Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-156
Combining Fractional Flow Reserve and Quantitative Flow Ratio Guided Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Three-Vessel Coronary Artery Lesions
By Hehe Cui, Li Zhou, Hui Chen
Presenter
Hehe Cui
Authors
Hehe Cui1, Li Zhou2, Hui Chen2
Affiliation
Beijing Anzhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, China1, Beijing Friendship Hospital, China2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-156
IMAGING AND PHYSIOLOGIC LESION ASSESSMENT - Physiologic Lesion Assessment
Combining Fractional Flow Reserve and Quantitative Flow Ratio Guided Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Three-Vessel Coronary Artery Lesions
Hehe Cui1, Li Zhou2, Hui Chen2
Beijing Anzhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, China1, Beijing Friendship Hospital, China2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
CJF
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 59-year-old man complaint one episode of rest chest tightness transiently occurred three weeks before. The symptom radiated to the left arm and last almost 30 minutes. He had history of poorly controlled hypertension, hyperuricemia and well controlled type 2 diabetes. He smoked about 20 pieces of cigarette a day for 40 years. Vitals: Blood pressure 148 / 96 mmHg (left arm), 144 / 92 mmHg (right arm). Pulse 86 /minute. Body mass index 23.29 kg/m2. No positive sign in the cardiovascular system.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
An ECG was acquired (Figure 1 A). Cardiac troponin I 0.002 ng/mL (99 % URL 0.030). LDL-C 2.67 mmol/L. Echocardiogram showed good ejection fraction (63 %) and no wall motion abnormalities. A coronary computed tomographic angiography was performed, and calcified plaques with severe stenosis were revealed in the mid left descending artery (LAD), left circumflex (LCX), and posterior descending artery (PDA). (Figure 1 B). The patient was diagnosed with unstable angina (Brauwarld Grade II).
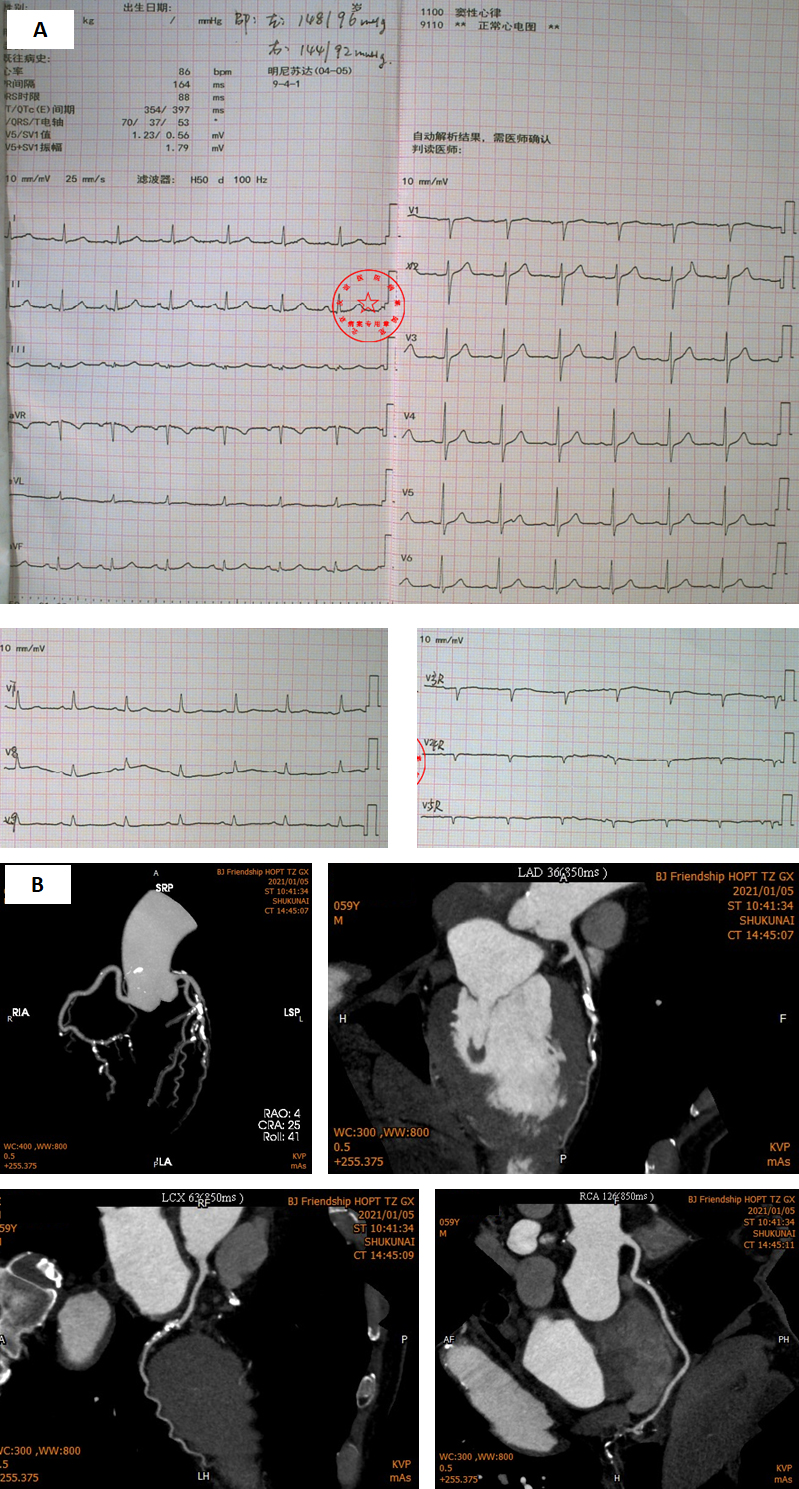

Relevant Catheterization Findings
The coronary angiography was performed to identify the lesions. The clips showed a right dominant distribution with coronary tortuosity, a 70 % - 80 % tubular stenosis in the distal LCX, a 70 % - 80 % diffuse stenosis in the proximal to mid LAD, a 90 % - 95 % local stenosis in the PDA and a subtotal occluded posterior lateral artery (PLA).
 RUN 1.avi
RUN 1.avi
 RUN 2.avi
RUN 2.avi
 RUN 3.avi
RUN 3.avi
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
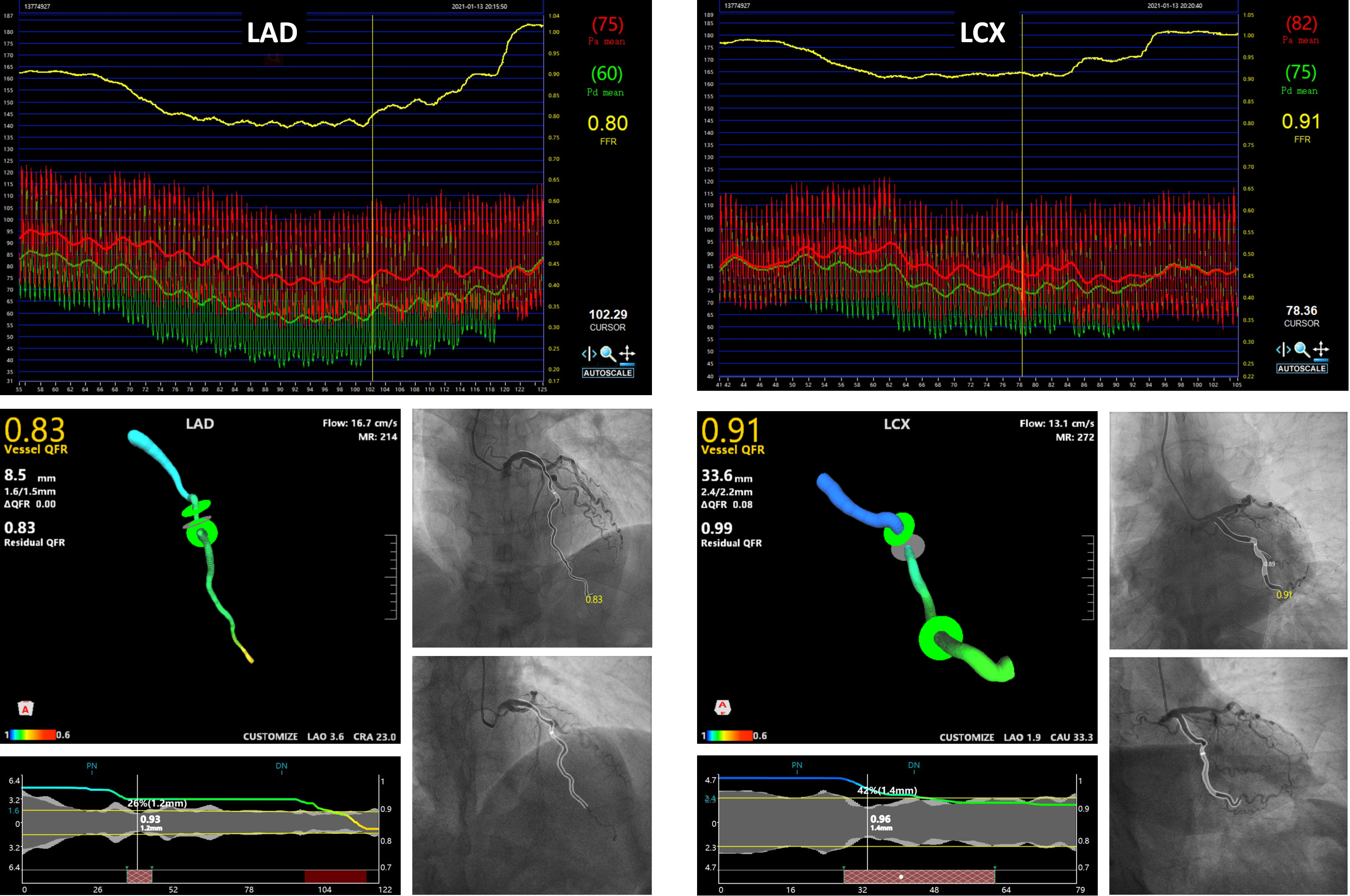
Fractional flow reserve (FFR) was adopted to evaluate intermediate lesions. The FFR value of the lesion in LAD was 0.80, and which for LCX was 0.91. Meanwhile, we tested quantitative flow ratio (QFR) and confirmed the consistency. The QFR value for LAD was 0.83, and the value for LCX was 0.91 (Figure 2). We used QFR to evaluate the flow in PDA because unstable plaque and tortuosity might embarrass manipulating the pressure wire. The QFR value of the lesion in PLA was 0.65 (Figure 3 A). Therefore we treated the lesions in PLA and PDA (Figure 4). A Fielder XT-R (ASAHI, Japan) was supported by Finecross 130 microcatheter (ASAHI) to pass the lesion in PLA when the Runthrough workhorse (Terumo, Japan) failed. A pre-dilation balloon (2.0 × 12 mm) and a non-compliance balloon (2.5 × 15 mm) were used sequentially in pre-dilation at 10 - 16 atmospheric pressure (atm), but the residual stenosis remained over 30 %, thus a drug eluting stent (DES) (2.25 × 32 mm) was deployed into the PLA at 8 atm, and the 2.5 × 15 mm balloon was used to post-dilate the stent. Then revascularization to PDA was performed. The 2.0 × 12 mm balloon and a non-compliance balloon (2.5 × 9 mm) at 10 - 16 atm could not pre-dilate the lumen completely, so another DES (2.5 × 14 mm) was deployed into the PDA at 8 atm, and the non-compliance balloon was used in post-dilation. The QFR value after revascularization were 0.97 for PLA and 0.96 for PDA, which meant a satisfactory revascularization (Figure 3 B).
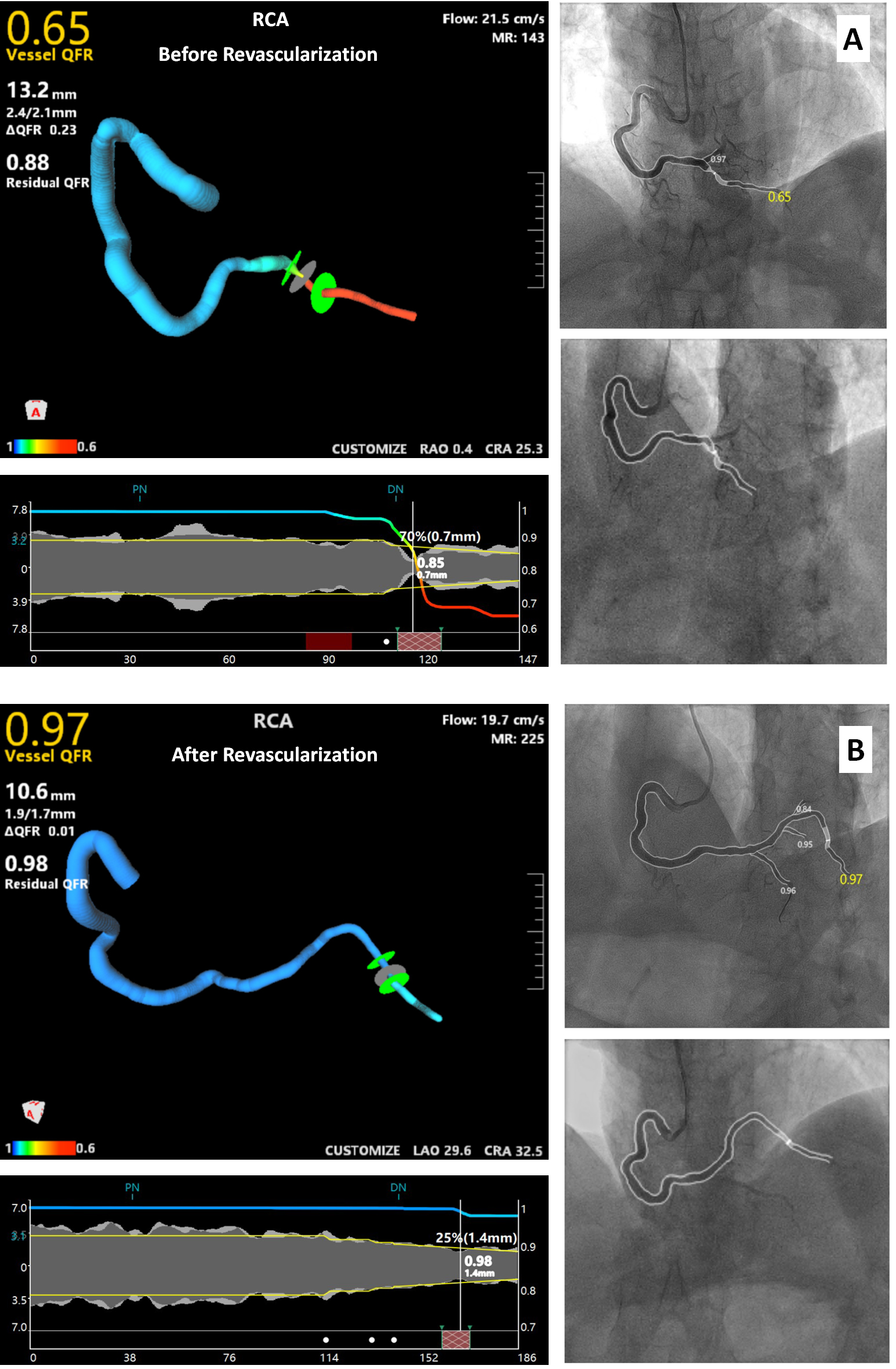




Case Summary
The FAVOR II study demonstrated QFR had a good consistency with FFR the gold standard. QFR was used in tortuous and eccentric lesions in this case avoiding wire manipulation and vasodilator, hence it reduced the operational time and interventional risk. Moreover, QFR for branches such as PDA and PLA could be assessed simultaneously. However, QFR is acquired from angiographic runs, it is affected by image quality and view angle,and it might increase contrast usage. Besides, in some extremely tortuous lesions displayed unclearly in angiography, QFR test might be limited. In general, selective or combinational using FFR and/or QFR might improve PCI quality.


