Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-128
Emergent Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair in Patient With Flying Elephant Trunk After Ascending and Total Arch Replacement
By Taofan Taofan, Andrew Parlautan
Presenter
Andrew Parlautan
Authors
Taofan Taofan1, Andrew Parlautan2
Affiliation
National Cardiovascular Harapan Kita Hospital, Indonesia1, RSUD Raja Ahmad Tabib, Indonesia2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-128
ENDOVASCULAR - Aorta Disease and Intervention
Emergent Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair in Patient With Flying Elephant Trunk After Ascending and Total Arch Replacement
Taofan Taofan1, Andrew Parlautan2
National Cardiovascular Harapan Kita Hospital, Indonesia1, RSUD Raja Ahmad Tabib, Indonesia2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
GS
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
52-year-old male with uncontrolled hypertension came to the emergency department because of sudden tearing sensation chest pain. Physical examination showed blood pressure of 132/89 mmHg, respiratory rate of 22 per minute and saturation of 97%. While in intensive care unit, patient fell into respiratory distress and was intubated. Semi Hybrid Open surgical repair was done with Ascending aortic and Total Arch replacement with flying elephant trunk followed by Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Chest X ray showed enlarged mediastinum
Laboratory result showed elevated D-dimer (5227 ng/mL)
Echocardiography revealed good LVEF of 69% with trace aortic regurgitation and intimal flap in ascending aorta
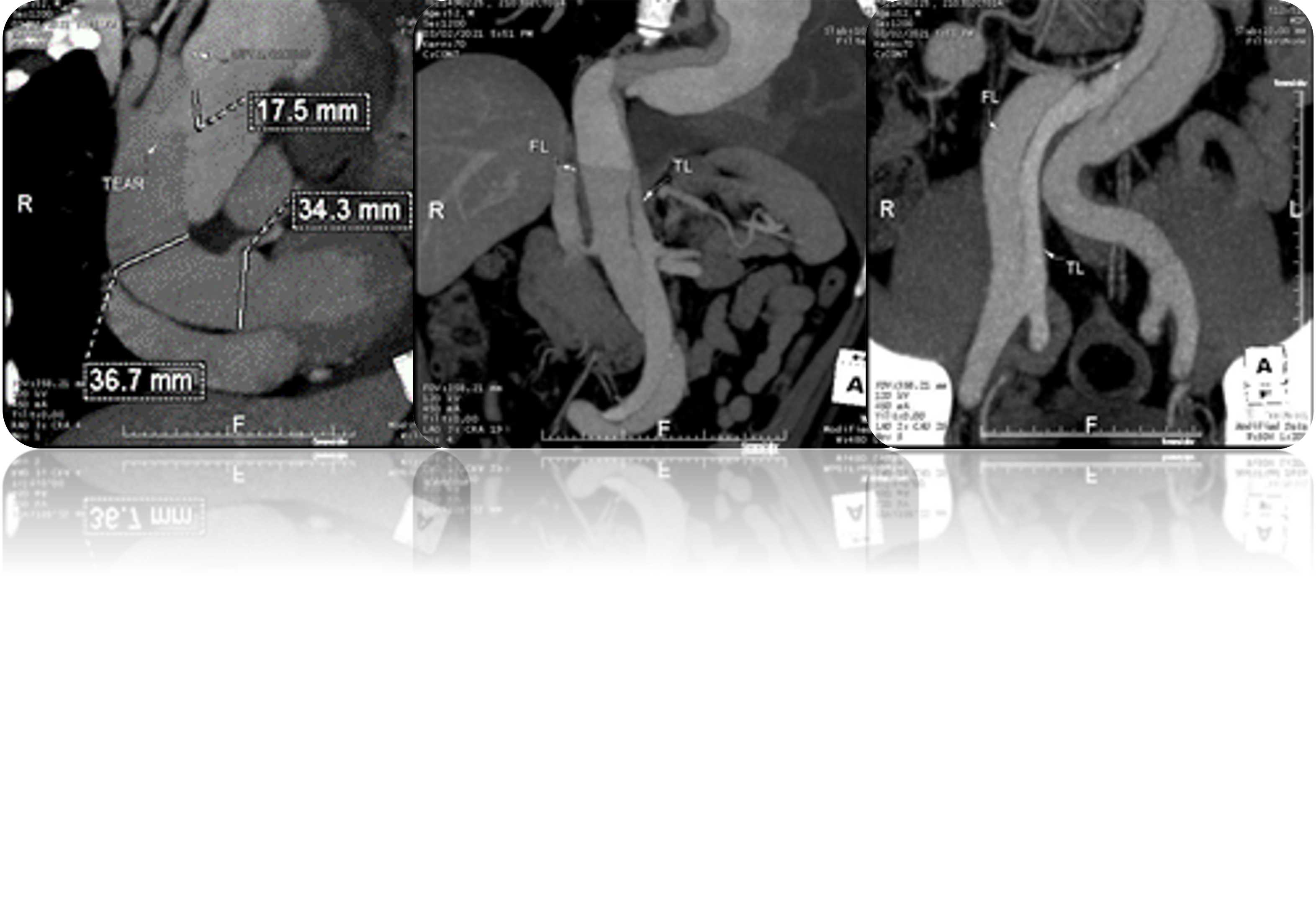
CT angiography showed Stanford type A Aortic Dissection DeBakey 1 in ascending and descending aorta extending into abdominal aorta, with visualized intimal flap between the proximal brachiocephalic artery and abdominal aorta, with contained rupture in descending aorta.
Laboratory result showed elevated D-dimer (5227 ng/mL)
Echocardiography revealed good LVEF of 69% with trace aortic regurgitation and intimal flap in ascending aorta
CT angiography showed Stanford type A Aortic Dissection DeBakey 1 in ascending and descending aorta extending into abdominal aorta, with visualized intimal flap between the proximal brachiocephalic artery and abdominal aorta, with contained rupture in descending aorta.



Relevant Catheterization Findings
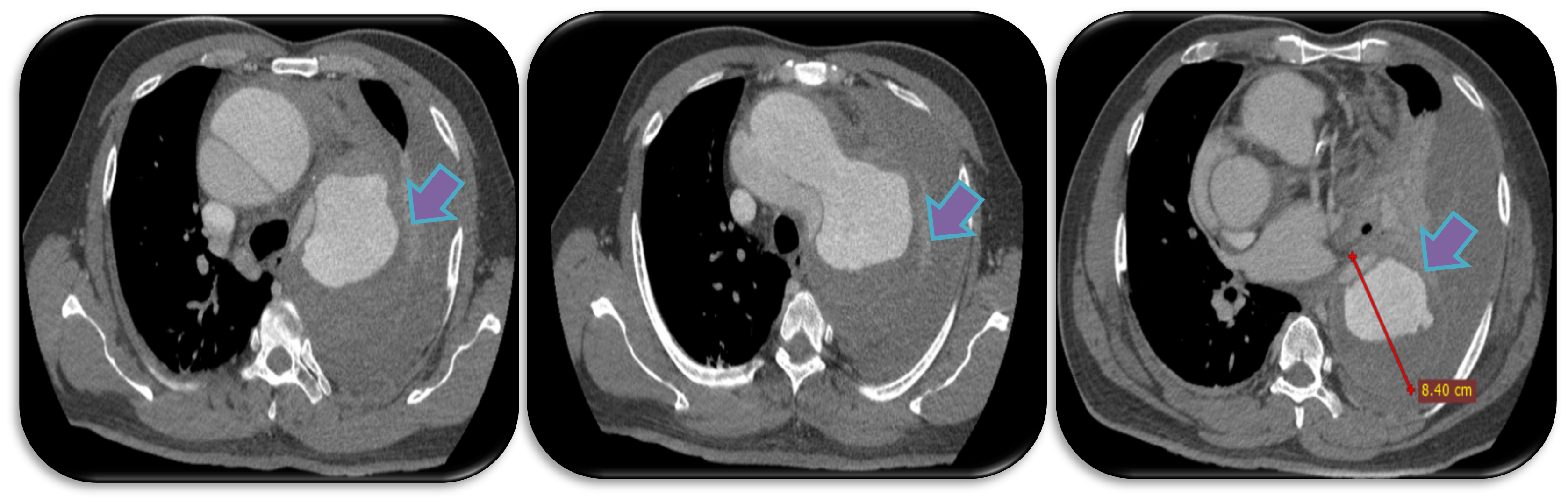
Aortography showed very mobile flying elephant trunk and ruptured area of descending aorta.
 Mobile elephant trunk.wmv
Mobile elephant trunk.wmv
 Ruptured of descending aorta.wmv
Ruptured of descending aorta.wmv
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
1. Proximal wire cannulation into descending aorta was attempted using Exchange Wire 300 cm from right radial access but failed due to false lumen entering
2. Access was changed to femoral access then mobile flying elephant trunk finally cannulated using Exchange Wire 300 cm, true lumen was confirmed by aortography using pigtail catheter
3. First aortic stent graft 30/200 mm was deployed from proximal of elephant trunk to descending aorta.
4. Aortopgraphy evaluation showed endoleak type 1B in distal part
5. Second aortic stent graft 34/200 mm was deployed overlapped with the first stent
6. Aortography revealed good position with no endoleak
Case Summary
This case presented the procedure of emergency TEVAR in Acute Stanford Type A Aortic Dissection who just underwent total arch replacement with an unattached conventional elephant trunk due to the aneurysm's length and diameter being bigger than the available elephant trunk's length. This technique could also be applied in carefully selected patients with similar conditions.


