Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-020
The Impact of Slender DCA
By Takuma Tsuda, Nao Yasuda
Presenter
Nao Yasuda
Authors
Takuma Tsuda1, Nao Yasuda1
Affiliation
Nagoya Ekisaikai Hospital, Japan1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-020
Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
The Impact of Slender DCA
Takuma Tsuda1, Nao Yasuda1
Nagoya Ekisaikai Hospital, Japan1
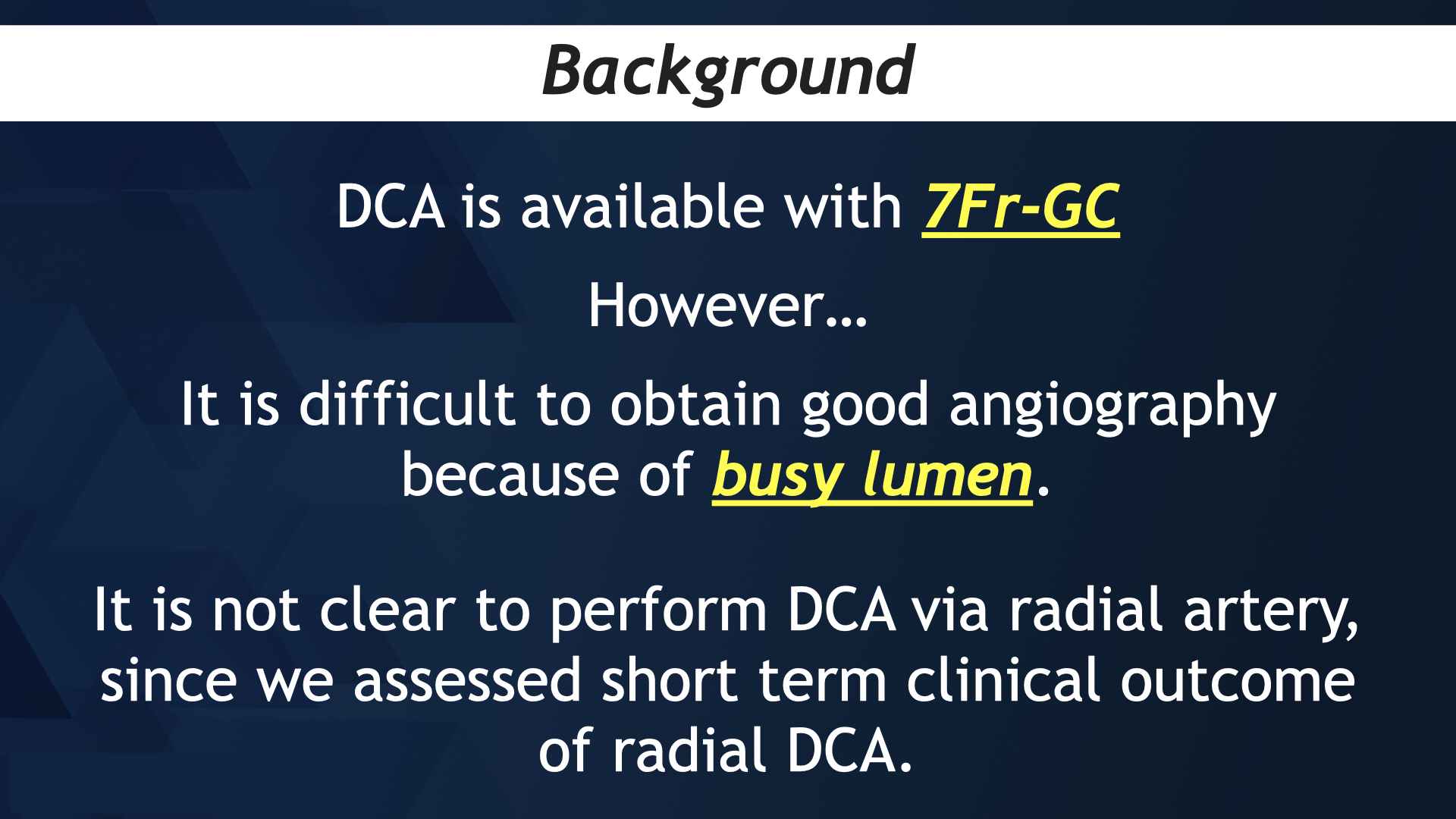
Background
DCA catheter (Atherocut; Nipro, Japan) usually need 8Fr guiding catheter because of its contrast effect however it is compatible for 7Fr guiding catheter. The aim of this study is to assess the clinical outcome of radial DCA with 7Fr guiding catheter.


Methods
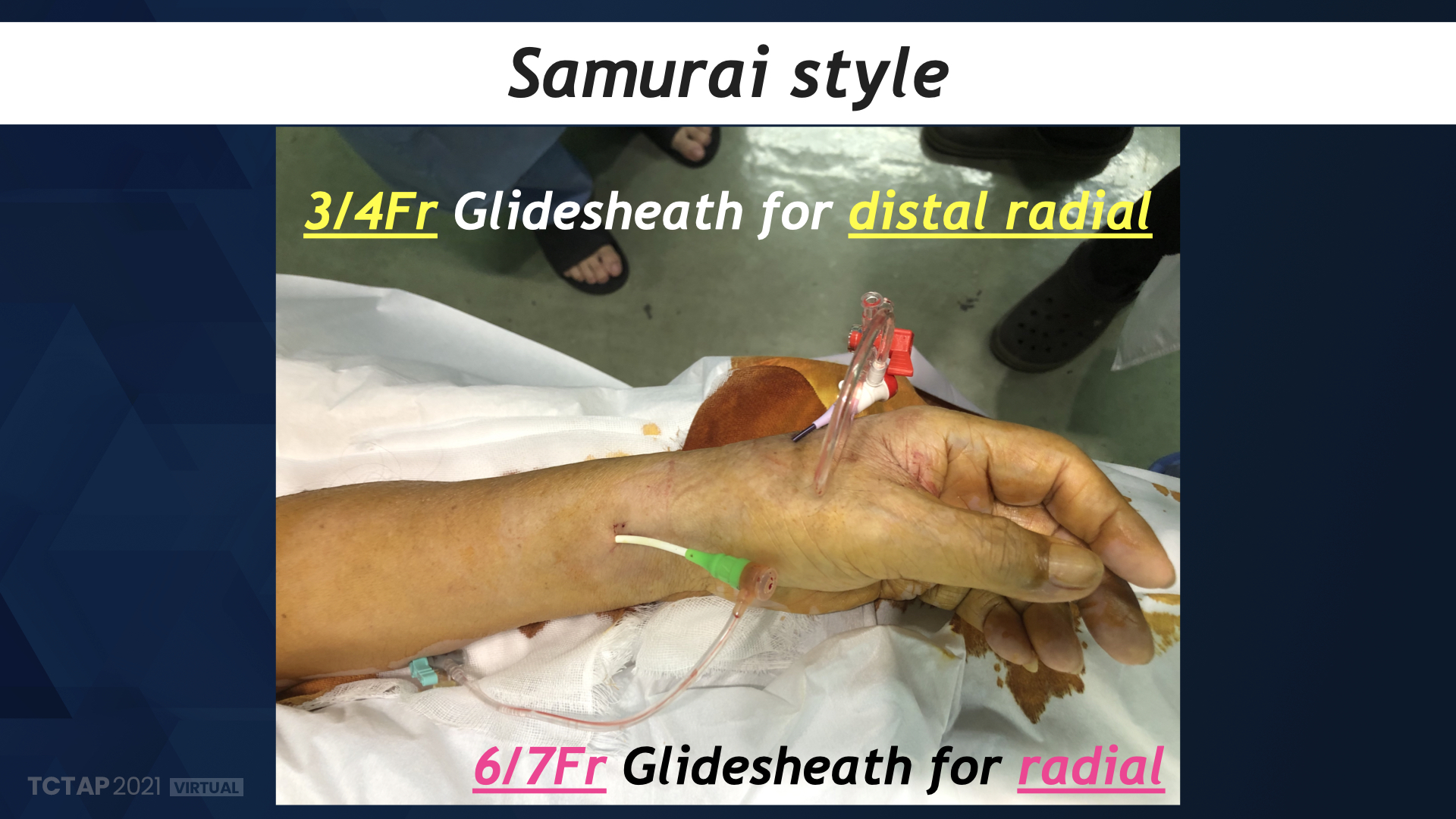
Consective 125 patients with 130 lesions, who was diagnosed as stable angina pectoris or acute coronary syndrome, was enrolled between July 2018 to January 2021, and divided 2 group; 8Fr-femoral (n=77) and 7Fr-radial (n=48). We assessed lesion characteristics (preMLA, pre %plaque area), post procedural endpoint (postMLA, post %plaque area), procedural success, procedural complication and access site complication. In radial group, 4Fr diagnositc catheter was used for angiography via brachial or distal radial approach.

Results
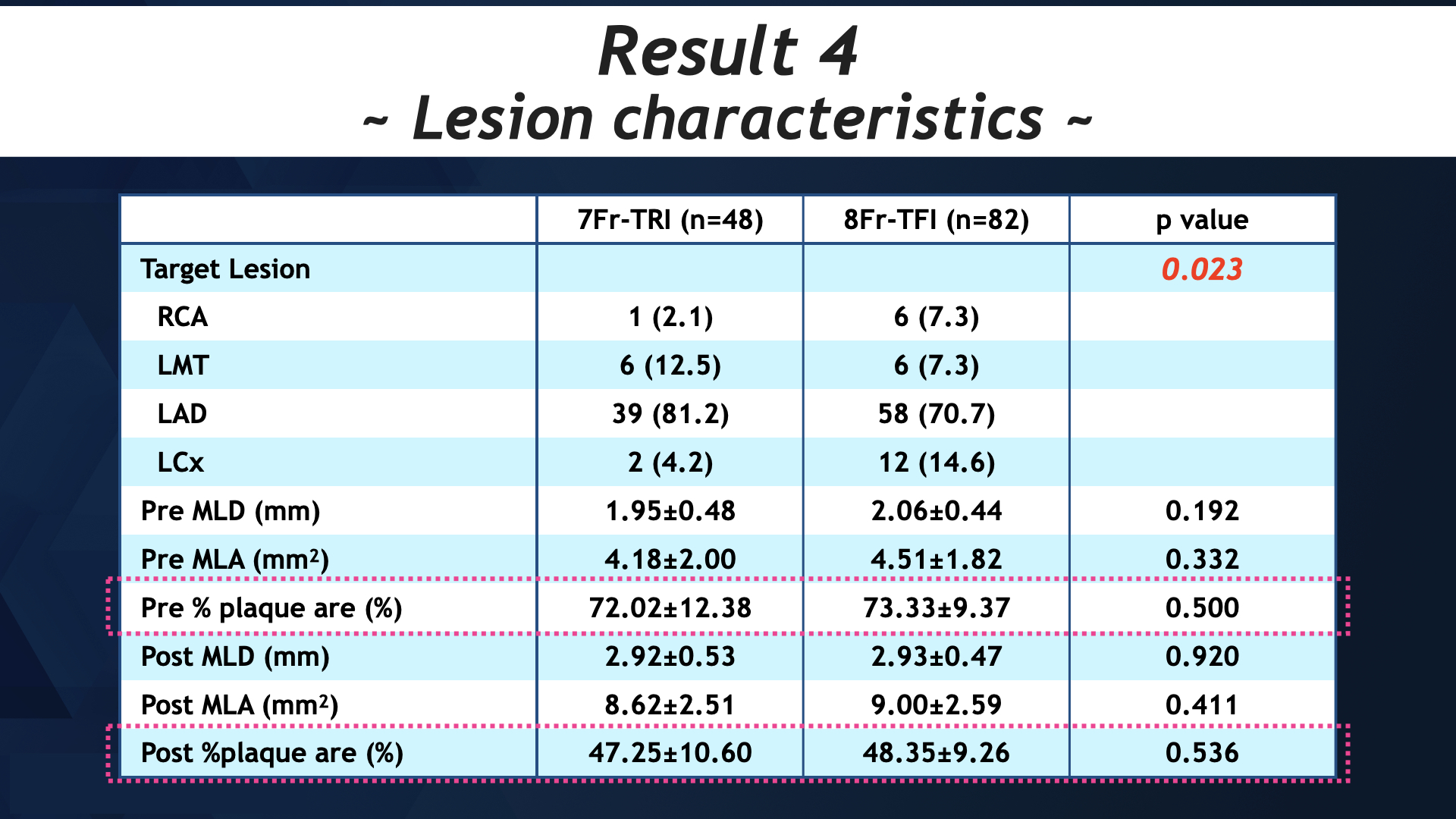
7Fr-radial group had the same lesion characteristics (preMLA:4.65 ± 2.17 mm2 vs 4.60 ± 1.79 mm2, p = 0.913, pre %plaque area:69.47 ± 12.39 vs 72.82 ± 10.16, p = 0.150), post procedural endpoint (post MLA:9.11 ± 2.98 mm2 vs 9.00 ± 2.48 mm2, p = 0.833, post %plaque area:47.11 ± 9.81 vs 48.15 ± 9.47, p = 0.615), procedural success (100 % vs 100 %, p = 1.00), procedural complication (0 (0 %) vs 4 (1; deep cut, 1; perforation, 2: slow flow) (4.9 %), p = 0.296) and access site complication (0 (0 %) vs 5 (2; aneurysm, 3; transfusion) (6.1 %), p = 0.157). Usage of contrast dye was significantly lower in radial group (88.62 ± 33.86 ml vs 105.60 ± 44.64 ml, p < 0.05).
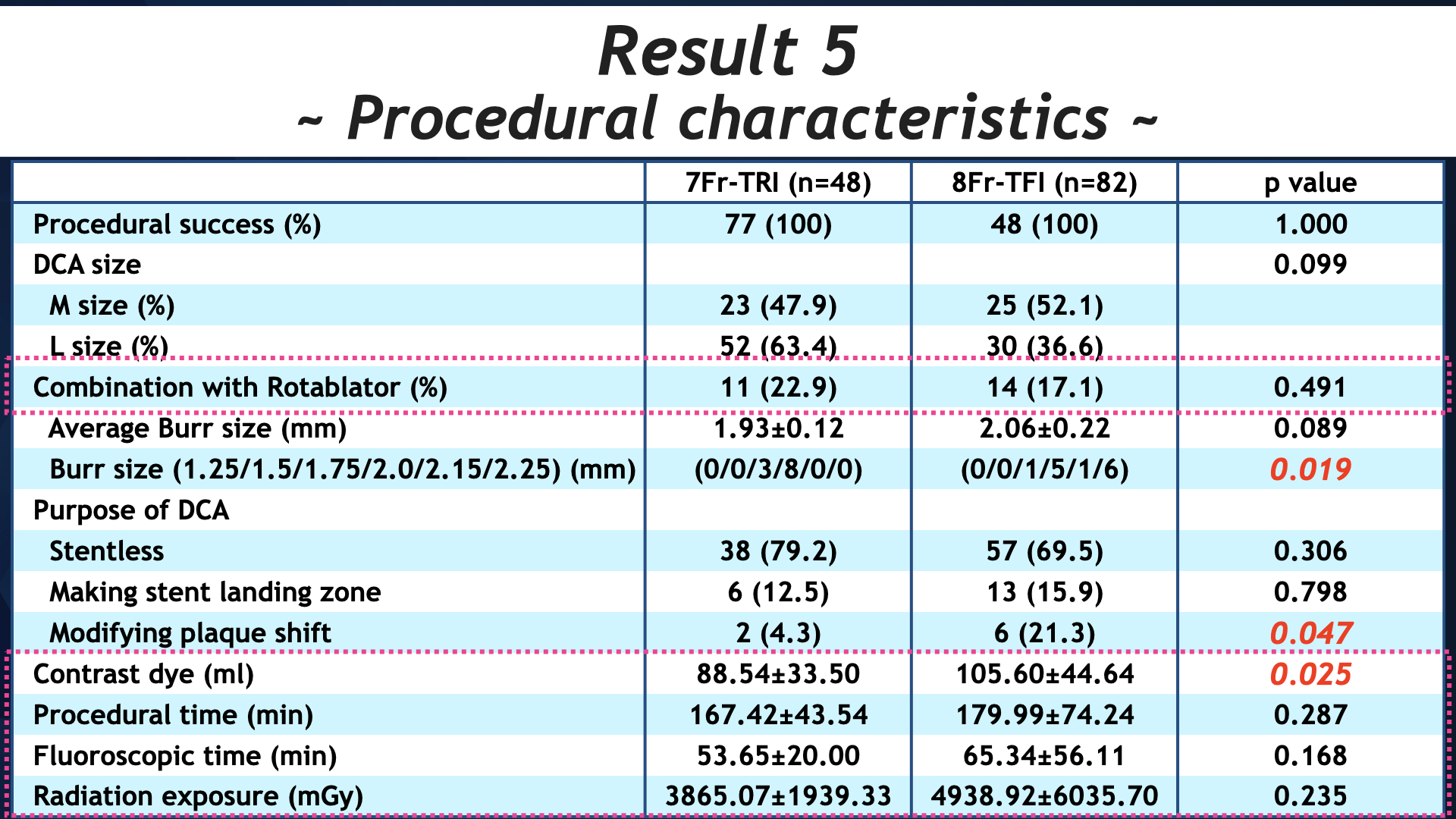
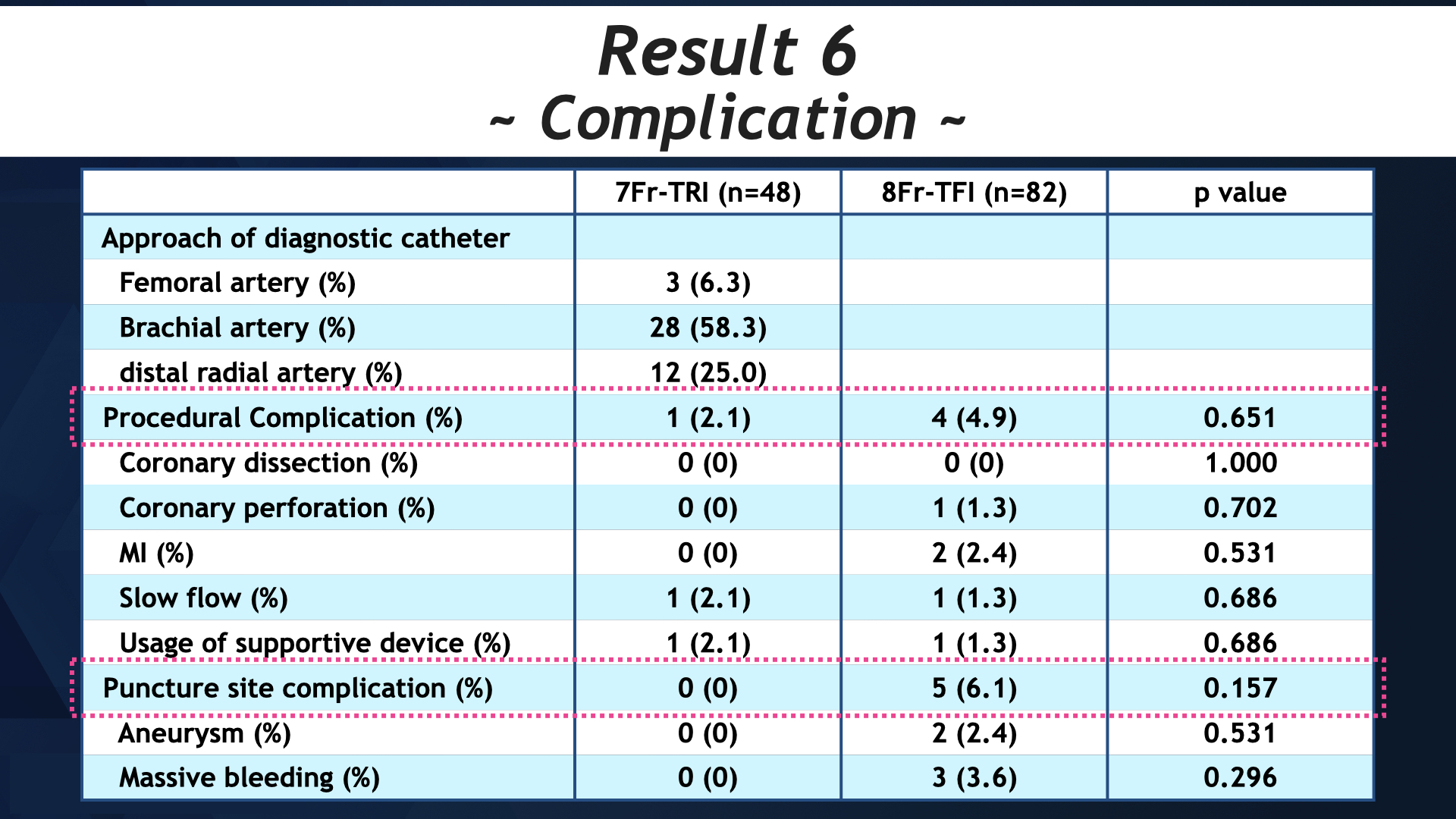



Conclusion
Radial DCA was the safe and effective as femoral approach in acute phase, moreover, could contribute for reduction of puncture site complication and contrast dye.




