Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-050
Calcified Plaque Detected on Optical Coherence Tomography With Deep Learning and Cross-validated With Optical and Ultrasonic Signals: A Complementary Appraisal and Preamble to the Use of Combined IVUS-OCT Catheter
By Jiayue Huang, Kai Ninomiya, Shengxian Tu, Shinichiro Masuda, Jouke Dijkstra, Miao Chu, Daixin Ding, Sean O. Hynes, Neil O’Leary, William Wijns, Yoshinobu Onuma, Patrick W. Serruys
Presenter
Jiayue Huang
Authors
Jiayue Huang1, Kai Ninomiya2, Shengxian Tu3, Shinichiro Masuda1, Jouke Dijkstra4, Miao Chu3, Daixin Ding1, Sean O. Hynes5, Neil O’Leary1, William Wijns1, Yoshinobu Onuma1, Patrick W. Serruys1
Affiliation
University of Galway, Ireland1, Iwate Medical University, Japan2, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China3, Leiden University Medical Center, Netherlands4, University Hospital Galway and National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland5
View Study Report
TCTAP A-050
Imaging: Intravascular
Calcified Plaque Detected on Optical Coherence Tomography With Deep Learning and Cross-validated With Optical and Ultrasonic Signals: A Complementary Appraisal and Preamble to the Use of Combined IVUS-OCT Catheter
Jiayue Huang1, Kai Ninomiya2, Shengxian Tu3, Shinichiro Masuda1, Jouke Dijkstra4, Miao Chu3, Daixin Ding1, Sean O. Hynes5, Neil O’Leary1, William Wijns1, Yoshinobu Onuma1, Patrick W. Serruys1
University of Galway, Ireland1, Iwate Medical University, Japan2, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China3, Leiden University Medical Center, Netherlands4, University Hospital Galway and National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland5
Background
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) and intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) provide complementary assessments of plaque morphology and tissue characterization. OCT-derived optical signals, IVUS-virtual histology (VH) and echogenicity have been validated on ex vivo human specimen and allow for in-vivo identification of different type of tissues. OCT deep learning (DL) emerged as a promising tool for automated plaque characterization and was derived from annotations of experts. The findings provided by this novel DL technology have not been previously cross-validated with optical and ultrasonic signals.
Methods
Five years after implantation of bioresorbable scaffold with radiopaque markers embedded at both ends of the device, 15 patients underwent intravascular imaging with OCT and IVUS. The endovascular radiopaque markers allow for precise co-registration of OCT and IVUS images. Calcified plaque detected by OCT DL were corroborated by/with signals derived from attenuation and backscattering of the OCT light intensity, as well as with ultrasonic radio-frequency signals (IVUS-VH), their grayscale envelopes (GS)-IVUS, and their echogenic brightness function using adventitia as reference (Figure 1). Concordant identification of calcified plaques by each modality was assessed by kappa statistics and calcium arc values compared by orthogonal linear regression.
Results
In 72 matched anatomic slices, DL detected 43 calcified plaques, of which the tissue composition was confirmed by optical properties in 41 (95%). The weighted kappa between OCT DL and GS-IVUS, IVUS-VH and echogenicity for calcified plaque detection were 0.69, 0.60 and 0.60, respectively. After having excluded artifactual optical shadowing (n=5) generated by the presence of either a guidewire or a radiopaque marker, the kappa increased to 0.77, 0.68 and 0.69, respectively, with agreements ranging between 90% to 93% (Figure 1). The calcium arc derived from OCT DL showed the following and respective correlation and agreement: 1) with the calcium arc derived from GS-IVUS (ICCa=0.81 [95% CI: 0.68-0.91], difference=1.73±15.25°); 2) IVUS-VH (ICCa=0.69 [95% CI: 0.54-0.81], difference=-5.60±21.19°) and 3) echogenicity (ICCa=0.65 [95% CI: 0.46-0.83], difference=10.28 ± 18.70°).
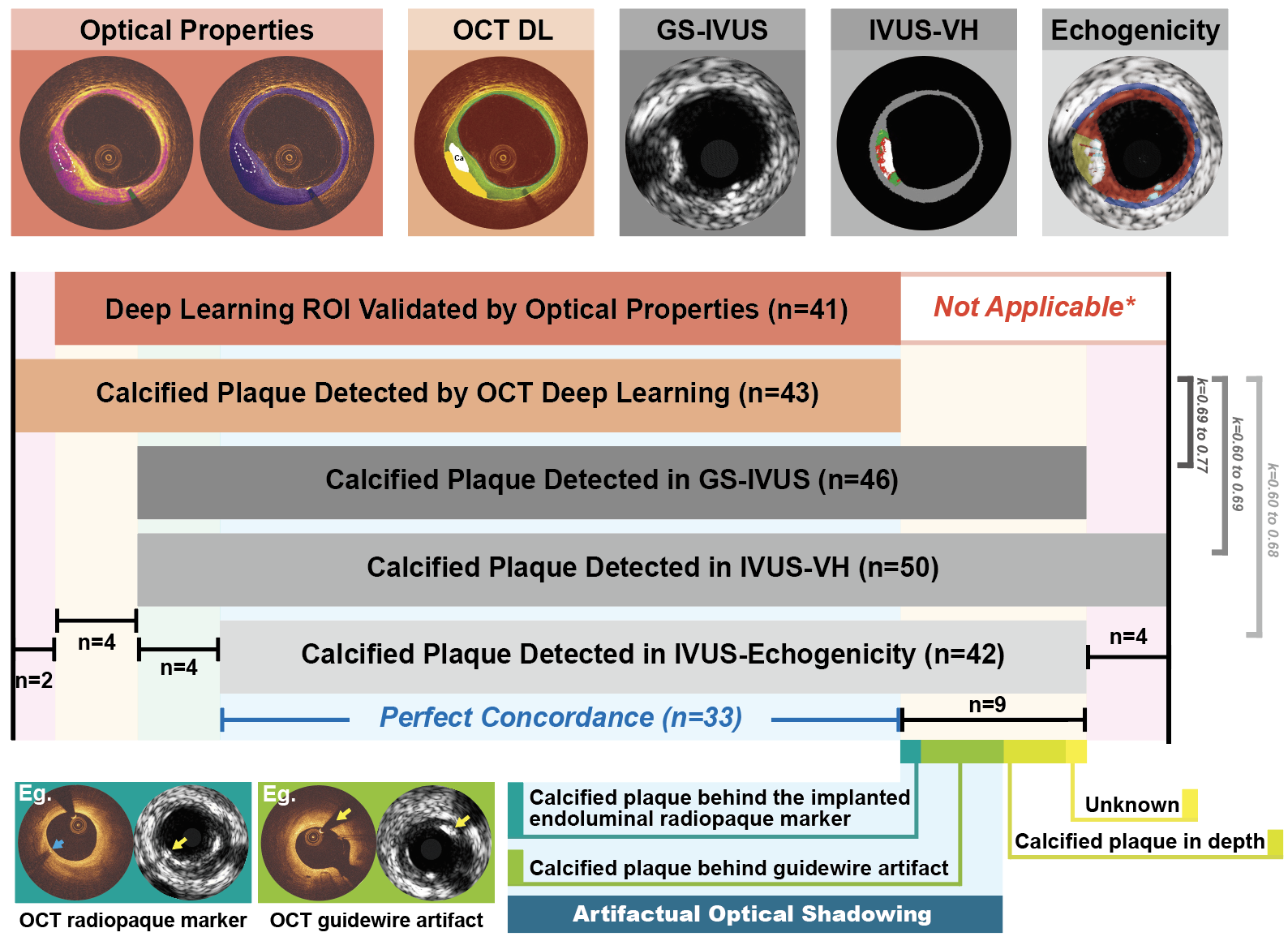

Conclusion
OCT empowered by DL showed substantial agreement with optical and ultrasonic signals for detecting coronary calcification. The comprehensive assessment provided by OCT and IVUS heralds the potential diagnostic value of combined IVUS-OCT catheters.


