Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-038
Mild Renal Function Impairment and Long-Term Outcomes in Patients With Three-Vessel Coronary Artery Disease: A Cohort Study
By Guyu Zeng, Deshan Yuan, Peizhi Wang, Tianyu Li, Jinqing Yuan
Presenter
Guyu Zeng
Authors
Guyu Zeng1, Deshan Yuan1, Peizhi Wang1, Tianyu Li1, Jinqing Yuan1
Affiliation
Fuwai Hospital, China1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-038
Cardiac Surgery/Hybrid Revascularization
Mild Renal Function Impairment and Long-Term Outcomes in Patients With Three-Vessel Coronary Artery Disease: A Cohort Study
Guyu Zeng1, Deshan Yuan1, Peizhi Wang1, Tianyu Li1, Jinqing Yuan1
Fuwai Hospital, China1
Background
Limited data are available on the long-term impact of mild renal dysfunction (eGFR 60-89 ml/min/1.73m2) in patients with three-vessel coronary disease (3VD).
Methods
A total of 5,272 patients with 3VD undergoing revascularization were included and were categorized into 3 groups: normal renal function (eGFR ≥90ml/min/1.73m2, n=2,352), mild renal dysfunction (eGFR 60-89, n=2,501) and moderate renal dysfunction (eGFR 30-59, n=419). Primary endpoint was all-cause death. Secondary endpoints included cardiac death and major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascularevents (MACCE), a composite of death, myocardial infarction and stroke. Propensity scores matching was performed for comparison between renal dysfunction groups and normal renal function group.
Results
During the median 7.6-year follow-up period, 555 (10.5%) deaths occurred. After multivariable adjustment, patients with mild and moderate renal dysfunction had significantly higher risks of all-cause death (adjusted HR: 1.36, 95% CI 1.07-1.70; adjusted HR 2.06, 95% CI 1.53-2.78, respectively) compared with patients with normal renal function. Patients after coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) had a lower rate of all-cause death and MACCE than those undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in the normal and mild renal dysfunction group, but not in the moderate renal dysfunction group (Figure 1). Results were similar after propensity score matching.
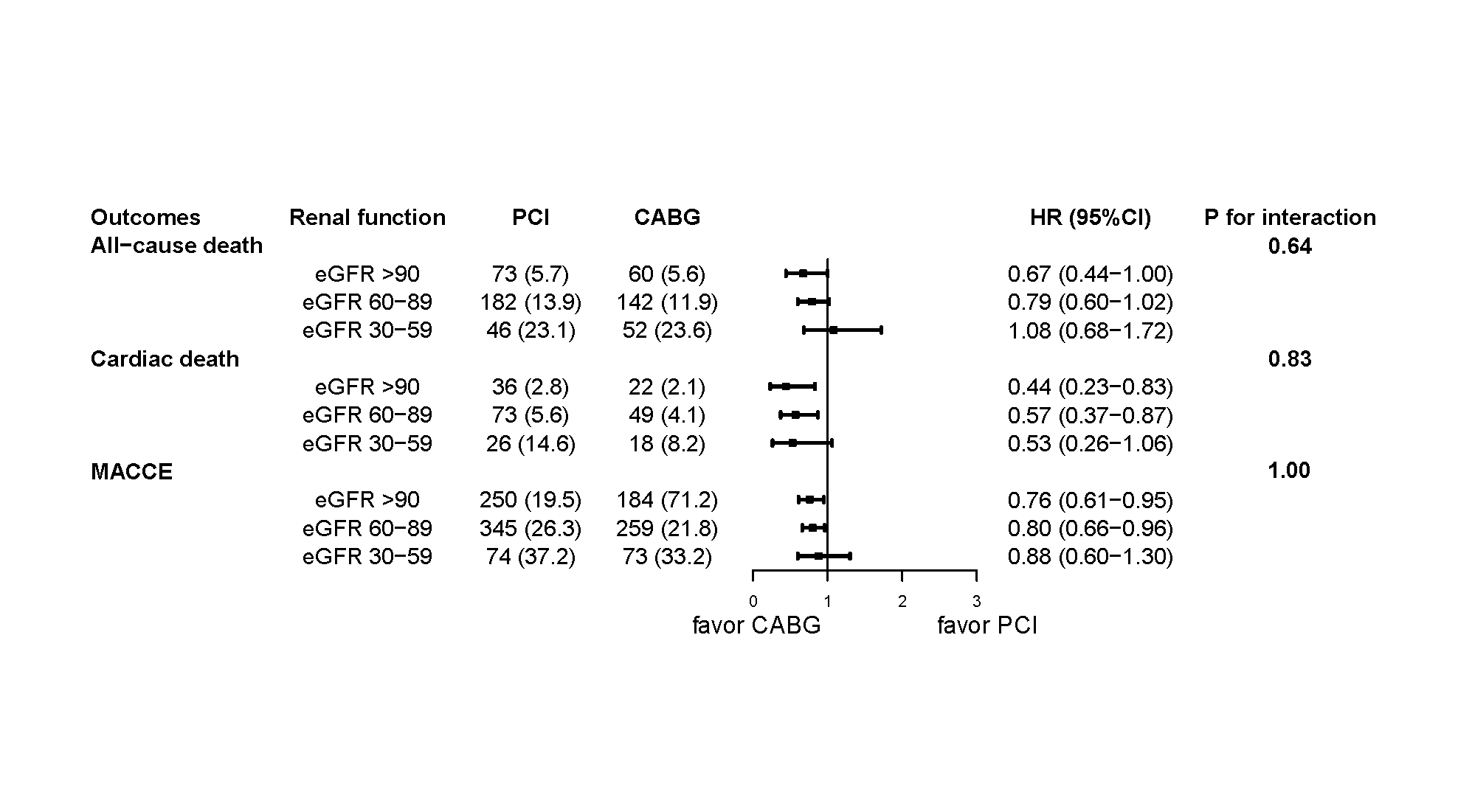

Conclusion
In patients with 3VD, even mild renal impairment was significantly associated with a higher risk of all-cause death. The superiority of CABG over PCI diminished in those with moderate renal dysfunction. Our study alerts clinicians to the early screening of mild renal impairment in patients with 3VD and provides real-world evidence on the optimal revascularization strategy in patients with renal impairment.


