Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-153
Optical Coherence Tomography Guided Management of Very Late Stent Failure and Old Unattended Dissection.
By Inderjeet Singh Monga
Presenter
Inderjeet Singh Monga
Authors
Inderjeet Singh Monga1
Affiliation
Command Hospital, India1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-153
IMAGING AND PHYSIOLOGIC LESION ASSESSMENT - Imaging: Intravascular
Optical Coherence Tomography Guided Management of Very Late Stent Failure and Old Unattended Dissection.
Inderjeet Singh Monga1
Command Hospital, India1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
72/male, Veteran Officer of Indian Army
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
Hypertensive
Non-Diabetic
Non-Smoker
Known case of Coronary Artery Disease
Double Vessel Disease
Post PCI to LAD CTO (2003)
2x Drug Eluting Stent (Taxus 2.75x28 mm mid LAD and 2.75x18 mm Taxus Prox LAD)
Presentation-Chronic Stable angina x 1 year and crescendo angina for 03 months
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
ECG- LVH with strain.
Echo- EF 55%, Conc LVH, no RWMA
Stress MPI- Large Reversible Perfusion defect in LAD Territory
Relevant Catheterization Findings
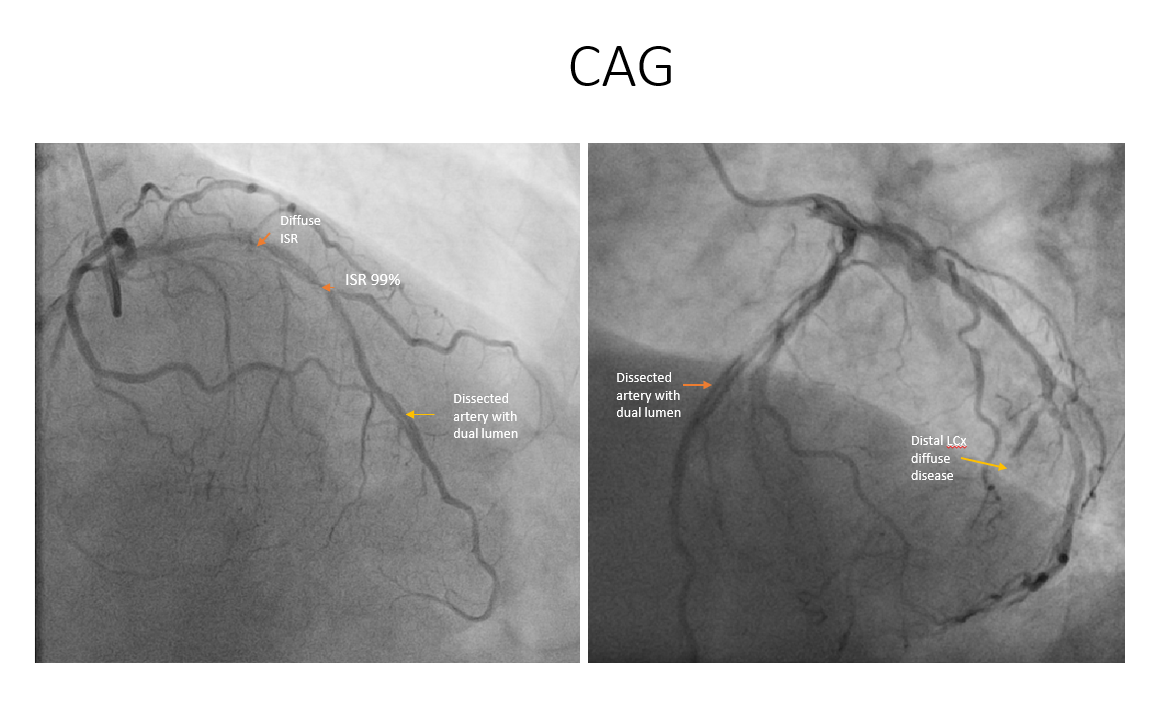
CAG revealed: DVDLAD ostial plq+ f/b Prox to mid stent diffuse ISR max 99% in mid, distal two lumens visible parallel to each other later joining to form single arteryLCX Dominant, distal diffusely diseased 99%, small caliber vessel, OM3/OMM Osteoprox 80-90%.RCA non-dominant.
Pre PCI OCT revealed: Distal dual Lumen and Proximal heterogenous ISR with fibro-calcific ISR. Calcium score 3/4 as per SHLOSHA protocol, Deep and Superficial calcium.
 OCT Pre PCI Pullback.mp4
OCT Pre PCI Pullback.mp4
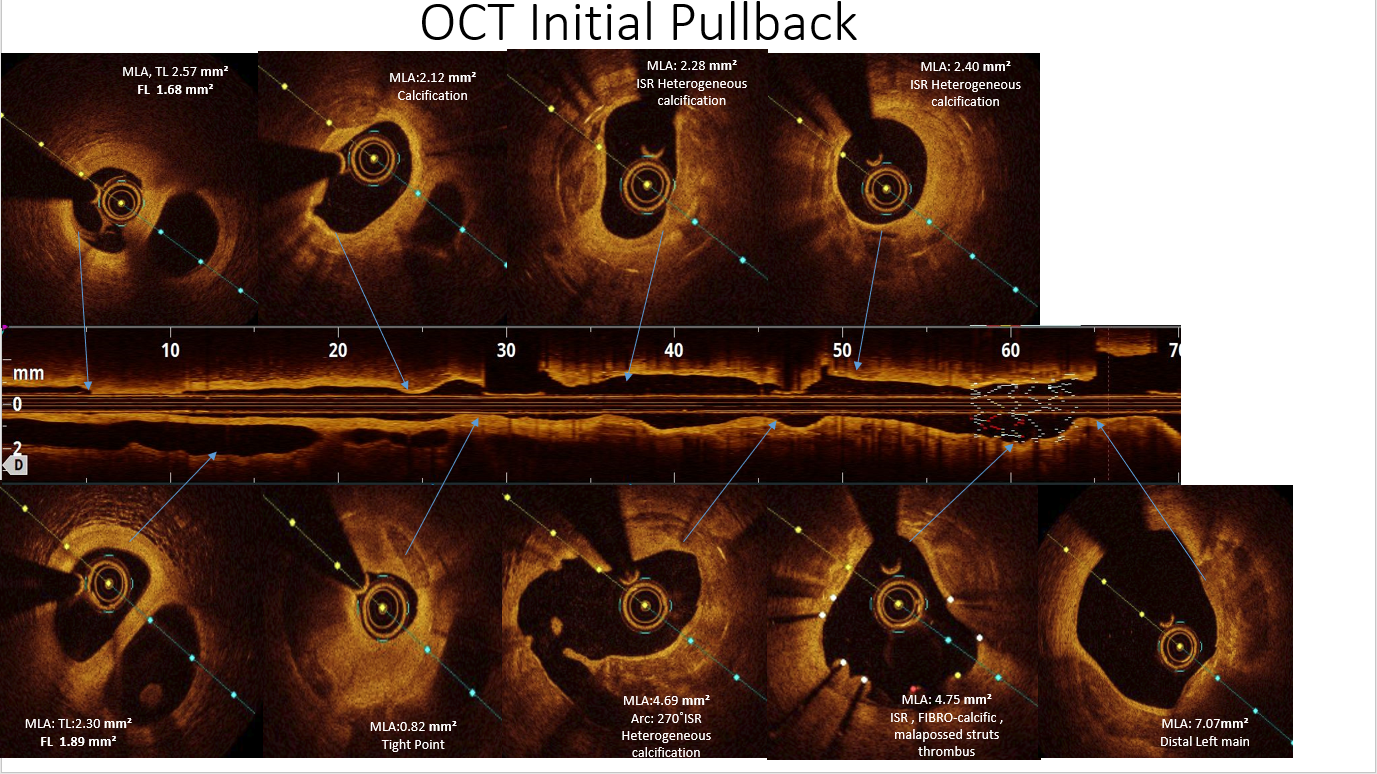
Pre PCI OCT revealed: Distal dual Lumen and Proximal heterogenous ISR with fibro-calcific ISR. Calcium score 3/4 as per SHLOSHA protocol, Deep and Superficial calcium.


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
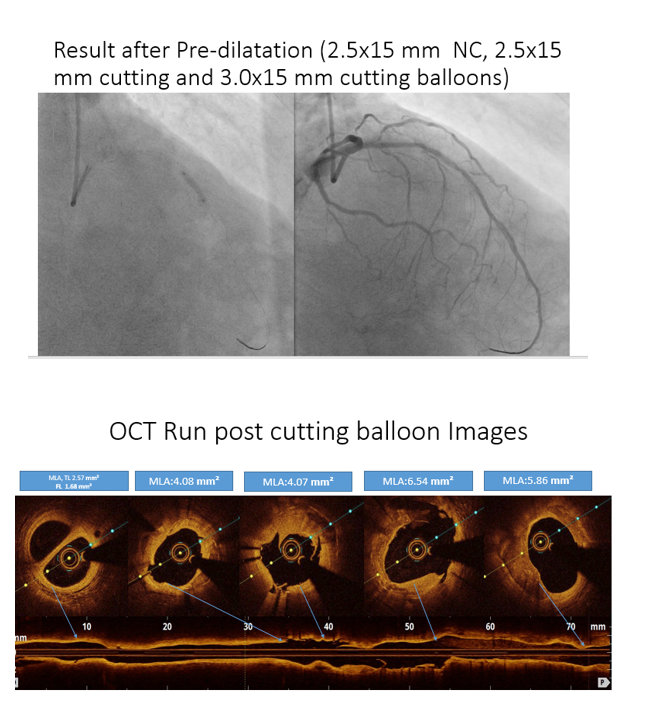
Step 1: LAD ISR Bed Preparation: OCT guided Pre Dilatation with 2.5 mm x 15 mm NC Balloon, 2.5 mm x 15 Cutting Balloon, 3 mm x 15 Cutting Balloon.
Step:2 OCT-guided Distal LAD stent deployment with XP-2.5x38.
Step 3: High-Pressure Dilatation with 3.15 mm OPN NC at 45 ATM in the distal segment and Proximal calcified segment for proper bed preparation and optimal stent expansion.
Step 4: Proximal stent Deployment 3x38 XP
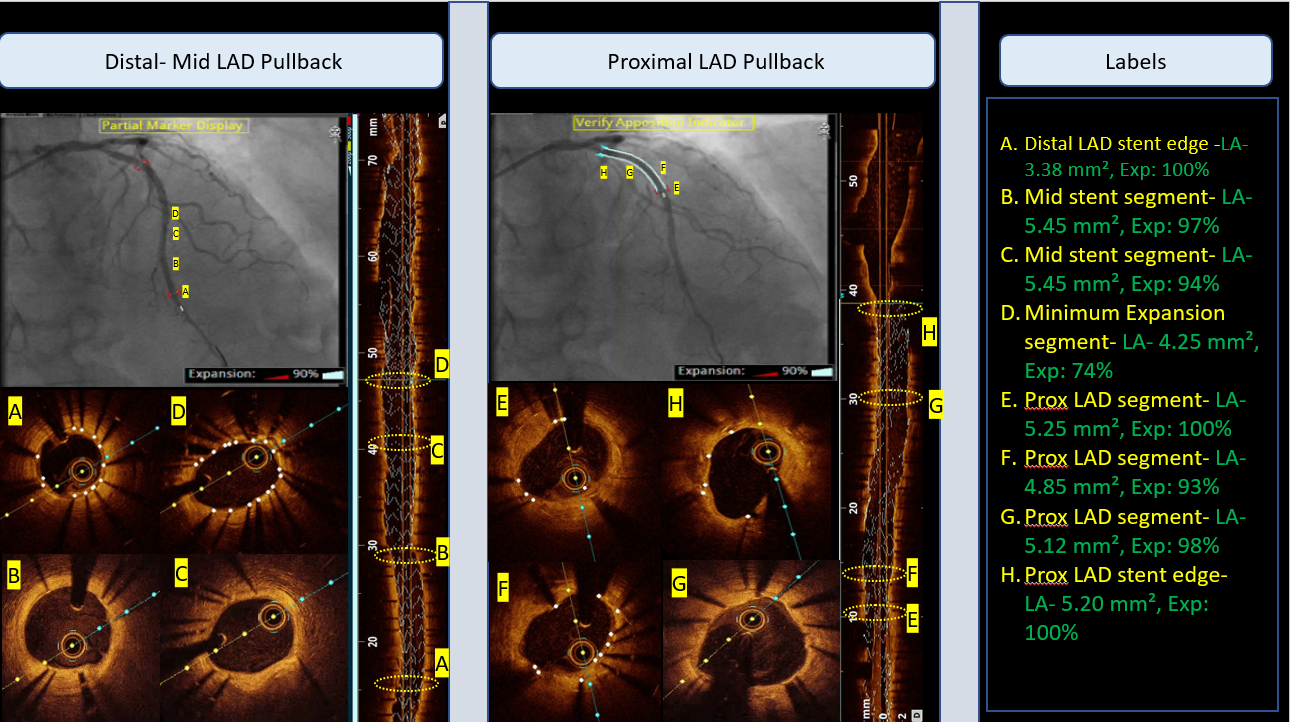
Step 5: Post Dilation with 3.5 x 12 mm NC at 24 ATM and PCI Optimization. OCT showed Optimal expansion of more than 90% in both proximal and distal segments, No Malapposition observed and no edge dissections at both proximal and distal edges.
Step 6: Staged PCI to distal LCx was done with 2.75 x 23 mm XP.
Step 7 : Follow up at 4 months with OCT imaging, showed proper neo-intimal coverage at stent struts and optimal MSA with no late acquired malapposition, stent failure or restenosis. Both stents were patent and optimally expanded with TIMI-III flow.
 Final Angio- OCT run.mp4
Final Angio- OCT run.mp4
Step:2 OCT-guided Distal LAD stent deployment with XP-2.5x38.
Step 3: High-Pressure Dilatation with 3.15 mm OPN NC at 45 ATM in the distal segment and Proximal calcified segment for proper bed preparation and optimal stent expansion.
Step 4: Proximal stent Deployment 3x38 XP
Step 5: Post Dilation with 3.5 x 12 mm NC at 24 ATM and PCI Optimization. OCT showed Optimal expansion of more than 90% in both proximal and distal segments, No Malapposition observed and no edge dissections at both proximal and distal edges.
Step 6: Staged PCI to distal LCx was done with 2.75 x 23 mm XP.
Step 7 : Follow up at 4 months with OCT imaging, showed proper neo-intimal coverage at stent struts and optimal MSA with no late acquired malapposition, stent failure or restenosis. Both stents were patent and optimally expanded with TIMI-III flow.


Case Summary
Calcified Neoatheroscleosis, uncovered stent struts, and old unattended dissection diagnosed in patient with very late stent failure presenting with ACS.
Patient optimally managed with cutting and OPN balloons followed by 2nd Gen EES using OCT guidance.
OCT helped us in managing the very late stent failure in first generation DES as well as old unattended complication of dissected lumen.
Patient optimally managed with cutting and OPN balloons followed by 2nd Gen EES using OCT guidance.
OCT helped us in managing the very late stent failure in first generation DES as well as old unattended complication of dissected lumen.


