Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-015
The Last Straw
By Korakoth Towashiraporn
Presenter
Korakoth Towashiraporn
Authors
Korakoth Towashiraporn1
Affiliation
Her Majesty Cardiac Center Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-015
CORONARY - Acute Coronary Syndromes (STEMI, NSTE-ACS)
The Last Straw
Korakoth Towashiraporn1
Her Majesty Cardiac Center Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
11020
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 68-year-old man with poorly controlled diabetes (HbA1C 10.1%) and hypertension. He underwent primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) at left anterior descending artery (LAD) and staged PCI to left circumflex artery (LCX) since 2012. He was lost to follow up for 5 years. Today, he develops angina and palpitation for 6 hours. At our emergency department. Blood pressure was 120/81 mmHg. Heart rate was 108 beats per minute. The respiratory rate was 22 per minute. The lung was clear.
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
ECG demonstrated - Sinus tachycardia rate 105 BPM.- ST-segment depression V2-4 with tall R and upright T wave in leads V2-3.- ST-segment elevation V7-9.
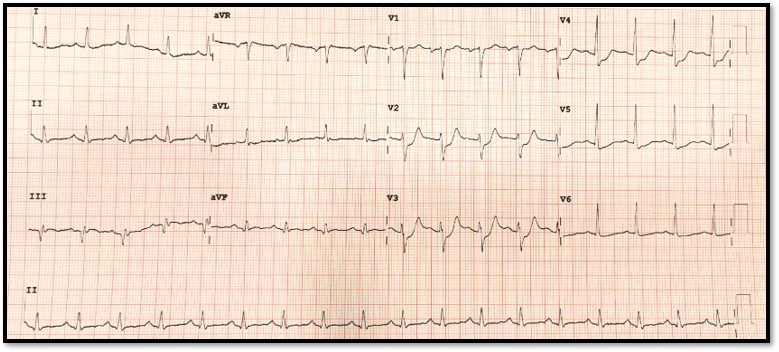
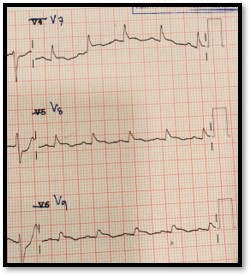


Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiography (CAG) demonstrated- Left main coronary artery was widely patent.- Left anterior descending artery (LAD) demonstrated in-stent restenosis (ISR) type III (Diffuse proliferative) with critical stenosis at ostial LAD.- Left circumflex artery (LCX) was totally occluded at proximal part with TIMI 0 flow. - Ramus intermedius was 80% stenosis at ostial.- Right coronary artery (RCA) had chronic total occlusion at mid part with faint collateral circulation from septal perforator.
 RAO cranial pre.mp4
RAO cranial pre.mp4
 RAO caudal pre.mp4
RAO caudal pre.mp4
 RCA.mp4
RCA.mp4
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
1. 6 Fr. EBU3.5 guiding catheter (Medtronic, USA) was cannulated to ostial left main coronary artery (LMCA).2. Rinato wire (Asahi Intecc, Japan) accompanied with Caravel microcatheter (Asahi Intecc, Japan) unable to cross culprit LCX.3. Successfully cross the culprit LCX using Fielder FC wire (Asahi Intecc, Japan). Tip injection was done to confirm true lumen entry.4. 2.0x15 mm. balloon was inflated at proximal LCX. TIMI 1 flow was achieved. Filling defect was visible.5. Aspiration thrombectomy was performed, red thrombus was retrieved.6. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) was recorded.7. A 3.0x22 mm. drug-eluting stent (DES) was deployed to proximal LCX.8. Rinato wire was passed to LAD and then, Ramus.9. Sequential balloon dilatation was done using a 2.0x15 mm balloon at LAD and then, Ramus.10. A 3.5x15 mm. balloon was inflated at proximal LAD, Blood pressure was running down to 60/40 mmHg. Dopamine and norepinephrine were infused.11. A 3.5x22 mm. DES was deployed to ostial LAD.12. Post dilatation was done using A 3.5x9 mm Non-compliance balloon up to 26 ATM.13. IVUS was performed for stent optimization.14. Final coronary angiography demonstrated no residual stenosis with TIMI 3 flow to distal LCX and LAD. Good collateral circulation from LAD to right coronary artery (RCA) via septal channel was demonstrated.15. Final arterial line (A-line) blood pressure 85/60 mmHg with low dose Dopamine and Norepinephrine.
 24 Final PA caudal.mp4
24 Final PA caudal.mp4
 26 Final RAO cranial.mp4
26 Final RAO cranial.mp4
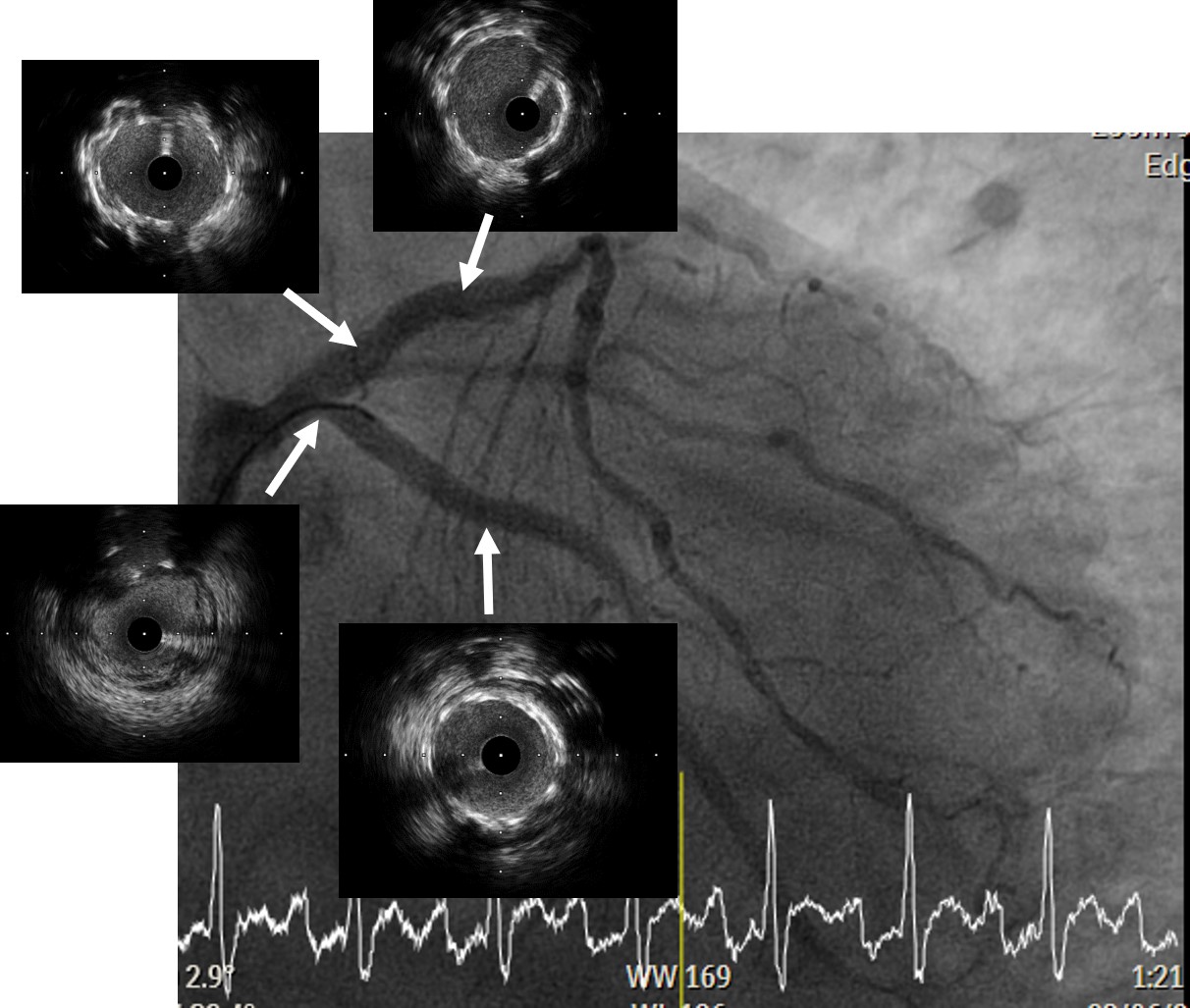

Case Summary
- The diagnosis of isolated posterior wall STEMI was often missed due to lack of ST-segment elevation in standard 12 leads ECG.- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) of the last remaining coronary artery is considered a high-risk procedure.- Intravascular imaging (IVUS) guided PCI associated with improved clinical outcomes.


