Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-054
Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Anomalous Right Coronary Artery Arising From Left Coronary Cusp
By Meei Wah Chan, Anwar Irawan Ruhani
Presenter
Meei Wah Chan
Authors
Meei Wah Chan1, Anwar Irawan Ruhani2
Affiliation
Hospital Serdang, Malaysia1, Hospital Tengku Ampuan Afzan, Malaysia2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-054
CORONARY - Chronic Total Occlusion
Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Anomalous Right Coronary Artery Arising From Left Coronary Cusp
Meei Wah Chan1, Anwar Irawan Ruhani2
Hospital Serdang, Malaysia1, Hospital Tengku Ampuan Afzan, Malaysia2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
AJ
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 60 year-old gentleman was referred from dialysis unit for intradialytic angina for 2 weeks . The patient had background history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia and hemodialysis dependent end stage renal disease. He had a percutaneous coronary intervention of left anterior descending artery done 6 months ago in another center. Upon admission, his blood pressure was 140/80 mmHg, heart rate 70 beats per minute, saturation 99%,his cardiac and lungs auscultation was unremarkable.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
His electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with T wave inversion at I, avL , V4 toV6. Echocardiogram revealed left ventricular ejection fraction of 38%,hypokinetic inferoseptal, inferior, apical and mid anteroseptal wall. His blood tests showed hemoglobin 10.9g/dl ,urea 13 mmol/L, creatinine 696 umol/L and normal cardiac enzymes. Coronary angiography was done to assess his coronary artery for intradialytic angina.
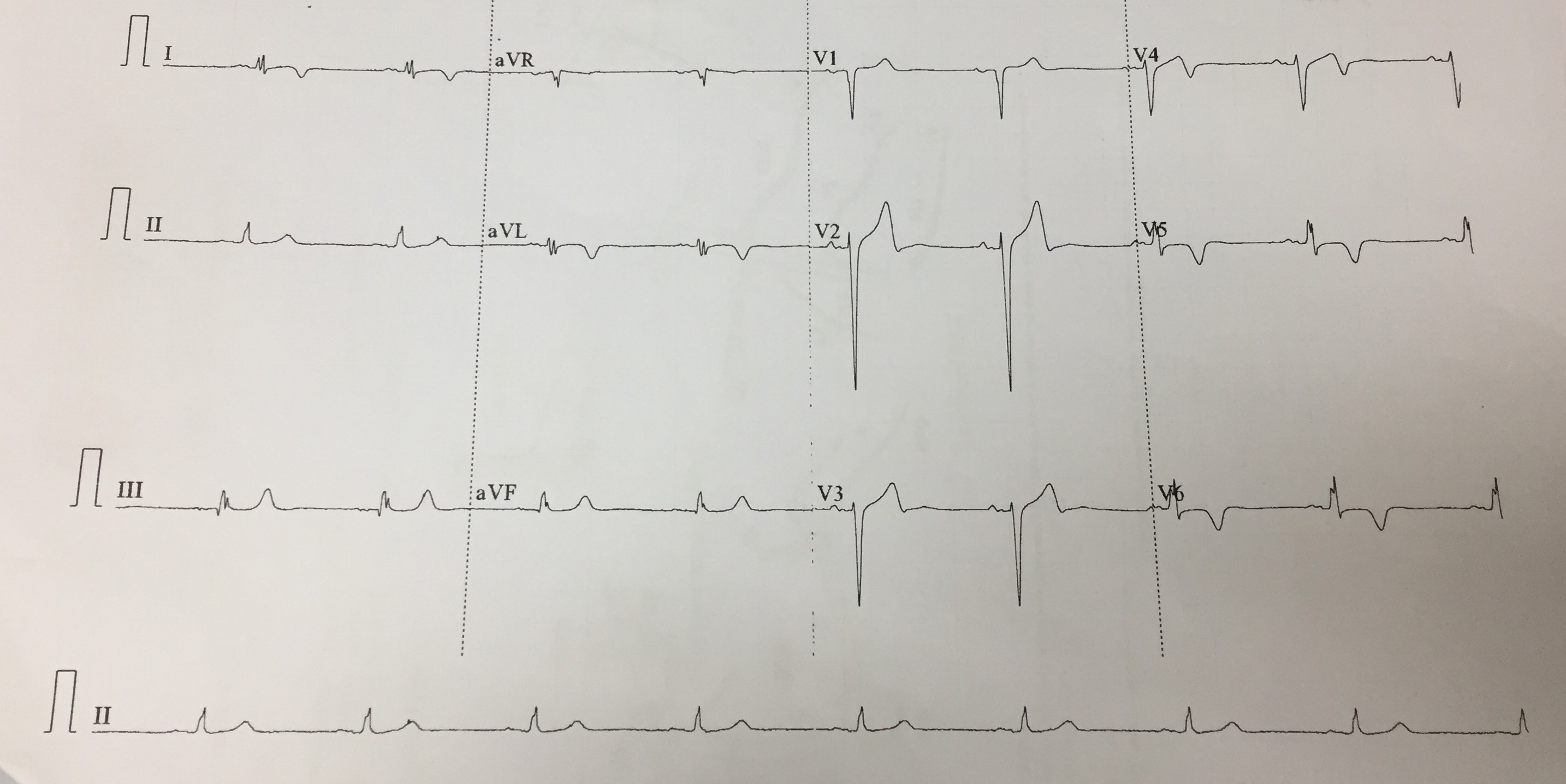

Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiography was performed via right transfemoral approach 6 Fr sheath. Left coronary artery engaged with JL 4.0 which showed normal left main , patent stent at left anterior descending artery and mild disease at left circumflex artery. Noted right coronary artery( RCA ) was originated from left coronary sinus of valsalva , unable to selectively cannulate RCA with JR 3.5 and JL 4.0 , injection done at left coronary sinus showed significant stenosis at proximal and mid RCA.
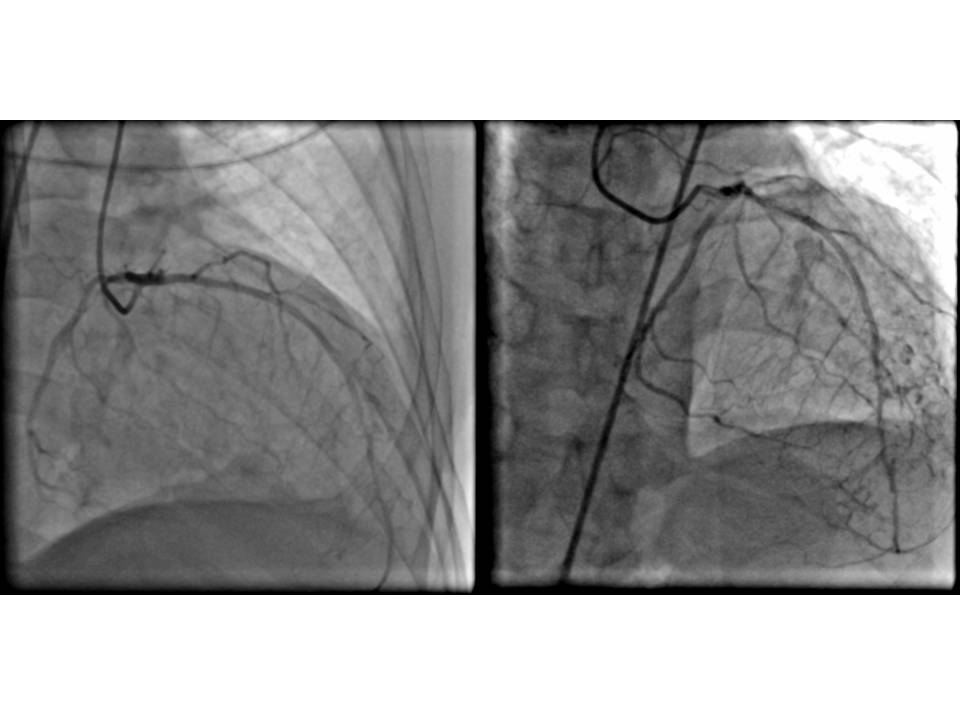
 RCA.mp4
RCA.mp4

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Percutaneous coronary intervention to RCA was performed. Guiding catheter EBU 3.5 was used to cannulate RCA, injection done and showed subtotal chronic total occlusion ( CTO ) at proximal and CTO at mid RCA with bridging collateral, TIMI 2 flow. RCA lesion attempted to cross with RT floppy and RT hypercoat wire, together with Finecross microcathter. Due to the poor guide support and non-coaxial alignment with RCA ostium, lesion was failed to cross. Subsequently, AL 1.0 catheter was used to engage RCA for better support. Again, lesion was failed to cross with RT floppy and RT hypercoat, escalated wire to Fielder XTA with Finecross microcatheter, however still unable to cross the mid CTO, subsequently escalated wire with Gaia 3, which successfully cross the CTO. Lesion was dilated with semi compliant balloon 2.0 x 15mm at 10 atm , drug eluting stent ( DES ) 2.5x23mm was deployed at mid RCA at 12atm and DES 2.75x28mm deployed at proximal RCA at 14atm. Post dilatation done with non compliant balloon 2.75x20mm at 16-24atm. The operational time was 3 hours and 15 minutes, dosage of contrast was 190 mL. Patient was asymptomatic post procedure, and discharged well on the next day.
 EBU.mp4
EBU.mp4
 cross wire.mp4
cross wire.mp4
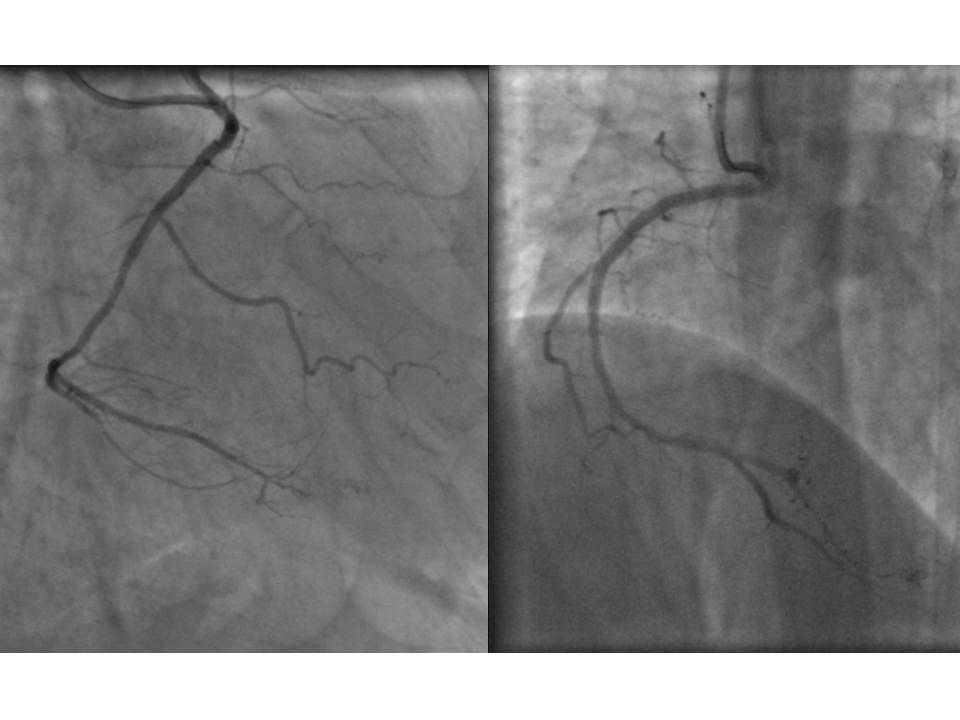

Case Summary
Anomalous origin of RCA constitute a small subset of coronary artery anomalies, it occurs with an incidence of 0.25%. Few challenges can be encountered when performing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) in anomalous origin of RCA. The challenges include selective RCA cannulation, guide catheter selection with good support and coaxiality, and manipulating skill from the operators. The PCI is usually associated with increased radiation, amount of contrast used and operational time. In our case, it took about 3 hours to complete the PCI with multiple catheters and wires were used. The CTO lesion made the procedure more challenging but the lesion was successfully treated.


