Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-133
A Complicated Carotid Endovascular Treatment: Type IV Stent Fracture of a Carotid Stent
By Yi Pan Li, Cheng-Han Lee
Presenter
Yi Pan Li
Authors
Yi Pan Li1, Cheng-Han Lee2
Affiliation
National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Taiwan1, Tainan Municipal Hospital, Taiwan2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-133
ENDOVASCULAR - Carotid & Neurovascular Intervention
A Complicated Carotid Endovascular Treatment: Type IV Stent Fracture of a Carotid Stent
Yi Pan Li1, Cheng-Han Lee2
National Cheng Kung University Hospital, Taiwan1, Tainan Municipal Hospital, Taiwan2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Mr. Hsieh
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
This 63-year-old man presented with frequent falling down episodes 2-3 months ago. The medical history included type 2 diabetes mellitus, hyperternsion, dyslipidemia and bronchiectasis. He had radiotherapy for hypopharyngeal cancer 17 years ago. He was diagnosed with bilateral common carotid artery and internal carotid artery stenosis status post successful stenting in left and right ICA-CCA. Within 6-month follow up, he had recurrent syncope without focal neurologic deficits.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
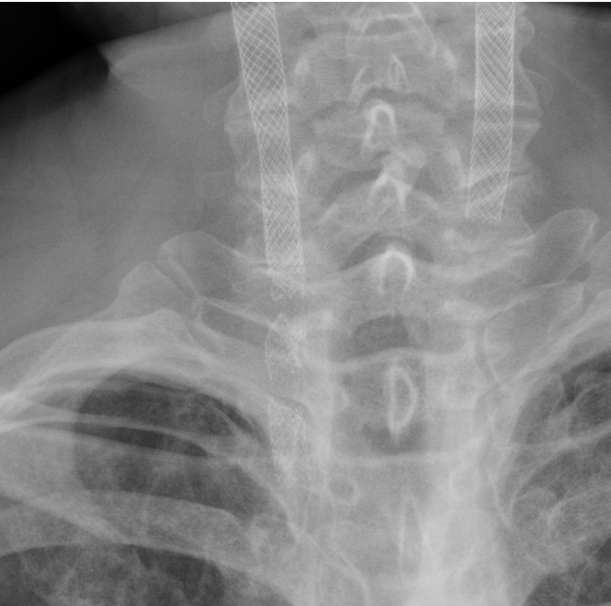
The chest film showed obvious stent fracture in right neck.
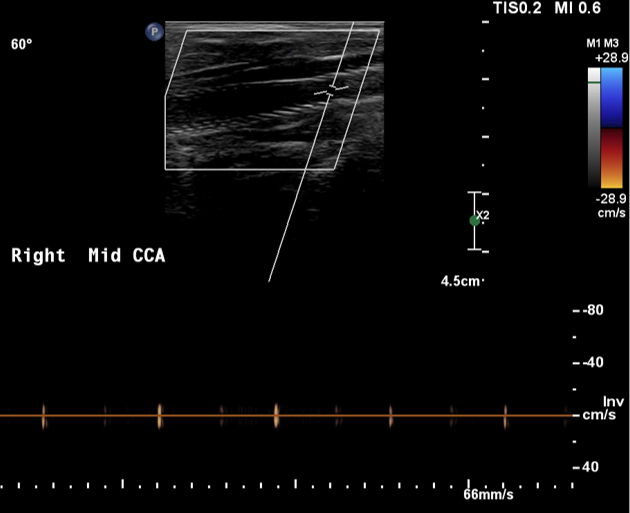
The carotid duplex demonstrated no flow in right common carotid artery, indicating total occlusion.


Relevant Catheterization Findings
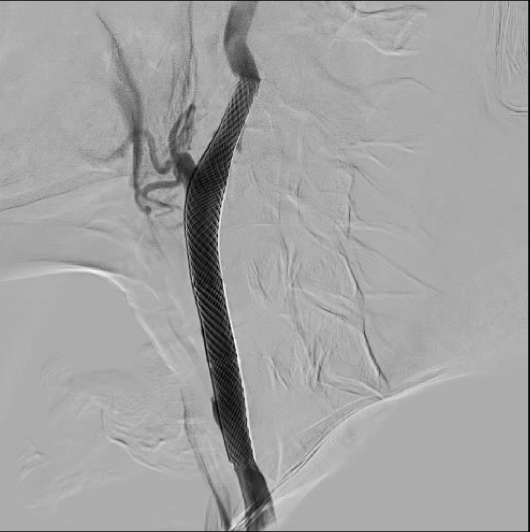
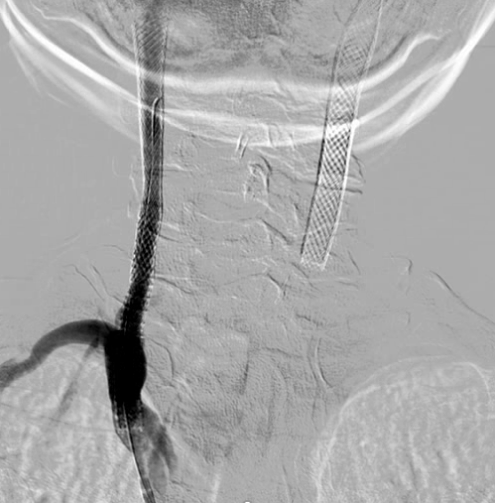
Right common carotid artery: post-stenting with type IV stent fracture (Express stent) and total occlusion (collateral flow from right vertebral artery)Right external carotid artery: total occlusion from common carotid artery (with collateral flow from right vertebral artery)Right internal carotid artery: collateral flow from right vertebral arteryRight vertebral artery: Diffuse atherosclerosis with 40-50% stenosis at cervical part
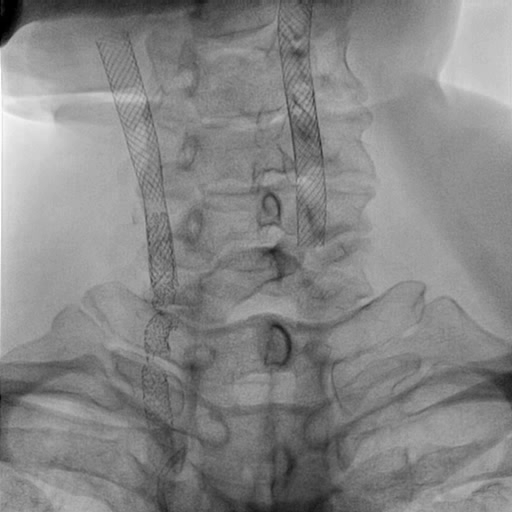


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
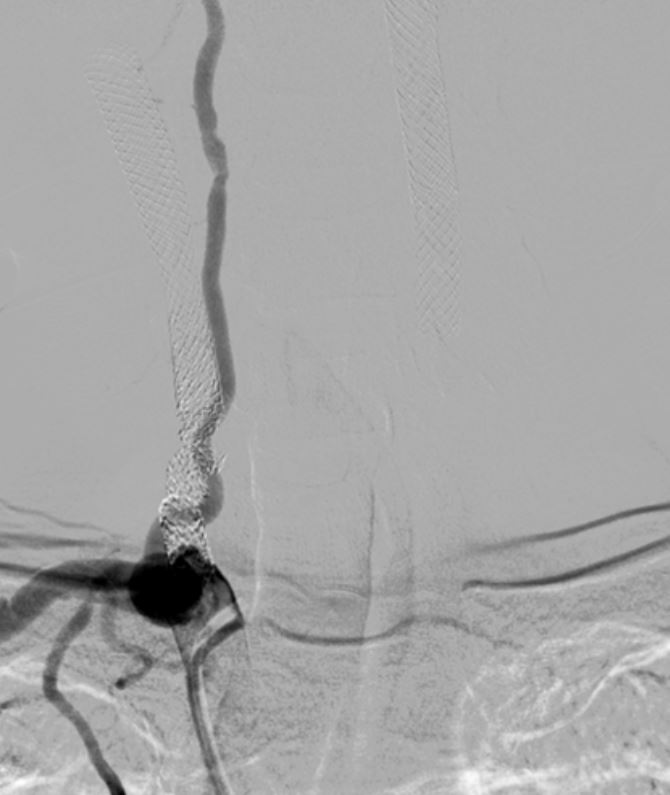
We used JR4 (8 Fr) guiding catheter and wire with Gaia Third supported by Excelsior microcatheter to cross into right ICA. The wire was changed to Fielder FC wire. The Legend balloon (1.5/20 mm) and(2.5/20 mm) were inflated to dilate right CCA. The Spider FX filter was placed at distal ICA. The Legend balloon (3.0/20 mm), NC Quantum balloon (5.0/15 mm) and Boston Sterling balloon (6.0/20 mm) were inflated to dilate right CCA sequentially. The angiogram showed large thrombus burden in right CCA so we did thrombus aspiration with Eliminate™ Aspiration Catheter. The following angiogram still showed residual thrombi. In the context of visible thrombi, further stenting would fractionate the thrombus and probably caused subsequent embolic stroke. Therefore, we administered medical therapy with aspirin, clopidogrel and warfarin. The triple combined medical therapy last for 1 month, followed by aspirin and warfarin. During the follow-up of 2 years, the patient remains asymptomatic without recurrent syncope episode.
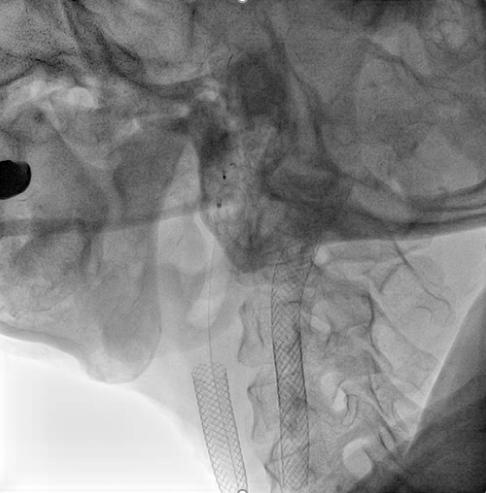
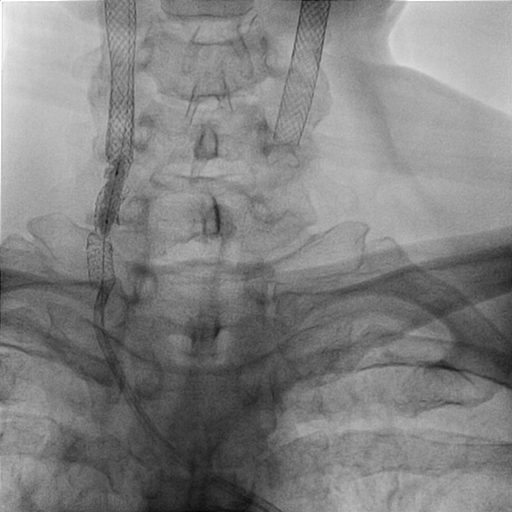
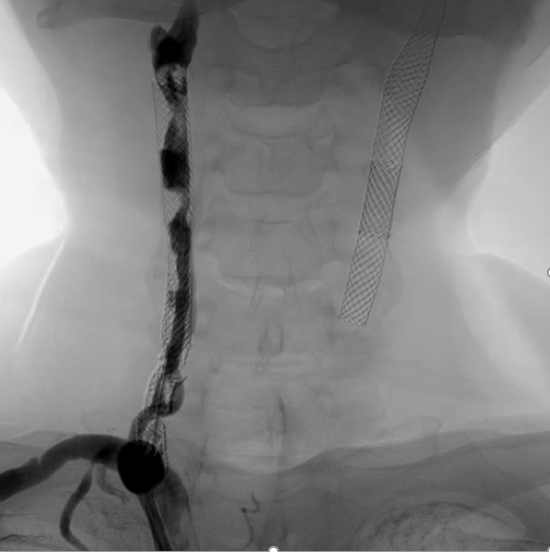
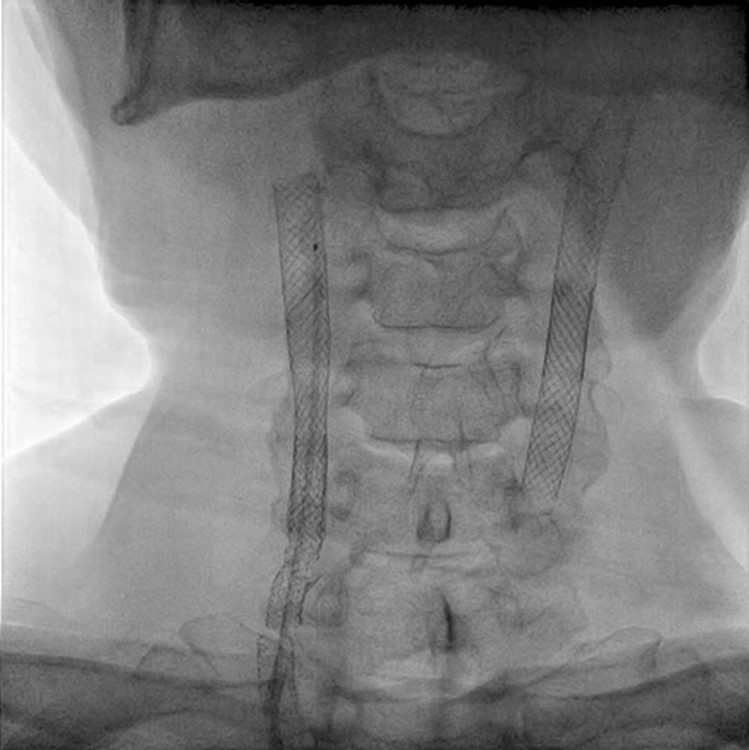
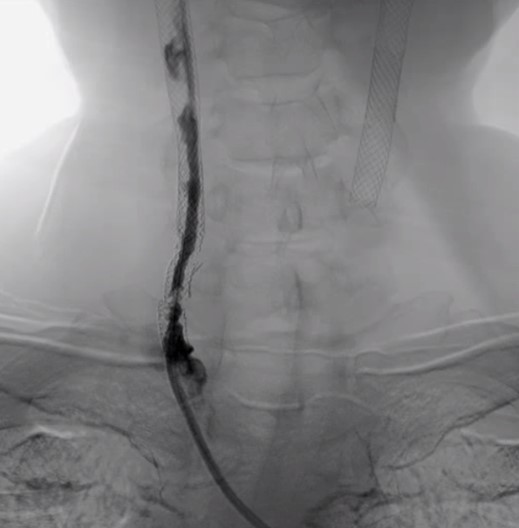





Case Summary
The risk factors for stent fracture in this case included post-irradiation status, severe calcification along the vessel wall, balloon expandable stent and overlapped stent. The patient had chronic cough due to bronchiectasis and it resulted in frequent neck flexion, related to stent fracture. We caught the movement of stent displacement while the patient was coughing during balloon angioplasty. The adverse effects of stent fracture are restenosis, thrombosis, pseudoaneurysm and embolization. We managed the stent fracture with balloon angioplasty, thrombus aspiration and medical therapy. The patient didn't develop severe complications, such as disabling stroke.


