Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-103
Management of Intramural Hematoma After Stenting
By Hao Yun Lo, Chih-Fan Yeh
Presenter
Hao Yun Lo
Authors
Hao Yun Lo1, Chih-Fan Yeh2
Affiliation
National Taiwan University Hospital Hsin-Chu Branch, Taiwan1, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-103
CORONARY - Complications
Management of Intramural Hematoma After Stenting
Hao Yun Lo1, Chih-Fan Yeh2
National Taiwan University Hospital Hsin-Chu Branch, Taiwan1, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
5004643
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 80-year-old male complained of chest tightness and dyspnea for 6 months. He had peripheral arterial occlusion status post percutaneous transluminal angioplasty to the left iliac artery in 2020 and dyslipidemia. He was performed Thallium dipyridamole stress test 5 years ago and showed stress-induced ischemia mixed at inferior and inferolateral walls. Coronary angiography was suggested, but the patient was lost follow up.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
The electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with early repolarization. The cardiac sonography showed preserved left ventricle ejection fraction without regional wall abnormality. Thallium-201 ECG-gated myocardial perfusion imaging with dipyridamole and resting test showed reduced flow reserve at the mid inferior wall was noted.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
LM: PatentLAD: middle stenosis 70 %, D1 stenosis 70 %, with collateral to LCX and RCA (apic) through septal branchLCX: proximal chronic total occlusion, JCTO score 1 (blunt entry shape)RCA: middle chronic total occlusion, JCTO score 0
 RAO 20.3 CAU 26.0.mp4
RAO 20.3 CAU 26.0.mp4
 LAO 49.2 CAU 21.7.mp4
LAO 49.2 CAU 21.7.mp4
 LAO 58.4 CAU 3.3.mp4
LAO 58.4 CAU 3.3.mp4
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Target 1: LCX CTO 1. Engaged a EBU3.5 6F guiding catheter to left coronary artery and wired ASAHI Sion to LAD.2. Antegrade wired GAIA Second with Terumo Finecross Micro Catheter to distal LCX through CTO lesion. Switched GAIA Second to Terumo Runthrough floppy.3. Performed balloon angioplasty and performed IVUS to LCX from stent sizing and landing zone evaluation.4. Performed balloon angioplasty to LCX lesion. However, the wire was removed during these treatments. Re-wired Terumo Runthrough floppy to distal LCX and keep balloon dilation.5. Deployed DES, Ony x 2.25*38 mm, from proximal to distal LCX.6. Post-dilated balloon to well expand the stent. However, TIMI II flow was noted from stent distal part to distal LCX.7. Performed IVUS. The distal stent was landed in false lumen, with intramural hematoma formation.8. Dilated cutting balloon, BOSTON cutting2.25*10mm, to stent distal part.9. TIMI III flow was noted in distal LCX.
Target 2: proximal to middle LAD (p-mLAD)1. Performed IVUS to p-mLAD from stent sizing and landing zone evaluation.2. Performed balloon angioplasty and deployed DES, COMBO DES 2.5*33mm, to p-mLAD.3. Post-dilated with NC balloon.4. Performed IVUS to LAD and the stent was well expanded. Performed IVUS and true-false-true lumen connection was noted.5. Post-dilated with NC balloon to proximal LCX. Performed IVUS again and the stent was well expanded.6. The final angiography showed TIMI III flow. We closed the procedure.
 post stent to LCX.mp4
post stent to LCX.mp4
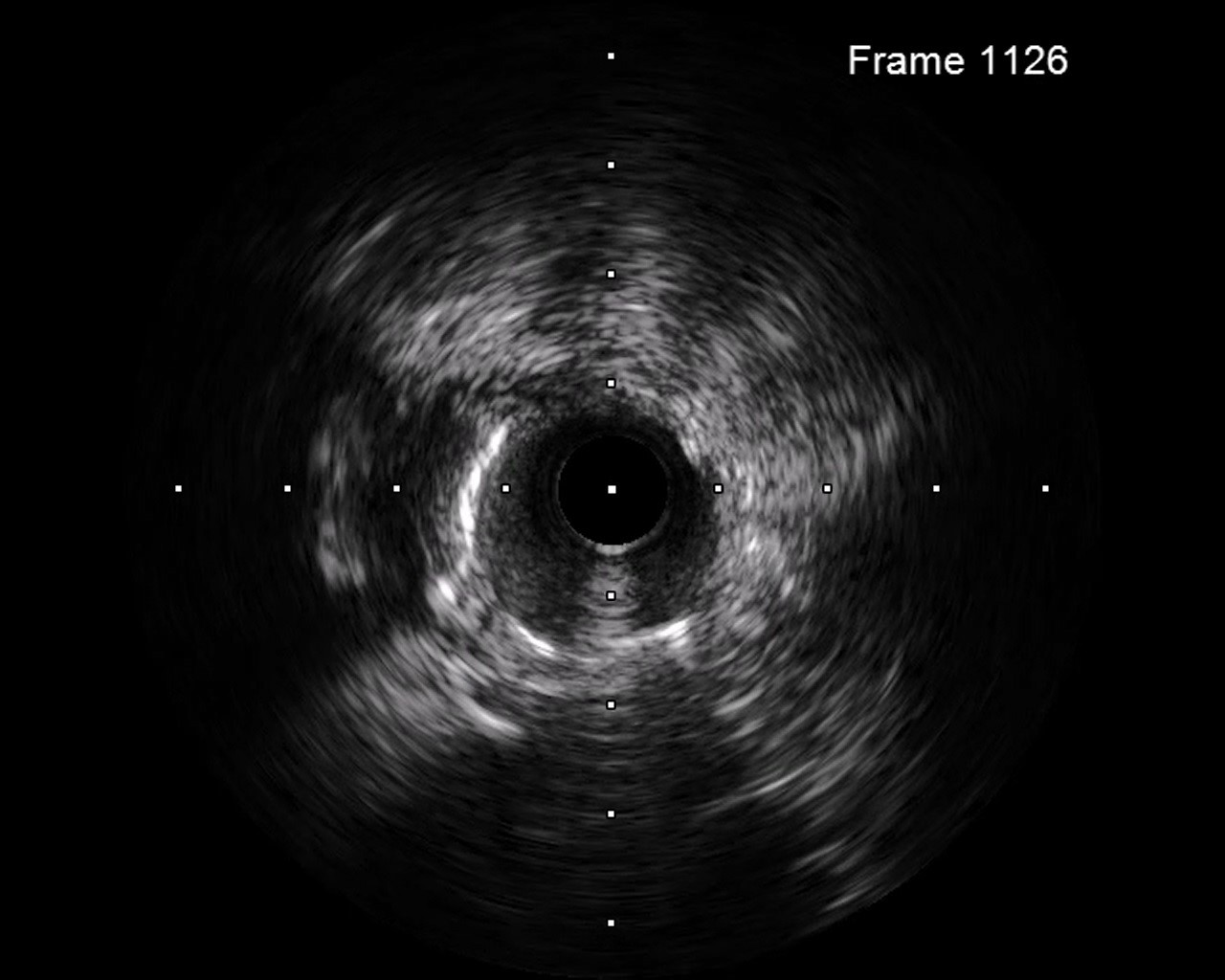
 Final.mp4
Final.mp4
Target 2: proximal to middle LAD (p-mLAD)1. Performed IVUS to p-mLAD from stent sizing and landing zone evaluation.2. Performed balloon angioplasty and deployed DES, COMBO DES 2.5*33mm, to p-mLAD.3. Post-dilated with NC balloon.4. Performed IVUS to LAD and the stent was well expanded. Performed IVUS and true-false-true lumen connection was noted.5. Post-dilated with NC balloon to proximal LCX. Performed IVUS again and the stent was well expanded.6. The final angiography showed TIMI III flow. We closed the procedure.

Case Summary
Wiring through true-false-true lumen is not rare in CTO lesions treatment. Management of stent deployed in true-false-true lumen with intramural hematoma formation have not been well studied. We performed a case with this condition, and successfully treated with intravascular ultrasound-guided fenestration and cutting balloon.


