Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2023. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-003
Optical Coherence Tomography Findings of High-Risk Plaques on Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography
By Daisuke Kinoshita, Keishi Suzuki, Yoshiyasu Minami, Tomoyo Sugiyama, Haruhito Yuki, Takayuki Niida, Hang Lee, Iris McNulty, Tsunekazu Kakuta, Maros Ferencik, Ik-Kyung Jang
Presenter
Daisuke Kinoshita
Authors
Daisuke Kinoshita1, Keishi Suzuki2, Yoshiyasu Minami3, Tomoyo Sugiyama4, Haruhito Yuki2, Takayuki Niida2, Hang Lee2, Iris McNulty2, Tsunekazu Kakuta4, Maros Ferencik5, Ik-Kyung Jang2
Affiliation
Yamagata Univercity, Japan1, Massachusetts General Hospital, USA2, Kitasato University School, Japan3, Tsuchiura Kyodo General Hospital, Japan4, Oregon Health and Science University, USA5
View Study Report
TCTAP A-003
Imaging: Intravascular
Optical Coherence Tomography Findings of High-Risk Plaques on Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography
Daisuke Kinoshita1, Keishi Suzuki2, Yoshiyasu Minami3, Tomoyo Sugiyama4, Haruhito Yuki2, Takayuki Niida2, Hang Lee2, Iris McNulty2, Tsunekazu Kakuta4, Maros Ferencik5, Ik-Kyung Jang2
Yamagata Univercity, Japan1, Massachusetts General Hospital, USA2, Kitasato University School, Japan3, Tsuchiura Kyodo General Hospital, Japan4, Oregon Health and Science University, USA5
Background
Although patients with high-risk plaques (HRP) on coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA) are reported to be at increased risk for future cardiovascular events, HRPs have not been systematically validated against high-resolution intravascular imaging. The aim of the study was to correlate HRP on CTA with plaque characteristics on optical coherence tomography (OCT).
Methods
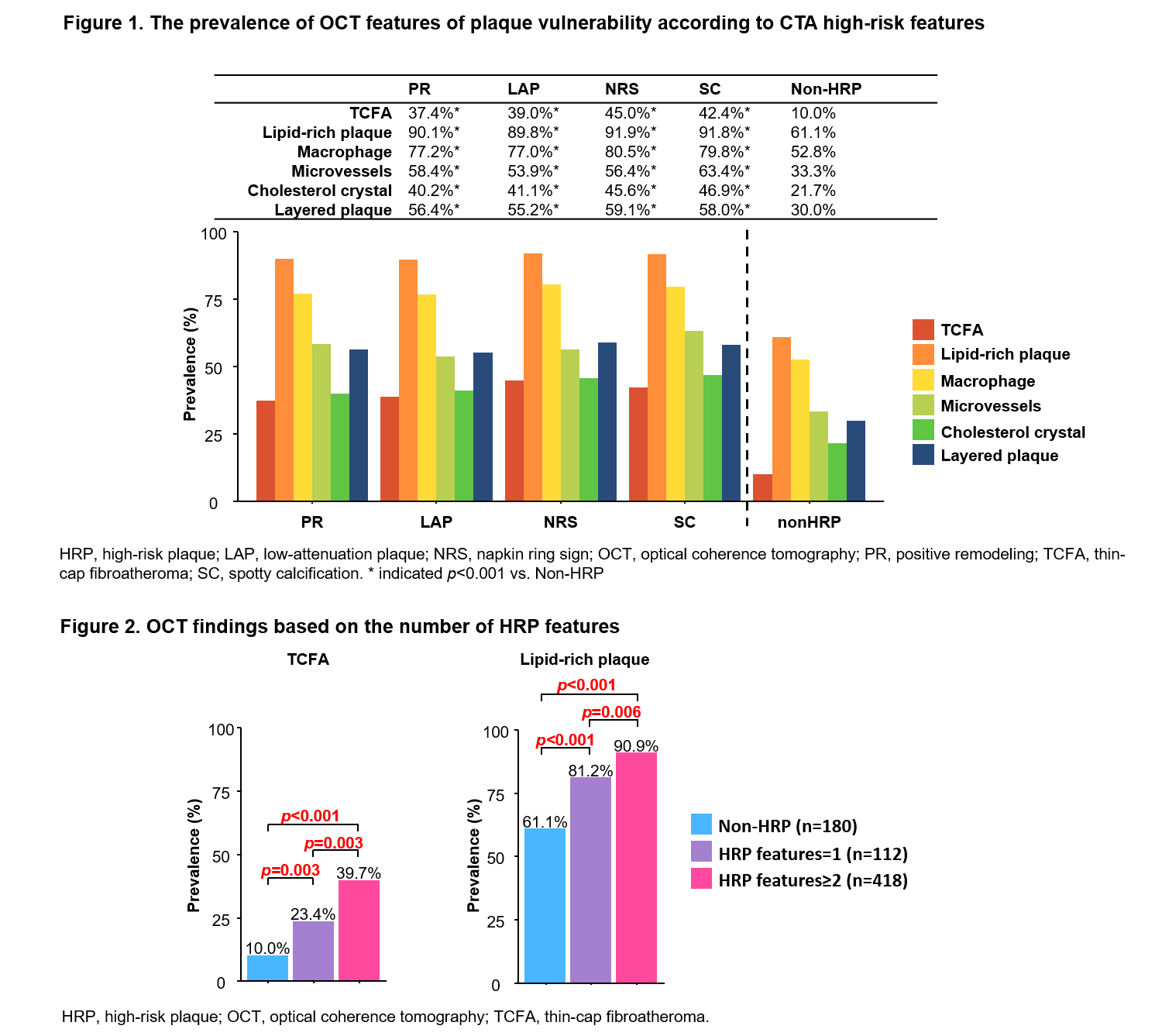
A total of 710 lesions with >30% diameter stenosis on angiogram from 455 patients (67 years, male 78%, ACS 43%) who underwent CTA and OCT were included. CTA-detected HRP features [positive remodeling (PR), low-attenuation plaque (LAP), napkin ring sign (NRS), and spotty calcification (SC)] and OCT-defined vulnerable features [thin-cap fibroatheroma (TCFA), lipid-rich plaque, macrophage, microvessel, cholesterol crystal, and layered plaque] were compared at the corresponding sites.
Results
Lesions with HRP, compared withnon-HRP, have significantly more frequent OCT features of plaque vulnerability(p<0.001 for all) (Figure 1). The prevalence of each OCT feature was similaramong 4 CTA-defined HRPs. The prevalence of TCFA was 3.7–4.5 times higher inHRP compared with non-HRP (37.4–45.0% vs. 10.0%). Lipid-rich plaque andmacrophage were both highly prevalent among lesions with HRP (89.9–91.9% and77.0–80.5%, respectively). Microvessels, cholesterol crystals, and layeredplaques were 1.5–2.2 times more frequent in HRPs than in non-HRP (53.9–63.4%vs. 33.3%, 40.2–46.9% vs. 21.7%, 55.2–59.1% vs.30.0%, respectively). Theprevalence of TCFA and lipid-rich plaque were significantly more prevalent asthe number of HRP feature increased (Figure 2).
Conclusion
OCTfeatures of plaque vulnerability were more frequently observed in HRP on CTA.Plaques with one or more HRP features had significantly more frequent OCTfeatures of plaque vulnerability than those without HRP.