Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-169
Transcatheter Septal Closure of Post-Myocardial Infarction Ventricular Septal Rupture in Patient With Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction and Cardiac Arrest on VA ECMO
By Piyoros Lertsanguansinchai, Vorarit Lertsuwunseri, Pornthep Lertsapcharoen, Thitima Limjaroen, Chaisiri Wanlapakorn, Siriporn Athisakul, Suphot Srimahachota
Presenter
Piyoros Lertsanguansinchai
Authors
Piyoros Lertsanguansinchai1, Vorarit Lertsuwunseri1, Pornthep Lertsapcharoen1, Thitima Limjaroen1, Chaisiri Wanlapakorn1, Siriporn Athisakul2, Suphot Srimahachota1
Affiliation
King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Thailand1, Kcmh, Thailand2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-169
STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE - Others (Structural Heart Disease)
Transcatheter Septal Closure of Post-Myocardial Infarction Ventricular Septal Rupture in Patient With Inferior Wall Myocardial Infarction and Cardiac Arrest on VA ECMO
Piyoros Lertsanguansinchai1, Vorarit Lertsuwunseri1, Pornthep Lertsapcharoen1, Thitima Limjaroen1, Chaisiri Wanlapakorn1, Siriporn Athisakul2, Suphot Srimahachota1
King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, Thailand1, Kcmh, Thailand2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
5697064
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 75-year-old female with a history of hypertension was admitted to province hospital with acute inferior wall myocardial infarction. Primary PCI was done to mid RCA at province hospital. Two hours after primary PCI, she developed cardiac arrest. Echocardiography revealed a LVEF of 65% with ventricular septal rupture (VSR) of 12 mm in diameter at basal inferoseptum. She was referred to our hospital for VSR closure and VA ECMO due to cardiogenic shock and multiple organ failures.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
The initial electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with ST-segment elevation in lead II, III and aVF, suggestive acute inferior wall STEMI. Transthoracic echocardiography was performed after cardiac arrest, revealed a LVEF of 65% with ventricular septal rupture of 12 mm in diameter atbasal inferoseptum with a significant left-to-right shunt (Qp:Qs = 6.9) and akinetic wall motion at the inferior wall.On admission, laboratory data revealed AKI, ischemic hepatitis, thrombocytopenia, and high lactate.
 VSR 1 echo TCTAP.mp4
VSR 1 echo TCTAP.mp4
 VSR 2 echo TCTAP.mp4
VSR 2 echo TCTAP.mp4
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Emergent coronary angiography at the province hospital revealed total occlusion of the mid right coronary artery (RCA) thrombus and 50% stenosis at mid left anterior descending (LAD) artery. After aspiration thrombectomy and placement of drug eluting stent, coronary blood flow was TIMI 3. After being referred to our hospital, IABP and VA ECMO were performed to support and stabilize hemodynamics due to cardiogenic shock with multiple organ failures from VSR.
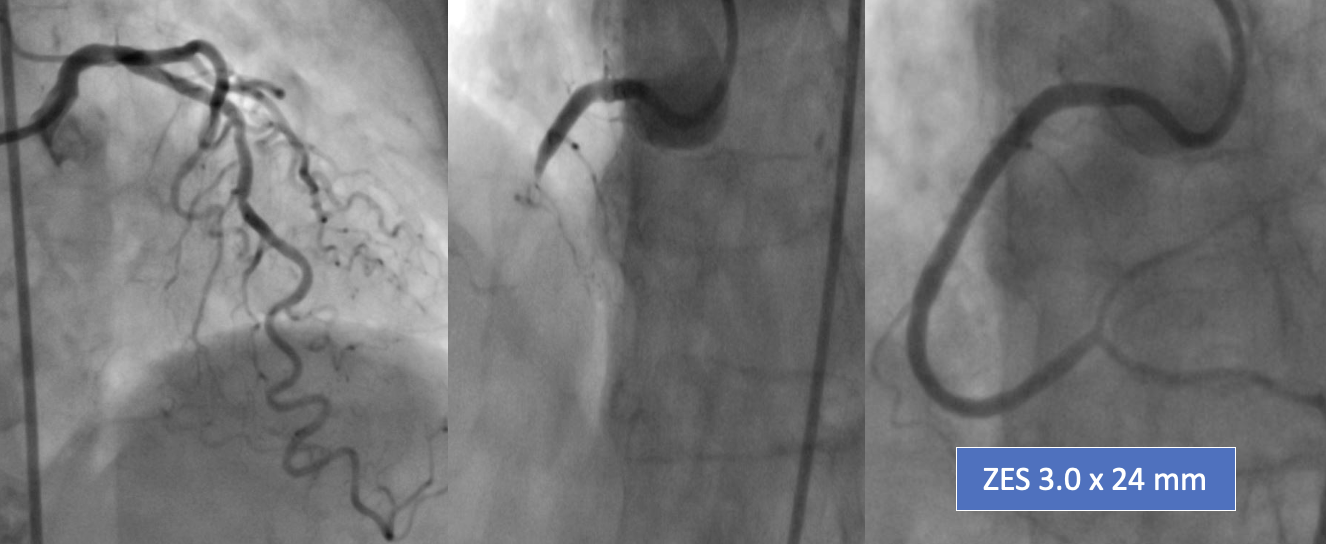

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Due to old age and the patient being too sick for surgical repair, then transcatheter closure (TSC) Of VSR was performed on day 9 of admission. Since both VA ECMO catheters were placed in the left groin, we decided to use the right femoral artery (RFA) and vein (RFV) by removing IABP. We advanced a 5Fr JR4.0 catheter to cross the defect from LV to RV with 0.035 Terumo long-wire and landed the wire into the pulmonary artery (PA). We advanced a 6Fr Multipurpose catheter to PA then snare Terumo wire and externalized it via RFV to form an arteriovenous rail. We inserted a 24 mm sizing balloon via RFV to measure the VSR defect size. The VSR was about 20 mm. We chose a 24-mm Cocoon ASD occluder device for closing the VSR defect. We advanced a 12Fr septal occluder sheath via RFV to load the device by leaving the Terumo wire in the system to stabilize the position of the loader sheath. The 24-mm occluder device was then delivered to the LV. Then the delivery sheath was withdrawn until the LV disc was opened under TEE guidance to ensure that the device did not open in the mitral apparatus. The sheath was continued to RV to release the RV disc.Before releasing the occluder device from the delivery cable, we performed TEE to confirm good septal alignment, placement, and device size. Then Terumo wire was removed. After a satisfactory TEE evaluation, the device was deployed from the delivery cable. Final TEEwas performed to confirm the good placement position of the device.
 VSR closure TCTAP.mp4
VSR closure TCTAP.mp4
 VSR closure 2 TCTAP.mp4
VSR closure 2 TCTAP.mp4
Case Summary
After the TSC, the patient showed a decrease in Qp:Qs from 6.9 to 2.5 and TTE showed a successful reduction of the left-to-right shunt. Since the hemodynamic parameters improved significantly, IABP and VA ECMO were weaned off on day 2 after TSC. Day 1 after off VA ECMO, patient hadcardiogenic shock and TTE showed rupture chordae of the tricuspid valve causing acute severe TR, which might occur during advancement of 12Fr septal occluder sheath to load the device. Her relatives denied re-insertion of ECMO and TV repair. Eventually, the patient died from septic and cardiogenic shock. TSC is an emerging option for inoperable patients due to excessive surgical risk and may use as primary VSR repair.


