Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-051
Clinical Evaluation of Everoshine Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent in Coronary Artery Lesions
By Sridhar Kasturi, Shailender Singh, Vijay Kumar Reddy Shanivaram
Presenter
Sridhar Kasturi
Authors
Sridhar Kasturi1, Shailender Singh1, Vijay Kumar Reddy Shanivaram1
Affiliation
Sunshine Hospital, India1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-051
Stents (Bare-metal, Drug-eluting)
Clinical Evaluation of Everoshine Everolimus Eluting Coronary Stent in Coronary Artery Lesions
Sridhar Kasturi1, Shailender Singh1, Vijay Kumar Reddy Shanivaram1
Sunshine Hospital, India1
Background
The development of coronary drug-eluting stents has included the use of new metal alloys, changes in stent architecture, and the use of bioresorbable polymers. New-generation drug-eluting stents (DES) represent the current standard of care in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Biodegradable polymer DES (BP-DES) was recently developed to overcome the current limitations of newer-generation durable polymer DES(DP-DES) attributed to sustained inflammatory responses induced by permanent polymers. The Everoshine DES (Kamal Encon Industries Limited - Kamal Medtech, Faridabad, Haryana) is a novel thin-strut cobalt-chromium everolimus-eluting stent with a biodegradable polymer that features some of the latest developments in DES technology.
Methods
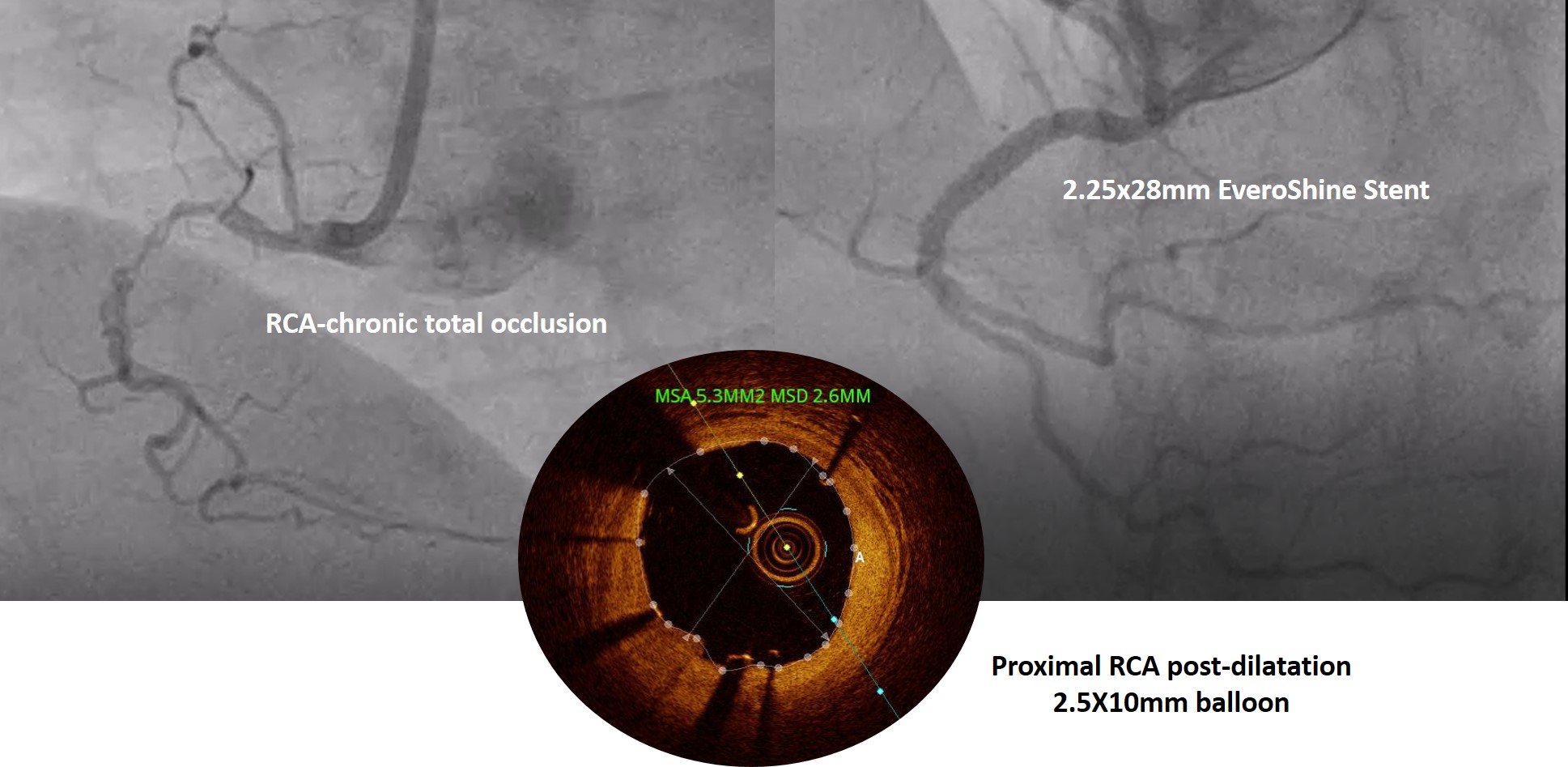
Thestudy population included a registry of 200 patients who underwent single ormulti-vessel revascularization with clinical presentations such as stableangina and acute coronary syndrome in the period between October 2020 and August2021 and who completes a one-year follow-up period. All the patients enrolledwere implanted with at least one Everoshine DES (Kamal Medtech, Faridabad, Haryana) stent and responded to follow-up. The endpoint of the study was the incidence of majoradverse cardiac events (MACE) defined as cardiac death, re-infarction, repeat coronaryrevascularization, and stent thrombosis.Clinical, telephonic follow-up was performed and MACE was analyzed at 30days, and 12 months.

Results
Overall193 patients were responded with 310 lesions treated with 260 Everoshine stents were enrolled in the study with a mean age of 57.8± 11.01 years among them 73.6% males were reported. And hypertensive, diabeticprevalence of 47.4% and 35.2% found respectively. The mean lesion length was26.77 ± 9.78mm with mean stent diameter 2.91 ± 0.39mm. At 12 months follow up, the efficacy endpoint MACEoccurred in 5 (2.6%) of 193 patients, consisting of 3 (1.5%) cardiac deaths, 2(0.7%) MI, 2 (0.5%) target lesion failures and stent thrombosis (ST) was observed in 2 (1.3%) patients.
| Parameter | 1 month | 12 months |
| All-cause mortality | 4 (2.07) | 5 (2.6) |
| Cardiac Death | 2 (1.03) | 3 (1.5) |
| MI | 2 (1.03) | 2 (1.03) |
| TLF | 2 (1.03) | 2 (1.03) |
| Stent Thrombosis | 2 (1.03) | 2 (1.03) |
| MACE | 4 (2.07) | 5 (2.6) |

Conclusion
The outperformance ofthe bioresorbable polymer everolimus-eluting stent system over the durablepolymer everolimus-eluting stent in a complex patient population undergoingpercutaneous coronary intervention suggests a new direction in improving nextgeneration drug-eluting stent technology.


