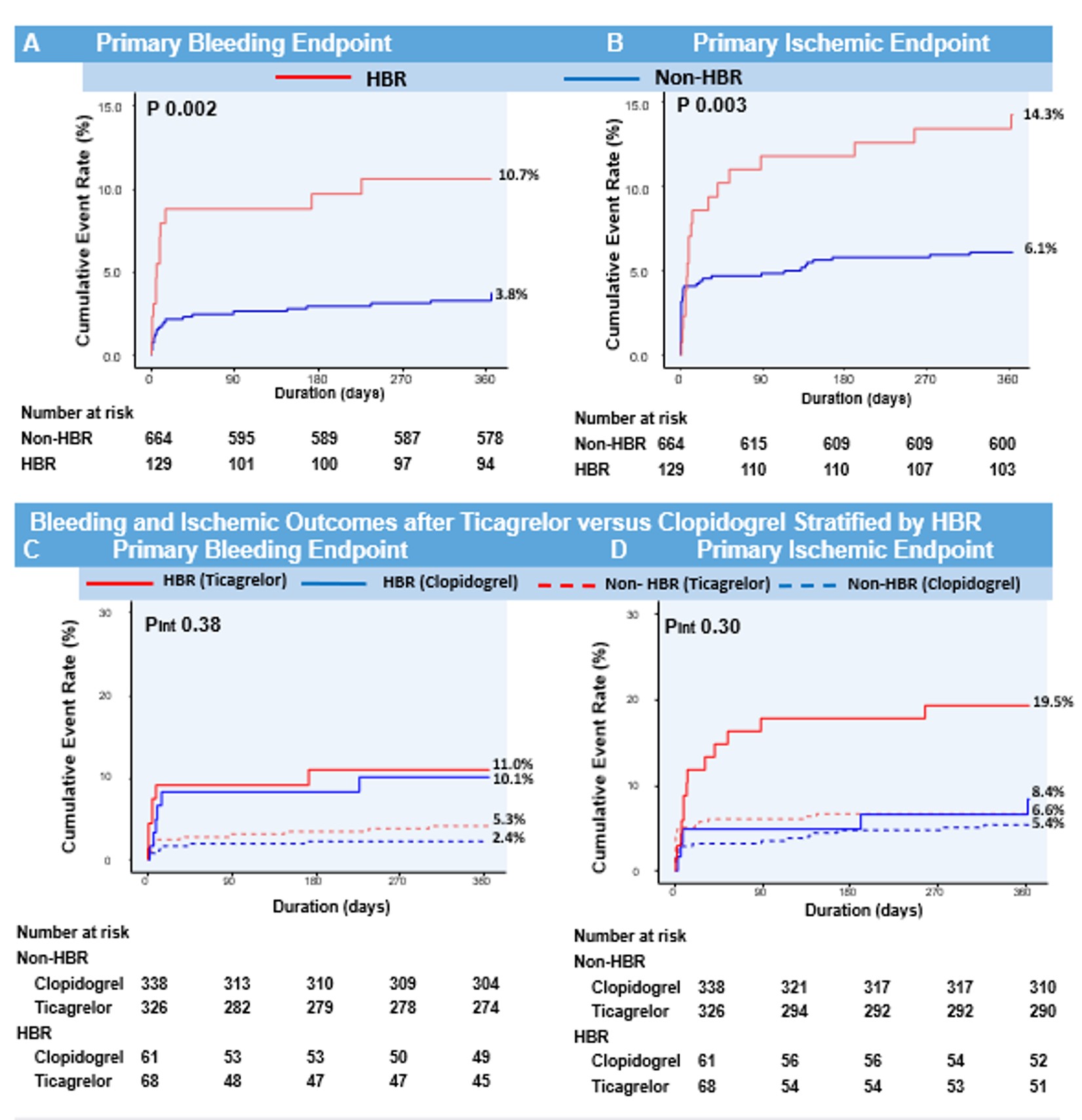

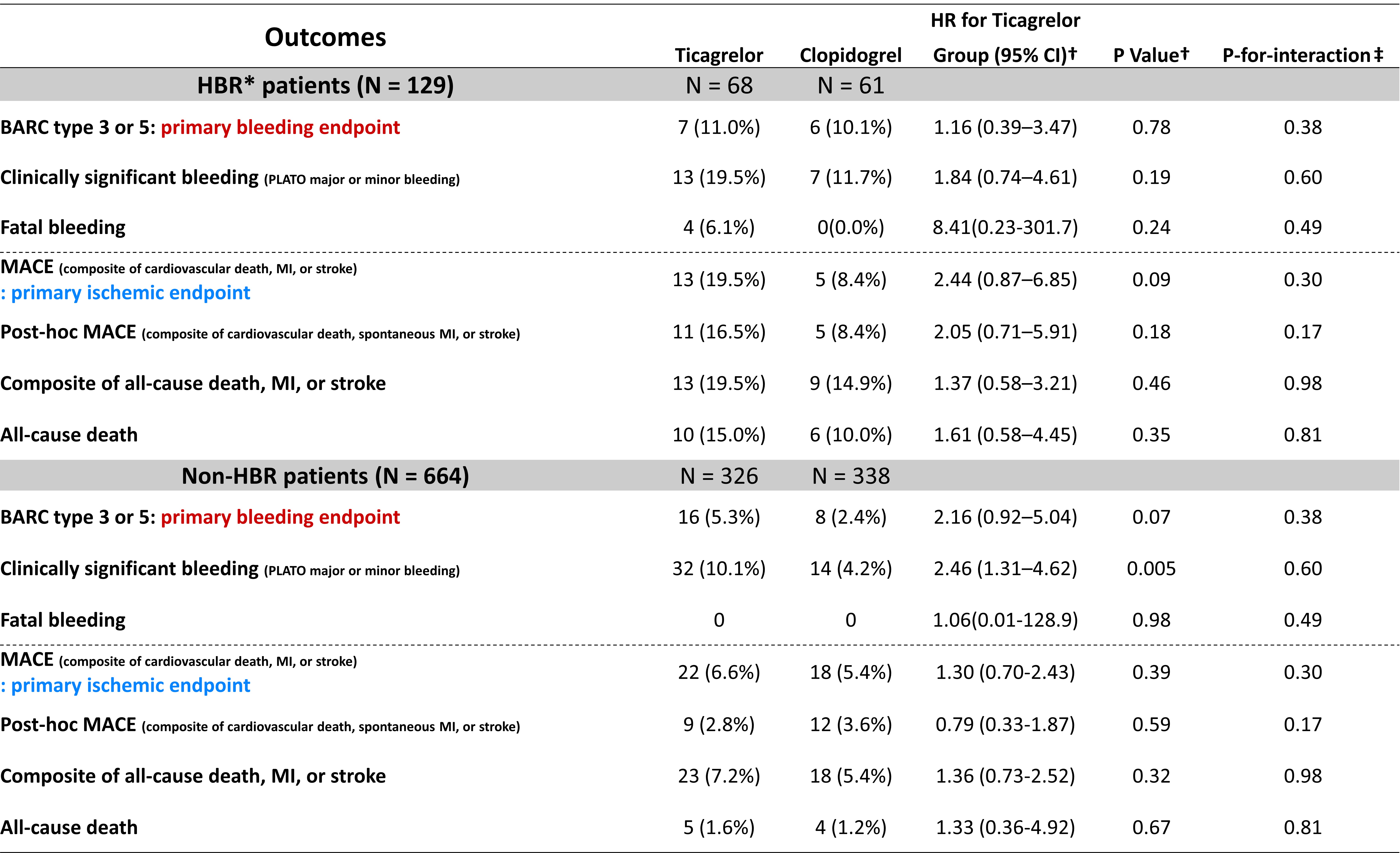



Conclusion
This study validates the ARC-HBR definition in Korean ACS patients. Approximately 15% of patients qualified as HBR patients who were at increased risk not only for bleeding but also for thrombotic events.The clinical application of ARC-HBR to determine the relative effect of different antiplatelet regiments should be further investigated


