Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-079
Left Main In-stent Restenosis; A Successful Story of Using Shockwave Technology.
By Khairul Shafiq Ibrahim, Mohd Firdaus Hadi, Rizmy Najme Khir, Zubin Ibrahim, Raja Ezman Raja Shariff, Sazzli Kasim
Presenter
Khairul Shafiq Ibrahim
Authors
Khairul Shafiq Ibrahim1, Mohd Firdaus Hadi2, Rizmy Najme Khir3, Zubin Ibrahim4, Raja Ezman Raja Shariff3, Sazzli Kasim1
Affiliation
Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Malaysia1, Avisena, Malaysia2, Hospital Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Malaysia3, Ara Damansara Medical Center, Malaysia4,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-079
CORONARY - Complex and Higher Risk Procedures for Indicated Patients (CHIP)
Left Main In-stent Restenosis; A Successful Story of Using Shockwave Technology.
Khairul Shafiq Ibrahim1, Mohd Firdaus Hadi2, Rizmy Najme Khir3, Zubin Ibrahim4, Raja Ezman Raja Shariff3, Sazzli Kasim1
Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Malaysia1, Avisena, Malaysia2, Hospital Universiti Teknologi MARA (UiTM), Malaysia3, Ara Damansara Medical Center, Malaysia4,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Mr AM
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
Mr AM is a 63-year-old man with history of ischaemic heart disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension and end stage renal disease on regular haemodialysis. He presented with acute onset of chest pain, centrally located, pressing in nature and associated with shortness of breath and diaphoresis. On examination, blood pressure was 168/88mmHg, heart rate of 98 beat per minute and saturation of 98% in room air. On auscultation, the heart sound was normal with minimal bi-basal crepitation.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
ECG on admission showed diffuse ST depression with ST elevation in AVR.
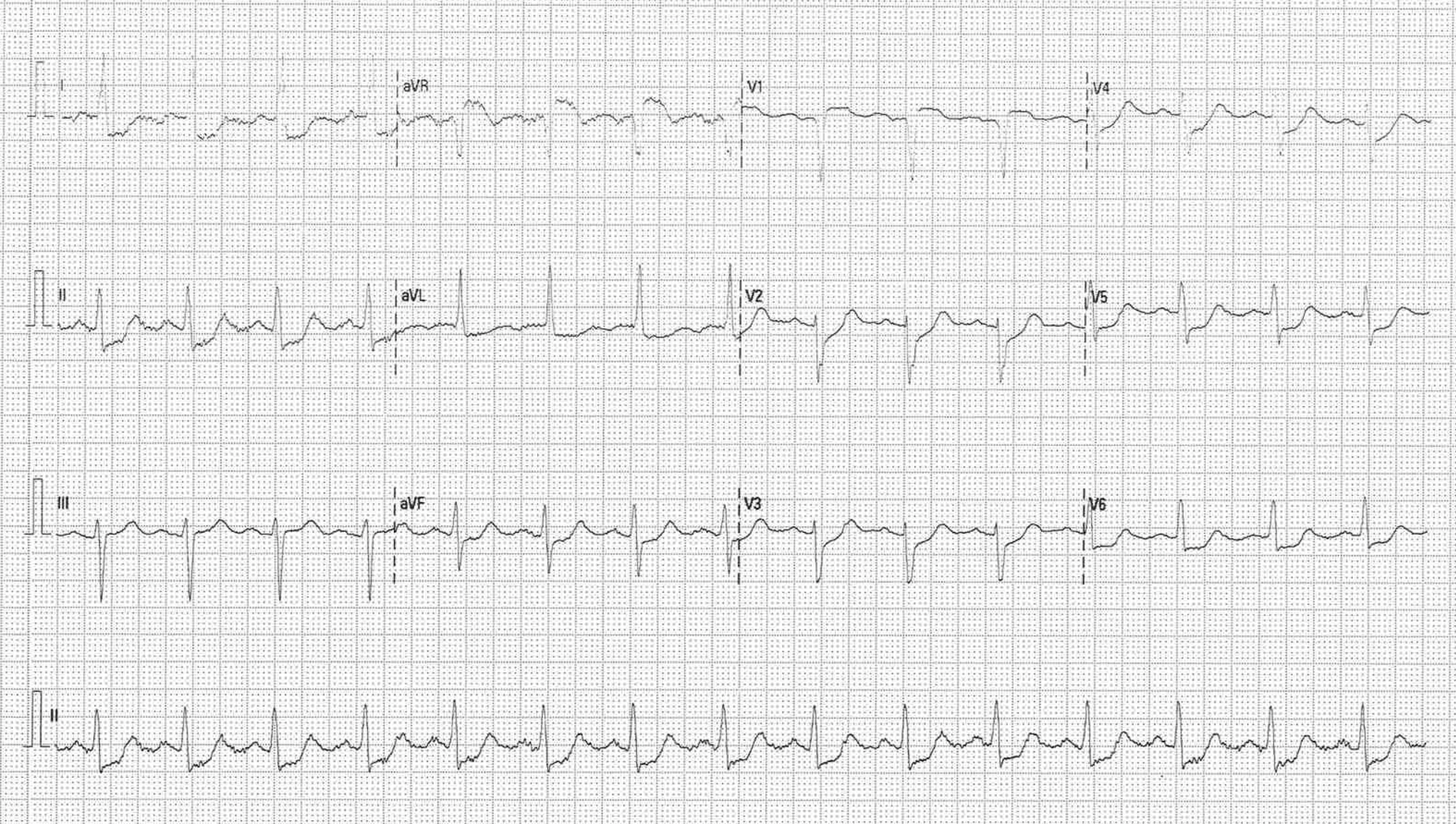

Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiogram showed severe in-stent restenosis at distal LM extending to proximal LAD. Mild to moderate lesion distal to the stent extended to mid LAD. The LCx was diffusely diseased and the RCA showed non obstructive disease.
 AM AP caud.mov
AM AP caud.mov
 AM RAo cra.mov
AM RAo cra.mov
 am rca lao1.mov
am rca lao1.mov
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
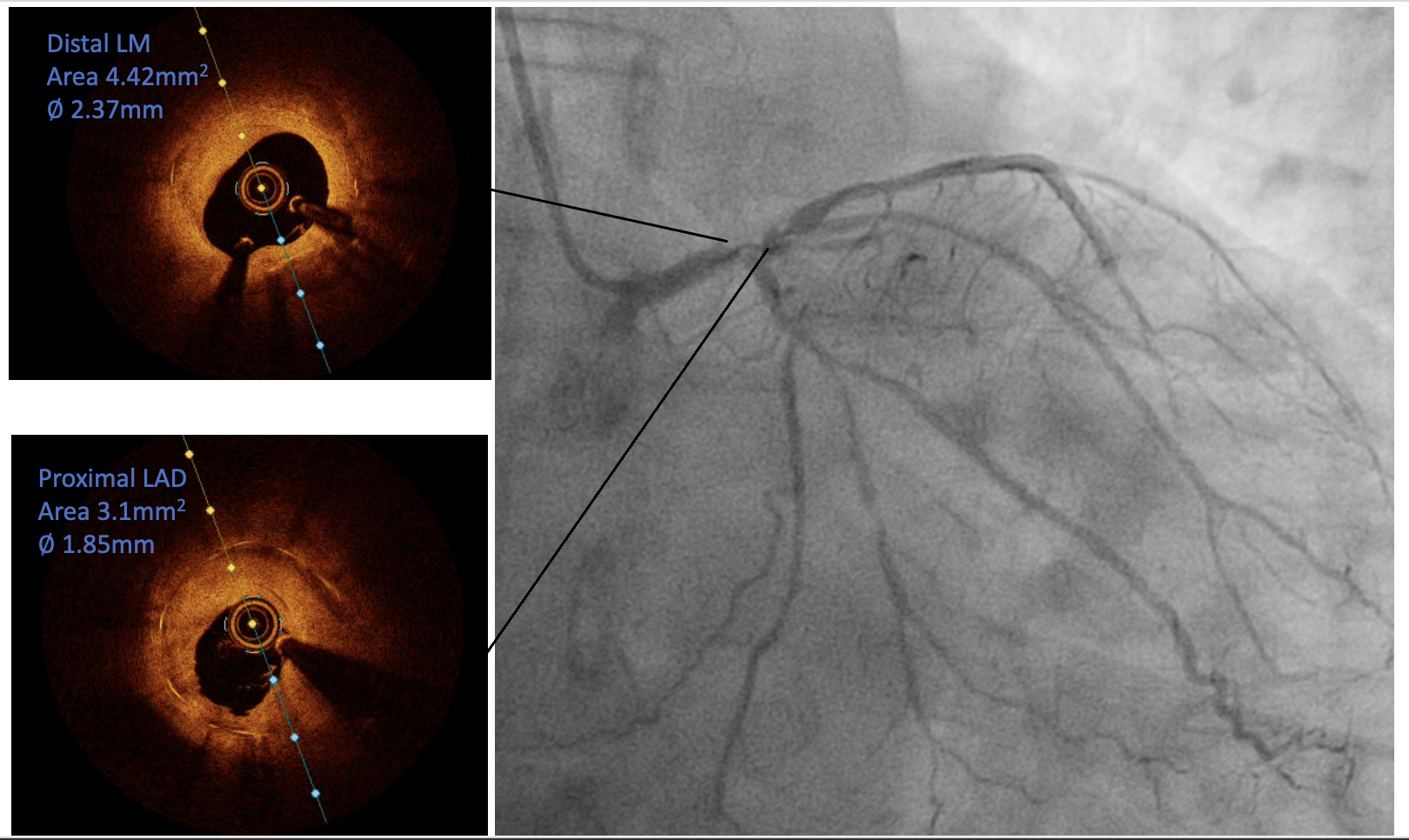
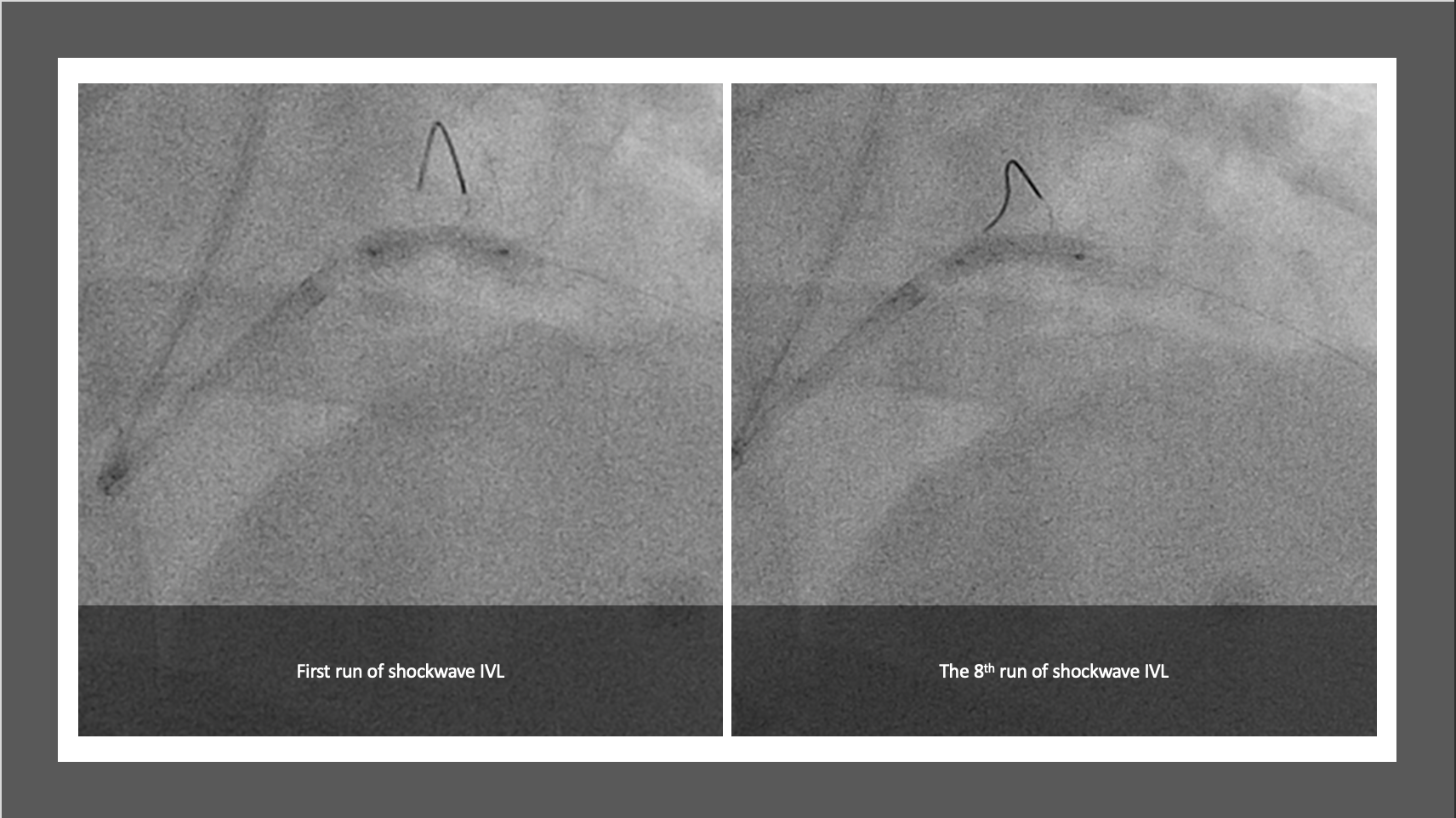
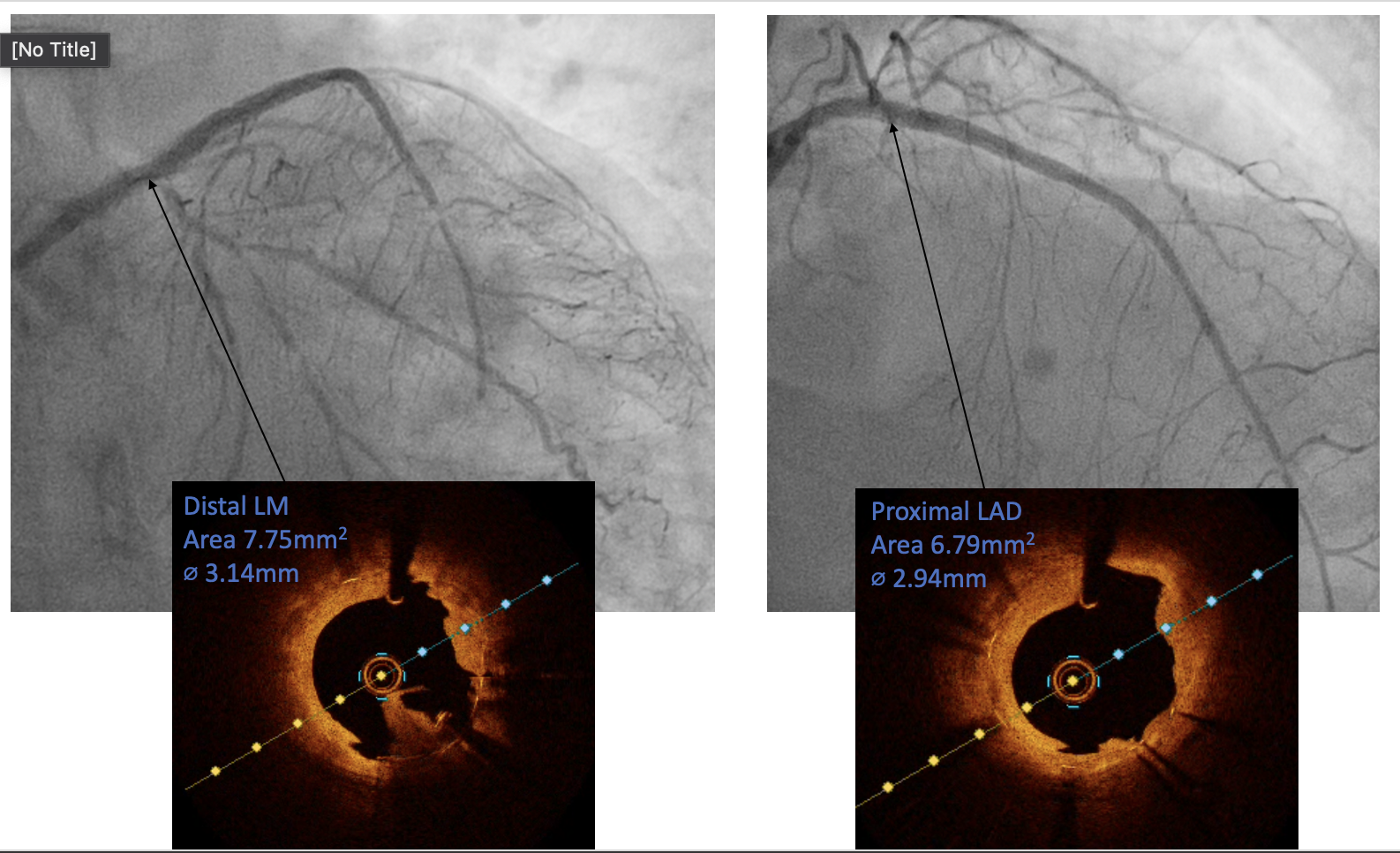
The PCI procedure was performed via right radial artery using a 7fr EBU 3.5 guiding catheter through 7Fr slender sheath. Two wires were used to provide better support for the procedure. Runthrough wire was passed down the LCx and sion blue wire was passed across the in-stent restenotic (ISR) lesion down to distal LAD. Different view was used to guide the process of crossing over the severely stenosis ISR. An NC 2.0/12 was used to predilate the ISR lesion to allow optical coherence topography (OCT) to cross the stenotic area. The first run OCT showed severe ISR at mid stent, between the distal LM and proximal LAD with 360° calcified plaque (Figure 1). There was also lesion extended distal to the stent into mid LAD. A 3.5/12 intravenous lithotripsy was used to crack the calcified ISR lesion. 8 run of IVL was delivered with a total of 80 pulse with good result (Figure 2). A 2nd run of OCT was performed which showed improvement in the ISR lesion. An NC 4.0/8 was then used to further predilate the ISR lesion. The lesion was subsequently treated with drug eluting balloon 3.5/20. The lesion distal to the old stent was prepared with NC 2.0/12 and stented with 2.75/33, overlapped with the old LM/LAD stent. The new stent was post dilated with NC 3.5, sparing the distal stent edge.



Case Summary
Mr AM has been well post procedure and has no major cardiac event 6 months post procedure. This case highlighted the feasibility and safety of the shockwave IVL application on treating calcium-mediated left main stem/proximal LAD in-stent restenosis. It also has the potential to yield promising short and mid-term results.


