Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-061
Impact of Minimal Lumen Area Measured by Intravascular Ultrasound on Revascularization Decision in Grey Zone Fractional Flow Reserve: Data From IRIS FFR Registry
By Joong Min Lee, Jinho Lee, Yeonwoo Choi, Hoyun Kim, Do-Yoon Kang, Jung-Min Ahn, Duk-Woo Park, Seung-Jung Park
Presenter
Joong Min Lee
Authors
Joong Min Lee1, Jinho Lee2, Yeonwoo Choi3, Hoyun Kim4, Do-Yoon Kang1, Jung-Min Ahn1, Duk-Woo Park1, Seung-Jung Park1
Affiliation
Asan Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)1, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)2, Changwon Hanmaeum Hospital, Korea (Republic of)3, Bucheon Sejong Hospital, Korea (Republic of)4
View Study Report
TCTAP A-061
Imaging: Intravascular
Impact of Minimal Lumen Area Measured by Intravascular Ultrasound on Revascularization Decision in Grey Zone Fractional Flow Reserve: Data From IRIS FFR Registry
Joong Min Lee1, Jinho Lee2, Yeonwoo Choi3, Hoyun Kim4, Do-Yoon Kang1, Jung-Min Ahn1, Duk-Woo Park1, Seung-Jung Park1
Asan Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)1, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Korea (Republic of)2, Changwon Hanmaeum Hospital, Korea (Republic of)3, Bucheon Sejong Hospital, Korea (Republic of)4
Background
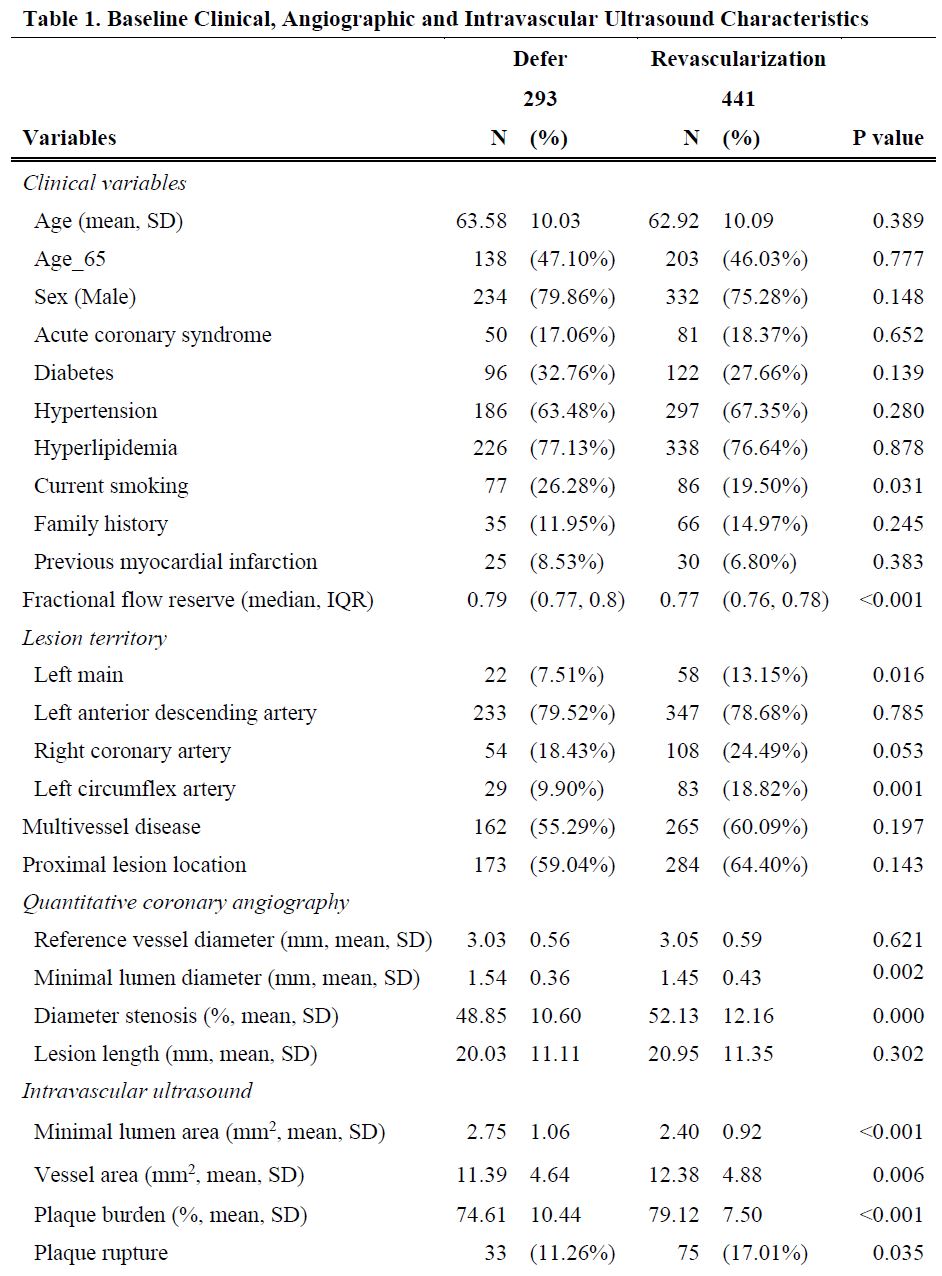
Theoptimal revascularization strategy for coronary stenosis with grey-zonefractional flow reserve (FFR) value (0.75-0.80) is still debated. This studyinvestigated the prognostic impact of the lesion characteristics measured byintravascular ultrasound (IVUS) in grey-zone FFR.
Methods
Atotal of 734 native coronary stenoses with grey-zone FFR in 734 patients fromthe prospective multicenter IRIS-FFR registry were simultaneously evaluated byIVUS. The primary outcome was a composite of cardiac death, myocardialinfarction (MI) and target vessel revascularization.
Results
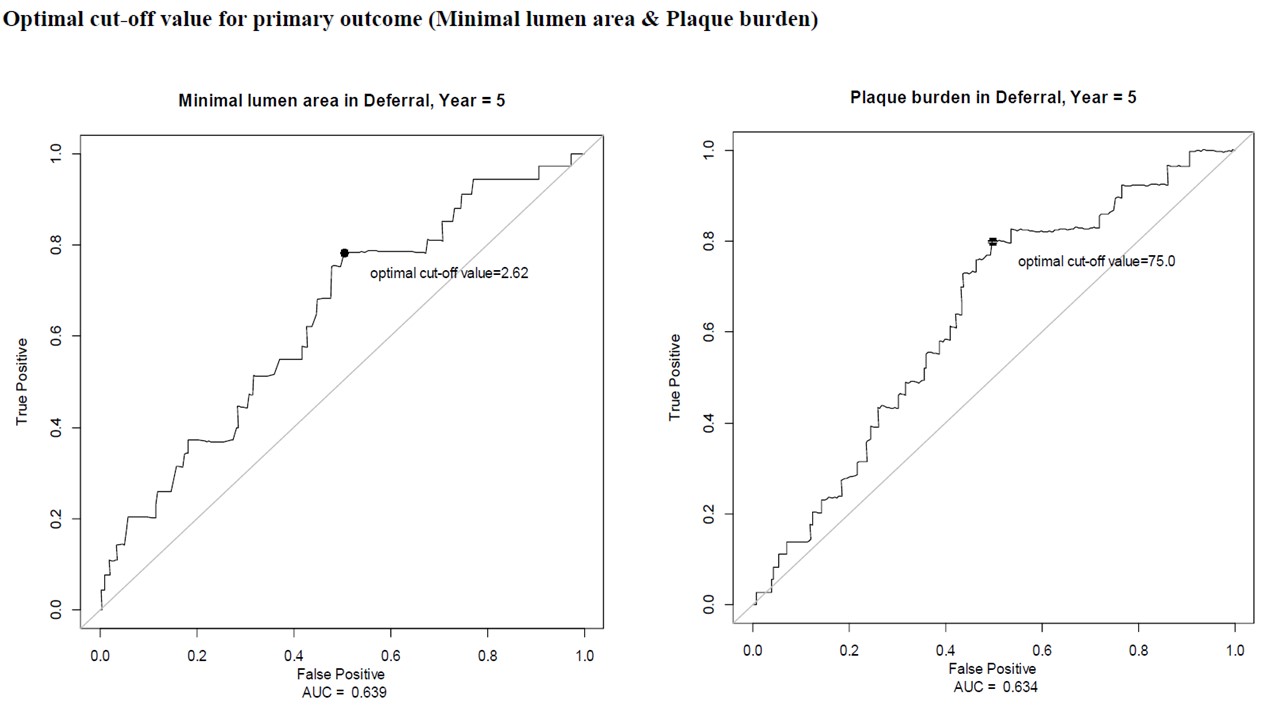
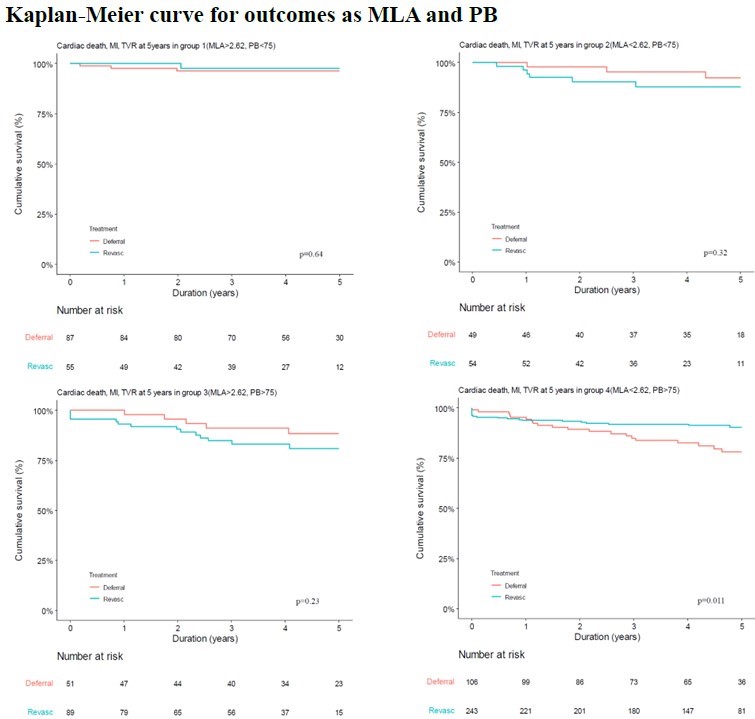
Among the 734 patients,revascularization was deferred for 293 patients and performed for 441. During amedian follow-up of 4.4 years, the primary outcome occurred in 31 (10.58%)patients in deferred group and 42 (9.52%) in revascularization group. Minimallumen area (MLA) measured by IVUS was an important factor of the primaryoutcome in deferred group, with the best cut-off value of 2.62 mm2(area under curve 0.639). The incidence rate of the primary outcome wassignificantly higher in deferred group than revascularization group if the MLAwas smaller than 2.62 mm2 (17.4% vs. 10.9%, adjusted hazard ratio[HR] 0.546, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.31-0.96, P=0.036). However, if MLAwas equal or larger than 2.62 mm2, the primary outcome was notdifferent between deferred and revascularization group (6.5% vs. 13.6%,adjusted HR 1.788, 95% CI 0.75-4.26, P=0.190).



Conclusion
Forcoronary stenoses with grey-zone FFR and smaller MLA measured by IVUS,revascularization was associated with better clinical outcomes. In addition,high plaque burden measured by IVUS also had clinical implication for the needfor revascularization. The incorporation of FFR and IVUS may improve therevascularization decision in native coronary stenoses with grey-zone FFR.


