Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2022. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-005
AVR ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Not So Urgent Cardiac Emergency. A Single Tertiary Center Experience in Malaysia
By Jian-Chen Lim, Ramachandran Sathappan, Yew Fung Kwan, Tze Ming Chan, Hazleena Mohamed Hasnan, Nor Hanim Mohd Amin
Presenter
Jian-Chen Lim
Authors
Jian-Chen Lim1, Ramachandran Sathappan2, Yew Fung Kwan3, Tze Ming Chan4, Hazleena Mohamed Hasnan5, Nor Hanim Mohd Amin5
Affiliation
Hospital Serdang, Malaysia1, Hrpb Ipoh, Malaysia2, Hospital Raja Permaisuri Bainun Ipoh, Malaysia3, Columbja Asia petaling Jaya, Malaysia4, Hospital Raja Permaisuri Bainun, Malaysia5
View Study Report
TCTAP A-005
Acute Coronary Syndromes (STEMI, NSTE-ACS)
AVR ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A Not So Urgent Cardiac Emergency. A Single Tertiary Center Experience in Malaysia
Jian-Chen Lim1, Ramachandran Sathappan2, Yew Fung Kwan3, Tze Ming Chan4, Hazleena Mohamed Hasnan5, Nor Hanim Mohd Amin5
Hospital Serdang, Malaysia1, Hrpb Ipoh, Malaysia2, Hospital Raja Permaisuri Bainun Ipoh, Malaysia3, Columbja Asia petaling Jaya, Malaysia4, Hospital Raja Permaisuri Bainun, Malaysia5
Background
AVR STEMI is well recognized as a sign of acute occlusion of the left main stem (LMS) or proximal left anterior descending(LAD) coronary artery. However, whether aVR STEMI is always associated with acute thrombotic coronary occlusion is still debatable.
Methods
Our objective is to investigate the incidence of an acute total occlusion in culprit coronary vessel in patients presenting with aVR STEMI and their 3 months outcome. A retrospective, single center study on all aVR STEMI admissions between January 2018 and January 2020. All electrocardiograms and coronary angiograms were analyzed by experienced cardiologists. aVR STEMI was defined as typical acute chest pain with ST elevation in aVR ≥ 1 mm, ST elevation in aVR ≥ V1, and widespread horizontal ST depression in other leads.
Results
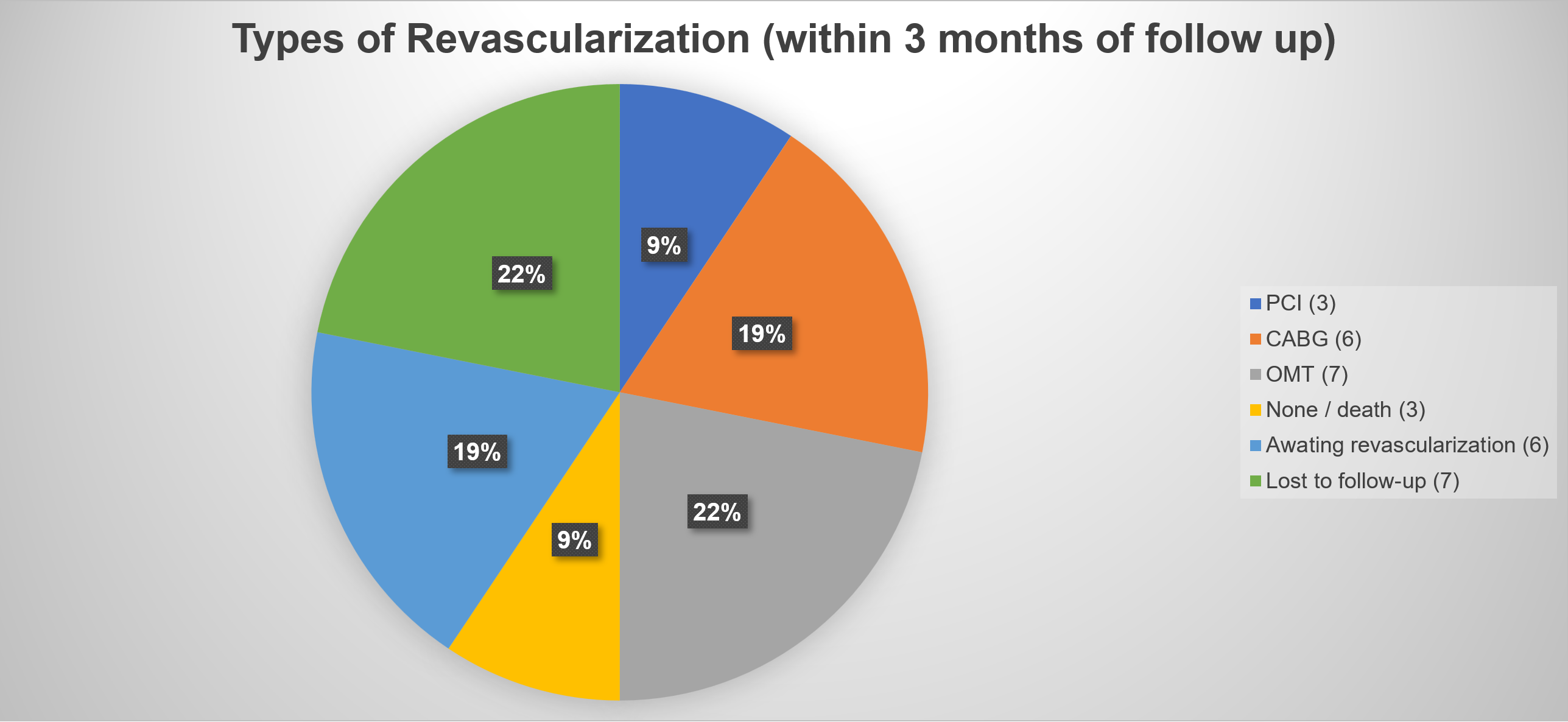
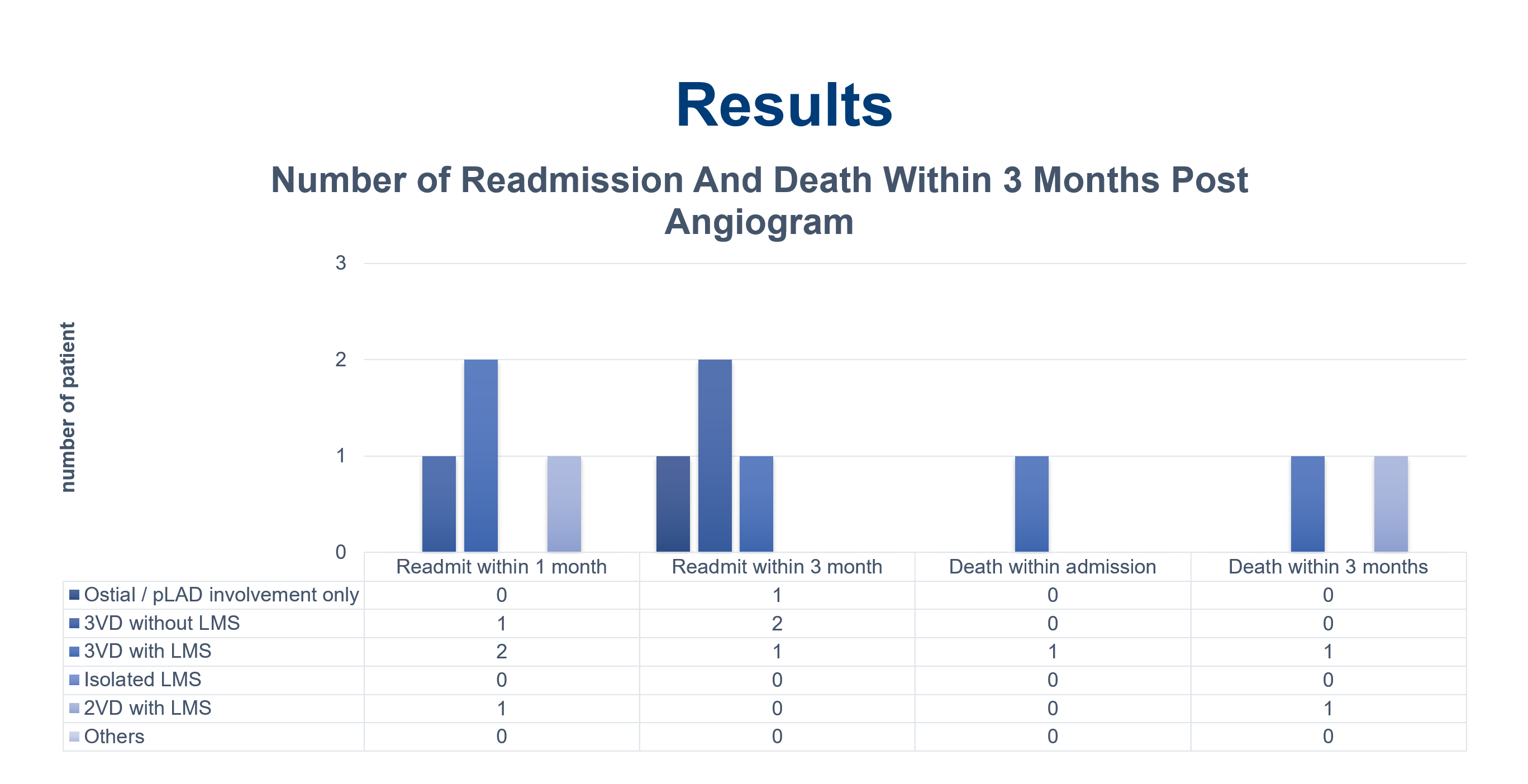
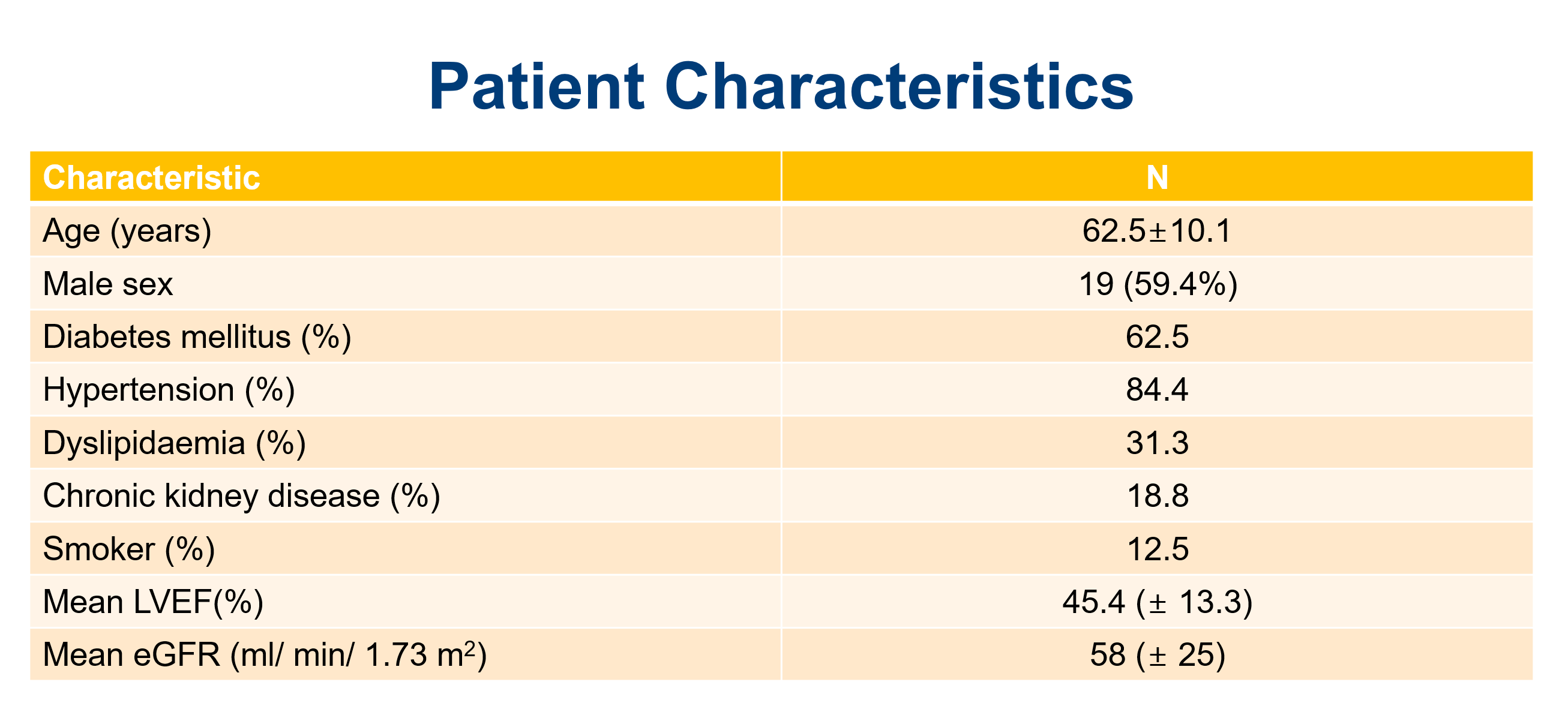
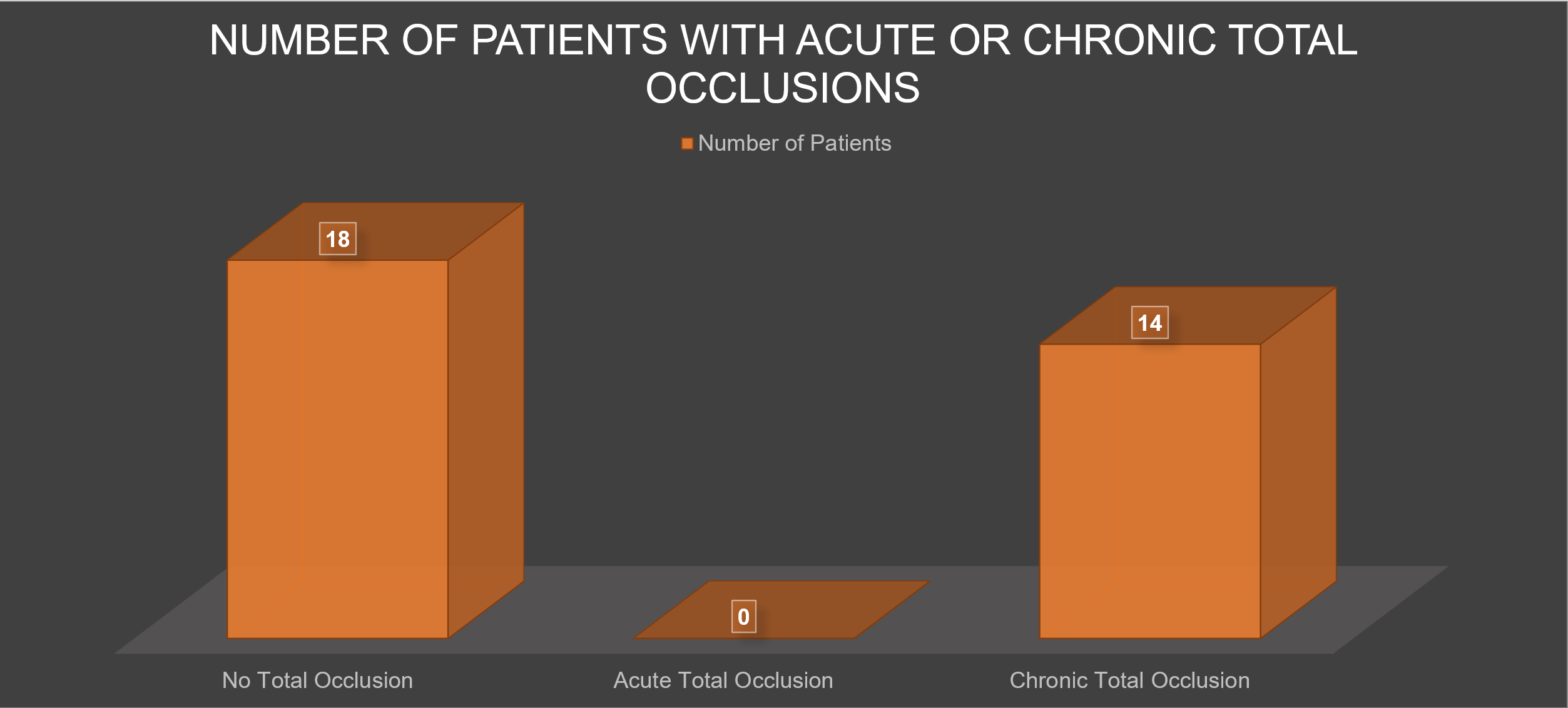
Among 1147 STEMI admissions, 32 (2.8 %) had aVR STEMI. 19 (59.4 %) were males with mean age of 62.5 ± 10.1 years. Among them, 20 (62.5 %) had DM, 27 (84.4 %) hypertension, 10 (31.3 %) dyslipidemia, 6 (18.8 %) chronic kidney disease, and 4 (12.5 %) were smokers. Mean LVEF was 45.4 (± 13.3) %. Mean eGFR was 58 (± 25) ml/ min/ 1.73 m2. None were thrombolysed but all undergone coronary angiography during index admission. Mean waiting time from admission to date of coronary angiography was 3.7 days. 31 (96.8 %) patients had significant coronary artery disease: 13 (41 %) had triple vessel disease (3VD) without LMS involvement, 12 (38 %) had 3VD with LMS involvement, 3 (9 %) had double vessel disease with LMS involvement, 2 (6 %) had ostial/ proximal LAD disease only, and 1 (3 %) isolated LMS involvement. No acute total coronary occlusion was identified, while 14 (43.8 %) patients had chronic total coronary occlusion. Mortality during first 3 months was significantly higher with presence of LMS involvement (3 patients), as compared to non-LMS involvement (18.3 % vs 0 %, p = 0.034). These 3 patients did not undergo any revascularization. Out of our 32 aVR STEMI patients, PCI to LAD was done successfully for 3 (9 %) patients, while CABG was done for 6 (19 %) patients within the first 3 months follow up.
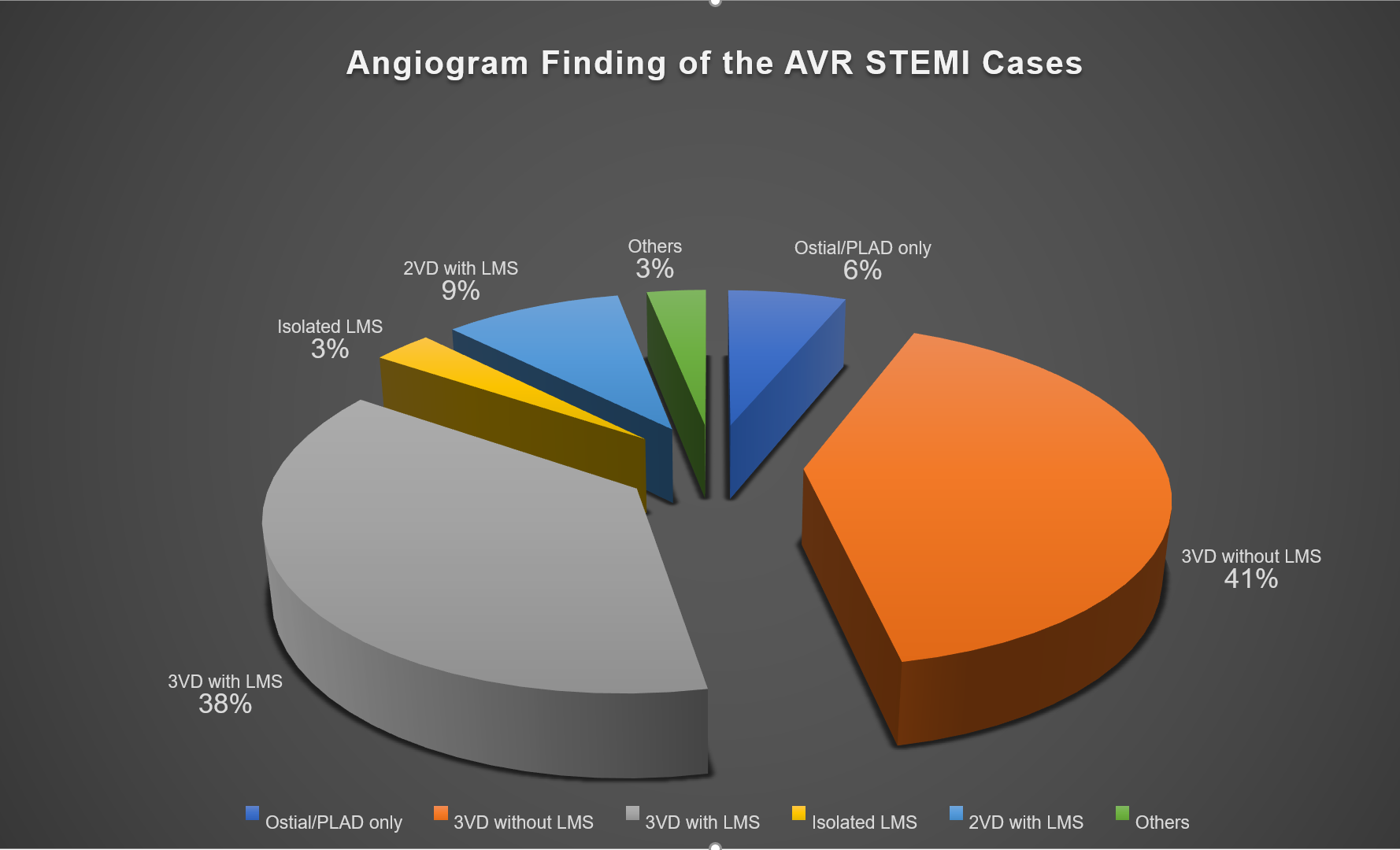



Conclusion
AVR STEMI was not associated with acute thrombotic coronary occlusion in our study population. Hence, thrombolysis or primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PPCI) may not be indicated. However early catheterization is important during index admission, although may not be within 24 hours of admission. Mortality is higher for patients with significant LMS lesion as compared to non-LMS involvement aVR STEMI patients. This study helps us to do risk stratification on which type of cases that need emergent catheterization particularly in a center with limited resources in terms of catheterization labs and manpower.