Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-106
Repair of Iatrogenic Aorto-Ostial Dissection Using Coronary Stenting With Intravascular Ultrasound Guided
By Gahn Nakornchai, Thitima Limjaroen, Vorarit Lertsuwunseri
Presenter
Gahn Nakornchai
Authors
Gahn Nakornchai1, Thitima Limjaroen2, Vorarit Lertsuwunseri2
Affiliation
Chonburi hospital, Thailand1, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Thailand2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-106
CORONARY - Complications
Repair of Iatrogenic Aorto-Ostial Dissection Using Coronary Stenting With Intravascular Ultrasound Guided
Gahn Nakornchai1, Thitima Limjaroen2, Vorarit Lertsuwunseri2
Chonburi hospital, Thailand1, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Thailand2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
L.A.
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 68-year-old Thai male presented with acute chest pain at rest. ECG showed deep symmetrical T wave inversion in V1-6 with elevated high-sense TnI consistent with NSTE-ACS. His past medical history are type 2 diabetic mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia and chronic kidney disease stage 3. He underwent diagnostic angiography at other center. Culprit was assumed to be LAD but failed PCI due to heavy calcification. He was transferred to our center for further management.
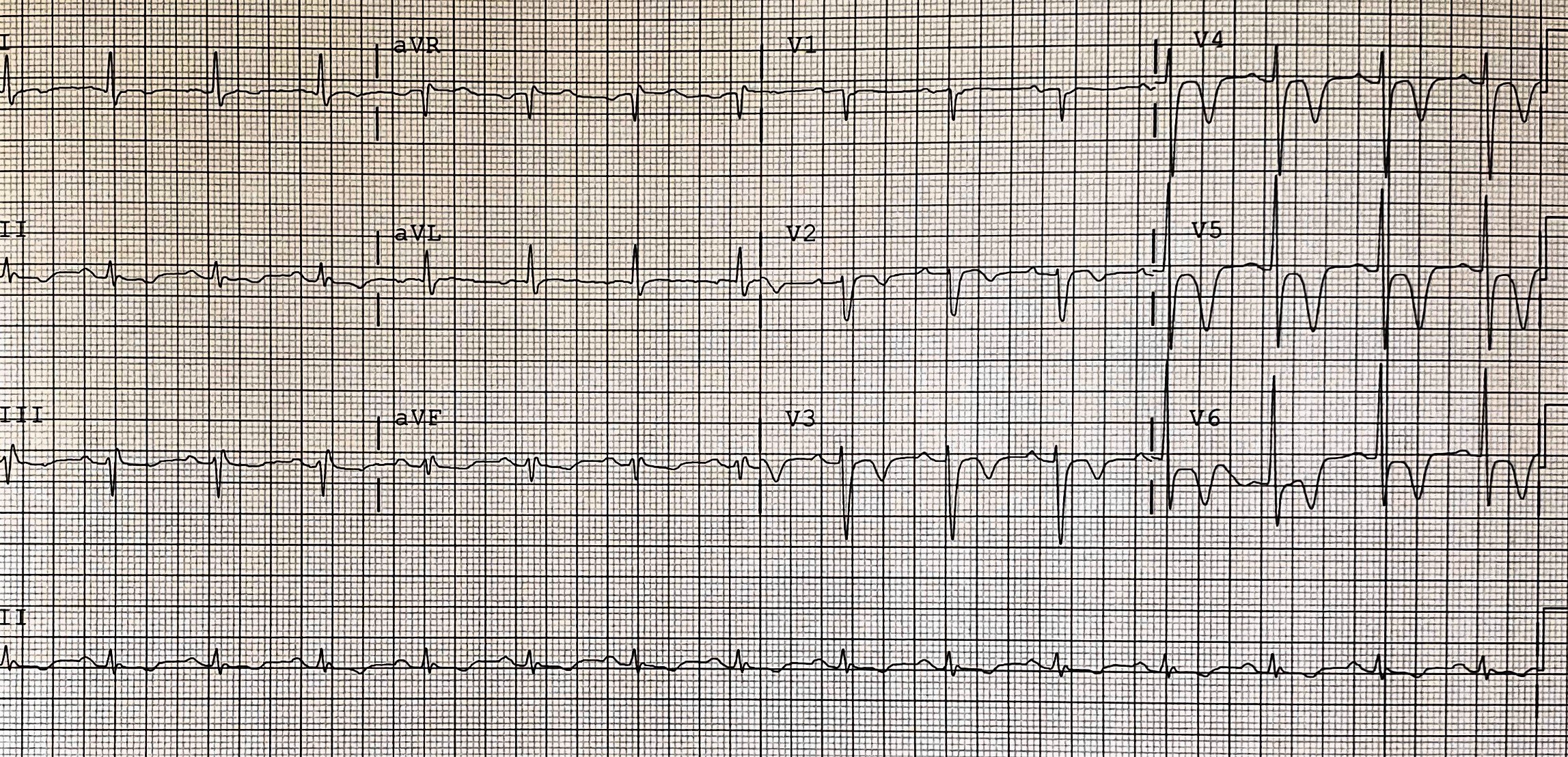

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Previous angiography showed heavy calcification and critical stenosis with TIMI flow 1 at mid LAD. "Shepherd Crook" type take off proximal RCA with heavy calcification and tight stenosis of proximal and mid RCA were noted. Re-evaluation of coronary anatomy and complexity demonstrated SYNTAX score of 39, which patient would stand to benefit from CABG. Patient and his family strongly denied surgery. PCI was successfully done at mid LAD with Rotablator and stage PCI at RCA was scheduled.
 Pre-PCI LAD RAO cranial.mp4
Pre-PCI LAD RAO cranial.mp4
 Post-PCI LAD RAO cranial.mp4
Post-PCI LAD RAO cranial.mp4
 Pre-PCI RCA LAO.mp4
Pre-PCI RCA LAO.mp4
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Patient were scheduled for PCI at RCA. Angiography demonstrated Shepherd Crook tortuosity of proximal RCA with heavy calcification along proximal to mid RCA and loop-like tortuosity at mid to distal RCA. Tight stenosis of proximal and mid RCA were visualized.
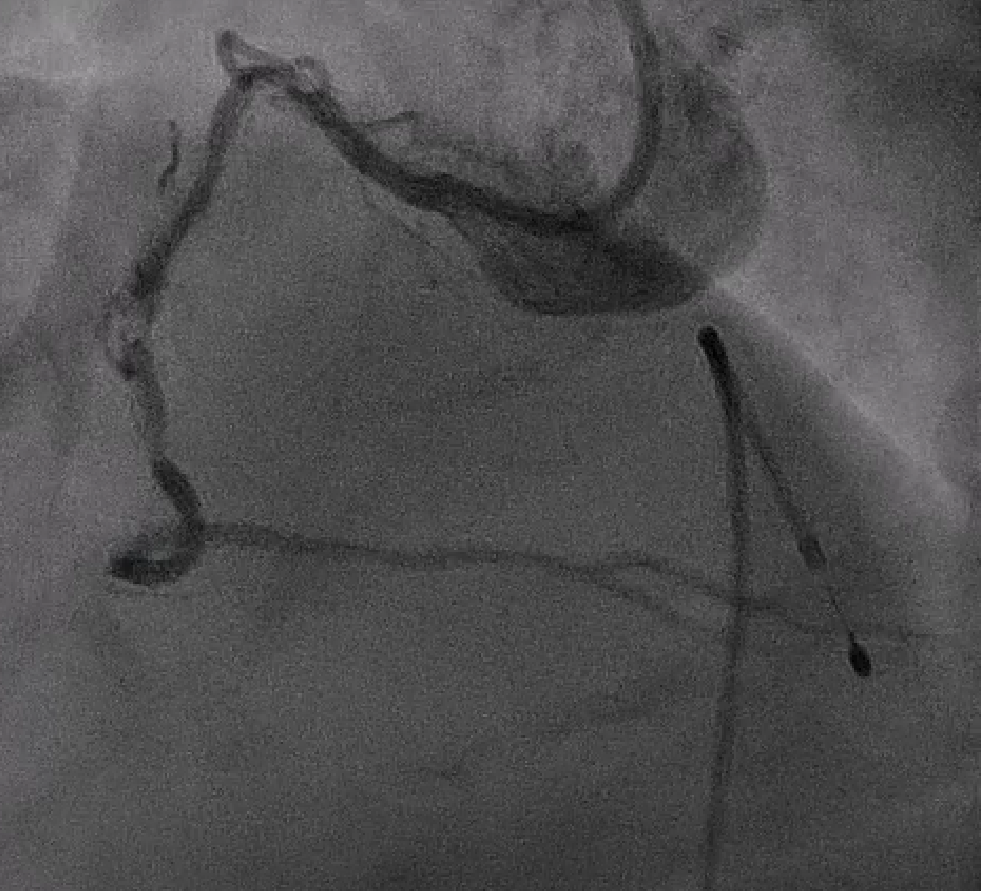

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Right femoral artery and vein were approach with 6-Fr sheath. Temporary pacemaker was placed prior to Rotablator. XB RCA guide catheter (Cordis, California) was selected to establish good guide support. Whisper ES (Abbott, Minnesota) with Finecross (Terumo) were wired into distal RCA with difficulty and Finecross failed to pass to distal RCA. Rota floppy was exchanged at mid RCA and finally wired to distal RCA. 1.5-mm Rotablator burr (Boston Scientific, Massachusetts) was performed at proximal to mid RCA. Angiography revealed contrast stained in right aortic cusp with suspected catheter induced aorto-ostial dissection of RCA. IVUS (Boston Scientific, Massachusetts) demonstrated dissection and intramural hematoma at proximal and ostial RCA. Wire was still in true lumen. Patient was clinically and hemodynamically stable. Our strategy was to deliver stent to mid RCA and came back to seal off dissection at ostium. Despite aggressive lesions preparation with Rotablator and NC balloons (2.75 x 15 mm), increase support with Guide Plus II (Nipro, Japan), delivery of 2.5 x 26 mm Firehawk (MicroPort, China) to mid RCA was unsuccessful. We decided to only seal off dissection at proximal to ostial RCA using 3.0 x 26 mm Resolute Integrity (Medtronic, Minnesota). IVUS demonstrated stent under expansion with gap between stent and ostium. 3.5 x 9 mm Resolute Integrity and 4.0 x 6 mm NC balloon were put between ostial gap. Final IVUS revealed good stent expansion and dissection was completely sealed.
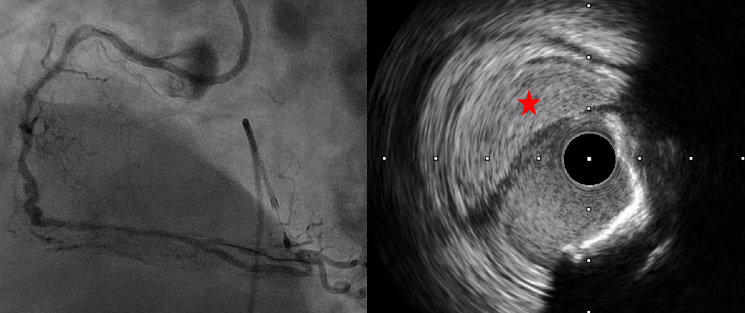
 IVUS after 3.0 x 26 mm Resolute Integrity.mp4
IVUS after 3.0 x 26 mm Resolute Integrity.mp4
 Final IVUS.mp4
Final IVUS.mp4

Case Summary
Guide catheter induced aorto-ostial dissection should be aware during coronary intervention. Treatment of aorto-ostial dissection with smallest volume of contrast injection and immediate stenting prevent further complication to aorta. IVUS helps identifying true lumen and guiding for better sealing off dissection.


