Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-160
Emergency Pericardiocentesis by CVC Kit in Patient With Cardiac Tamponade Due to Blunt Chest Trauma : A Rare Case From Remote District Hospital
By Belinda Suhuyanly, I Gede Sumantra, Umbu Jabu Anggung Praing
Presenter
Belinda Suhuyanly
Authors
Belinda Suhuyanly1, I Gede Sumantra2, Umbu Jabu Anggung Praing3
Affiliation
Waikabubak District Hospital, Indonesia1, Bandung Adventist Hospital, Indonesia2, General Hospital Umbu Rara Meha, Indonesia3,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-160
OTHERS - Others (Unclassified)
Emergency Pericardiocentesis by CVC Kit in Patient With Cardiac Tamponade Due to Blunt Chest Trauma : A Rare Case From Remote District Hospital
Belinda Suhuyanly1, I Gede Sumantra2, Umbu Jabu Anggung Praing3
Waikabubak District Hospital, Indonesia1, Bandung Adventist Hospital, Indonesia2, General Hospital Umbu Rara Meha, Indonesia3,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Mr. AD
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
39-year-old male was admitted to the emergency room with dypsnea and chest pain 5 hours after having a stone thrown to the chest. At presentation, he was alert, tachypnea with heart rate 128 beats/min, and in pain. On general examination, he was hypotensive, blood pressure of 80/50 mmHg, with peripheral hypoperfusion. There was bruise mark on the chest. Cardiovascular examination showed distended jugular venous pressured, muffled heart sound, and pulsus paradoxus.
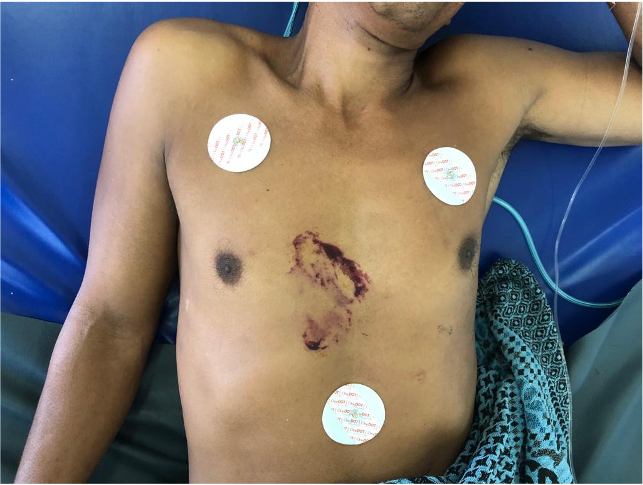
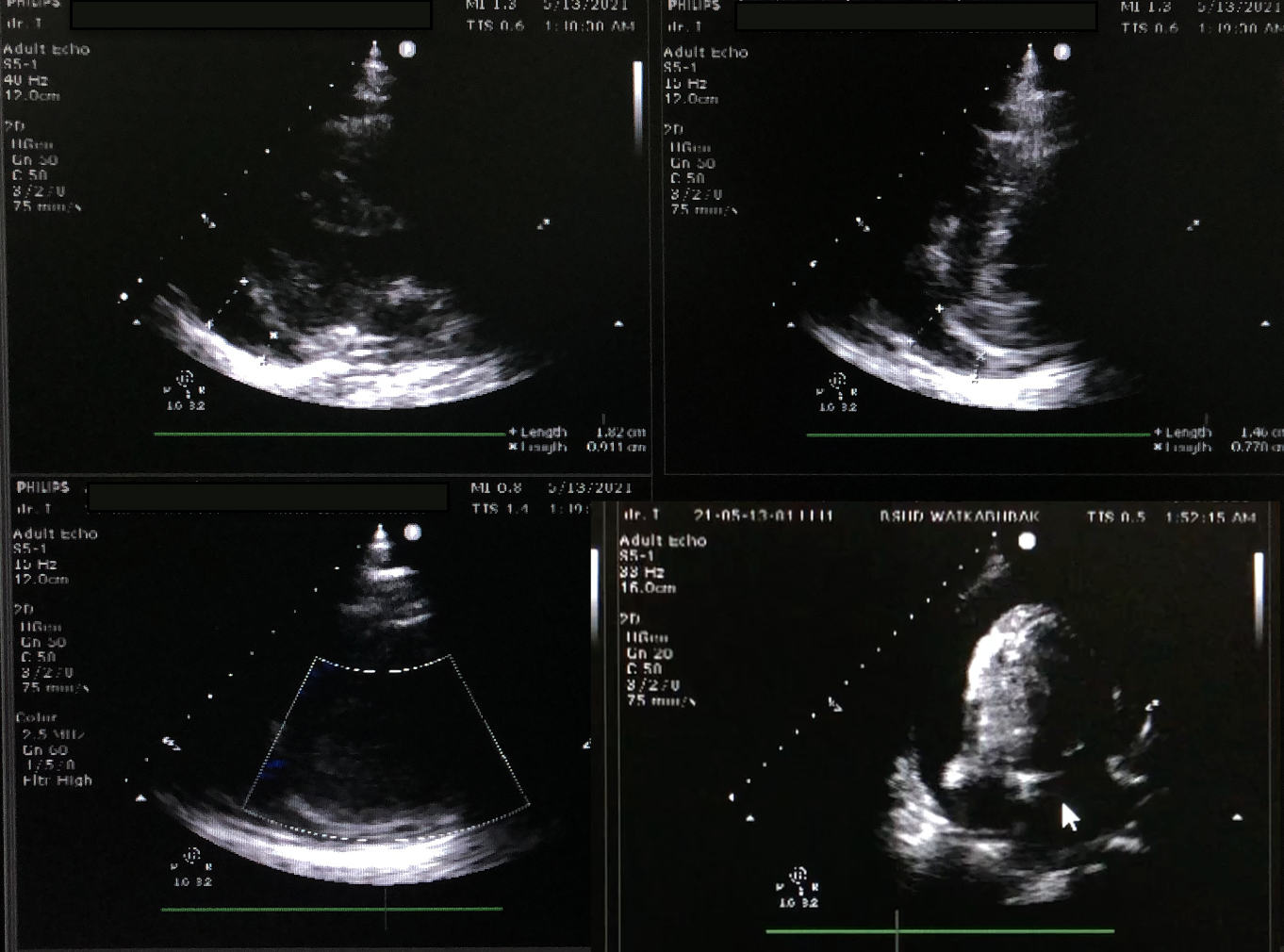
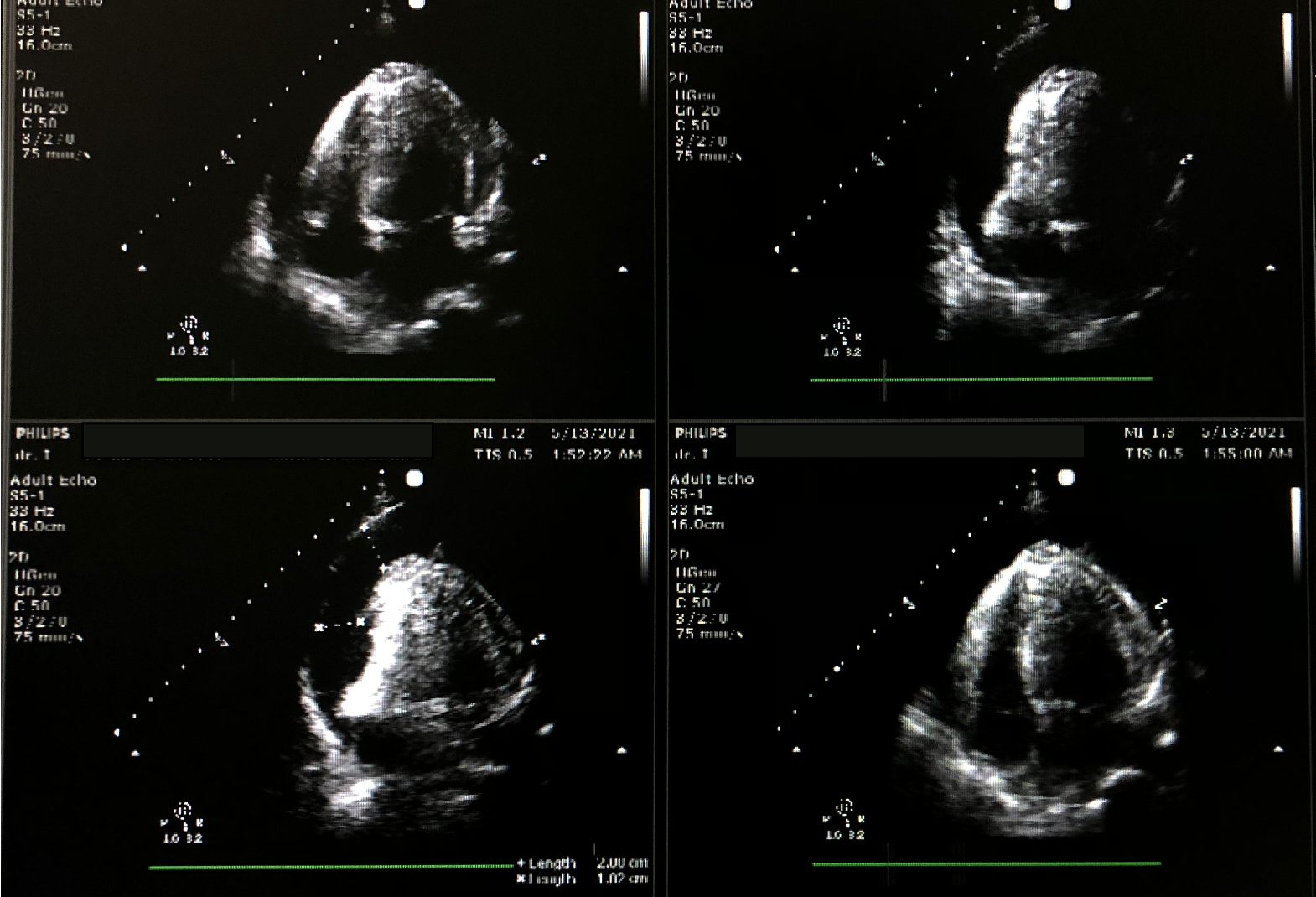



Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Echocardiography was performed to determine the ideal entry site (subxiphoid). Next, we prepared the CVC kit triple lumen 7 Fr x 16 cm and other equipment with aseptic technique. CVC kit triple lumen was rinsed with heparinised solution. The patient was placed in the supine position with the head of the bed elevated at 30 degrees. We cleansed the skin with an antiseptic solution and the patient was fully draped with exposure of only the subxiphoid. Lidocaine was injected. Under echocardiography guidance, we inserted a 16 G needle into the subxiphoid area toward the patient’s left shoulder while aspirating the syringe until the pericardial fluid was obtained. We then extracted 100 ml of bloody pericardial fluid. J wire was then passed through the needle into the pericardial space. The introducer and dilator were inserted over the guidewire and catheter was inserted after the removal of the dilator. The catheter was then fixed to the skin and pericardial drainage continued by connecting its end to infusion set and then to the urine bag with a goal of drainage was 150 ml/day. After the procedure, he was clinically improved, no complications were seen. Echocardiography evaluation showed a reduction in effusion size with a resolution of tamponade. Three days after the procedure, the drainage volume of bloody pericardial fluid was 10 ml. Echocardiogram evaluation showed minimal pericardial effusion with no signs of tamponade. He was then discharged from the hospital 5 days after admission.
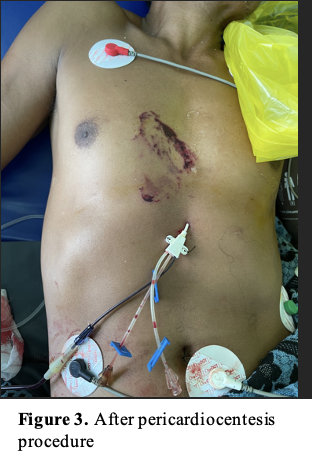
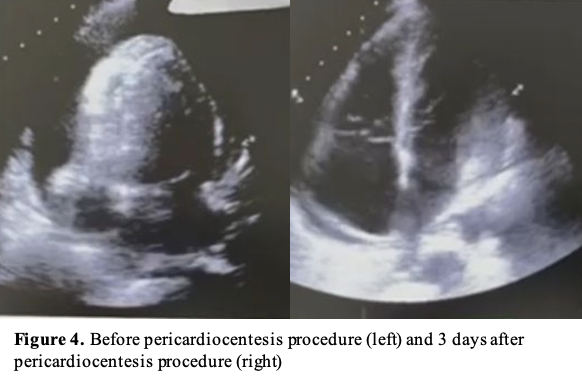


Case Summary
This is a case of cardiac tamponade as an uncommon and fatal complication of blunt chest trauma that was diagnosed clinically. Echocardiography was used as an imaging modality to confirm clinical suspicion and as a guide for treatment. The definitive treatment of cardiac tamponade is to reduce the intrapericardial pressure by pericardiocentesis. Pericardiocentesis serves as a procedure for therapeutic and diagnostic. Subxiphoid approach of pericardiocentesis is considered the safest method. Here, we demonstrate a good outcome of emergency pericardiocentesis in cardiac tamponade that was done by CVC kit triple lumen using Seldinger technique in a rural area with limited resources.


