Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-174
Successful Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement With SAPIEN 3 Valve in a Patient With Quadricuspid Aortic Stenosis
By Tomoki Ochiai, Futoshi Yamanaka, Noriaki Moriyama, Koki Shishido, Shigeru Saito
Presenter
Tomoki Ochiai
Authors
Tomoki Ochiai1, Futoshi Yamanaka1, Noriaki Moriyama1, Koki Shishido1, Shigeru Saito1
Affiliation
Shonan Kamakura General Hospital, Japan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-174
STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE - Valvular Intervention: Aortic
Successful Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement With SAPIEN 3 Valve in a Patient With Quadricuspid Aortic Stenosis
Tomoki Ochiai1, Futoshi Yamanaka1, Noriaki Moriyama1, Koki Shishido1, Shigeru Saito1
Shonan Kamakura General Hospital, Japan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
J.I
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 75-year-old woman with symptomatic severe aortic stenosis was referred for transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). Her past medical history included diabetes, coronary artery disease and chronic obstructive plumonary disease. There was a grade 4/6 aortic systolic murmur.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
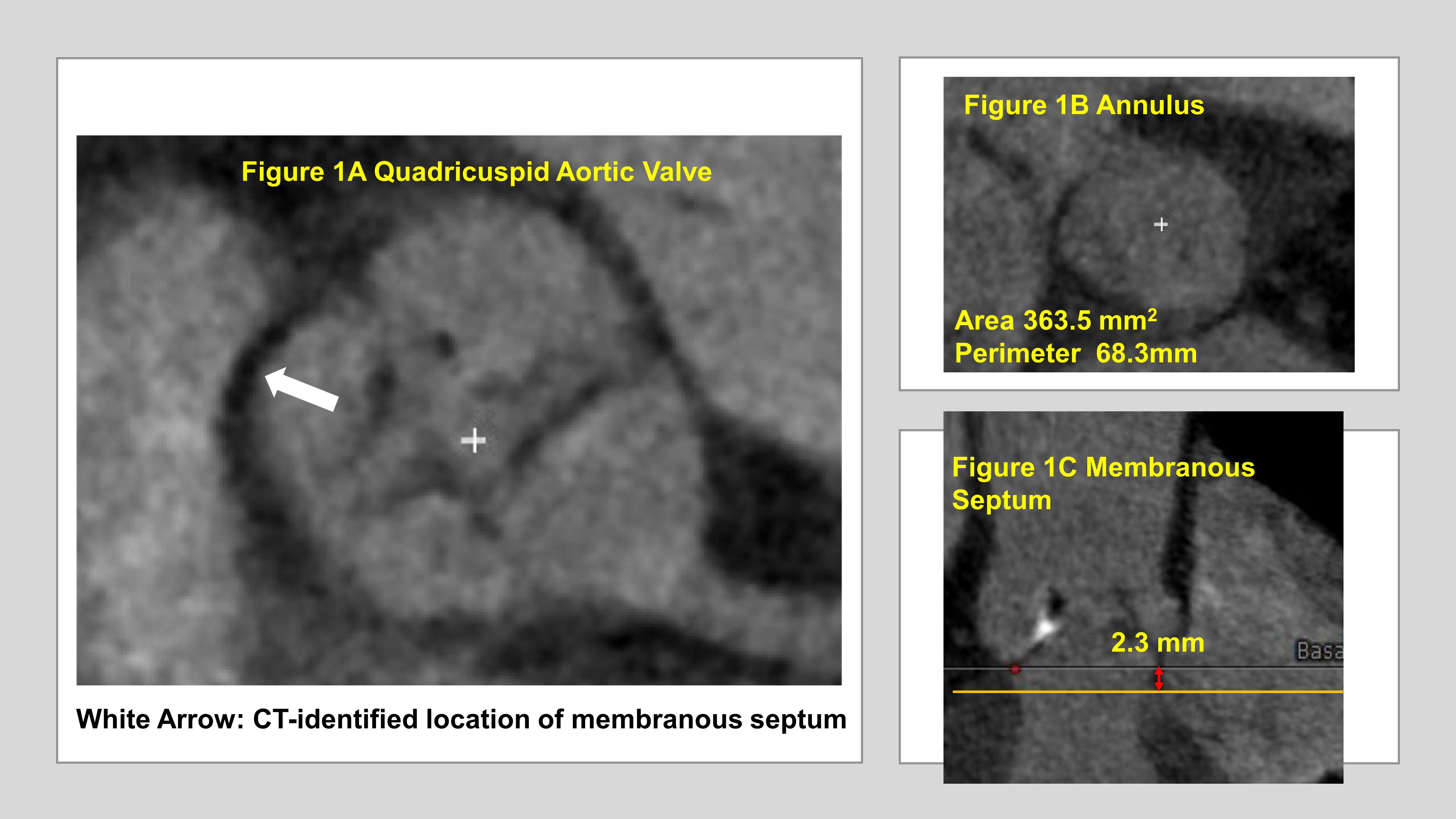
Pre-procedural transthoracic echo showed a severe calcified aortic stenosis with a mean gradient of 48 mmHg and a calculated valve area of 0.74 cm2, a normal left vetricular ejection fraction with mild aortic regurgitation (Video 1 and 2). Pre-procedural computed tomography revealed a quadricuspid aortic valve (QAV). The annular area and perimeter were 363.5 mm2 and 68.3 mm, respectively. The patient had relatively short membranous septum of 2.3 mm (Figure 1A, 1B and 1C).
 Video1.mp4
Video1.mp4
 Video2.mp4
Video2.mp4

Relevant Catheterization Findings
The coronary angiogram revealed a chronic total occlusion of the right coronary artery. There was no significant obstructive disease in left coronary artery (Video 3 and 4).
 Video 3.mp4
Video 3.mp4
 Video 4.mp4
Video 4.mp4
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
It was very challenging to identify an optimal fluoroscopic perpendicular valve projection showing all four cusps separately and in line. Thus, we implanted a valve using a three-cusp view where the left, right and another sinus which was located lower than the other one were identified in the same plane (Video 5). The patient underwent successful implantation of a 23-mm SAPIEN 3 valve via transfemoral access (Video 6 and 7). Post-procedural transthoracic echo showed well-functioning bioprosthetic aortic valve with no paravalvular regurgitation. Post-procedural ECG showed no new conduction disturbances. The patient had an uneventful postoperative course and was discharged home 72 hours pos t procedure.
 Video 5.mp4
Video 5.mp4
 Video 6.mp4
Video 6.mp4
 Video 7.mp4
Video 7.mp4
Case Summary
This case demonstrates that QAV stenosis can be treated using TAVR with favorable clinical outcomes. During TAVR for QAV stenosis, identifying an optimal fluoroscopic perpendicular valve projection showing all four cusps separately and in line is often challenging. In such cases, using a three-cusp perpendicular view may be a good alternative for successful valve implantation.


