Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2021 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
TCTAP C-071
Presenter
Phattaraphong Pheerawong
Authors
Phattaraphong Pheerawong1
Affiliation
Buriram Hospital, Thailand1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-071
CORONARY - Complications
Stent Embolization Caused by Automated CPR Machine
Phattaraphong Pheerawong1
Buriram Hospital, Thailand1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
NP263672
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 45 years old woman diagnosed with poorlydifferentiated adenocarcinoma of cervix stage IIIB, currently on palliativechemotherapy. She presented with acutechest pain for one hour. At the emergency room, her blood pressure was130/90 mmHg, HR 70/min. EKG showed sinusrhythm, ST depression at V1, V2, V3, ST elevation V7, V8,V9. The diagnosis was isolatedposterior wall STEMI
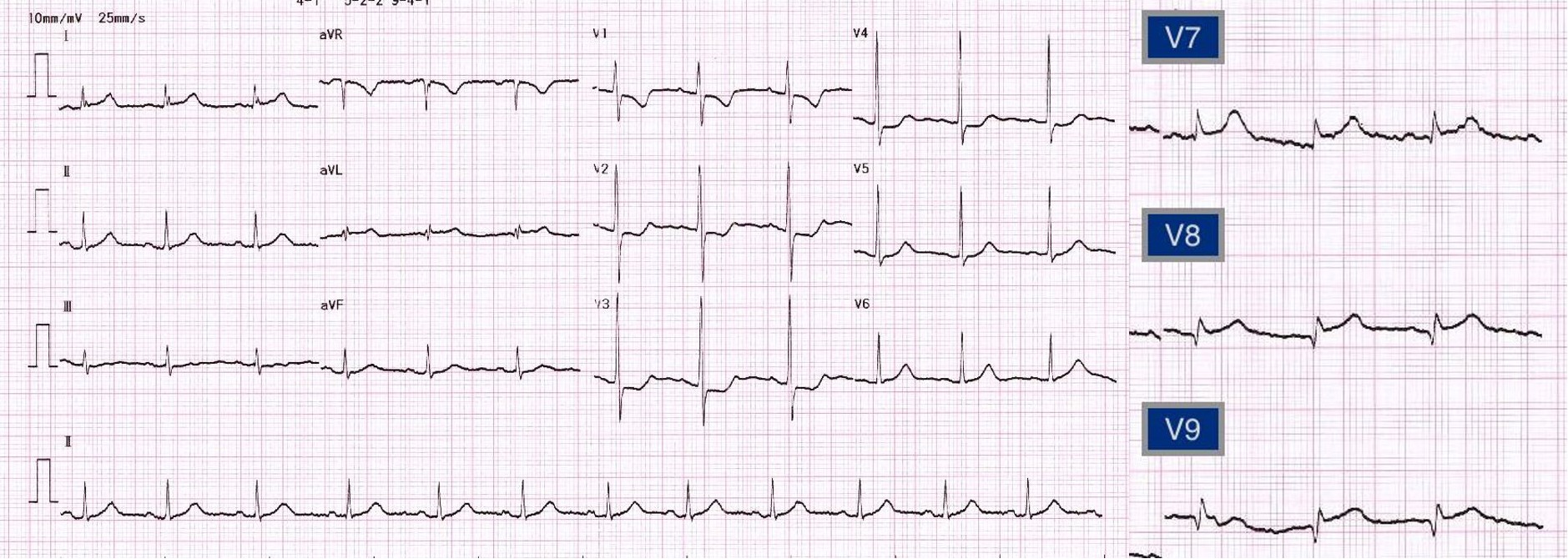

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
EKG showed sinus rhythm, ST depression at V1, V2, V3, STelevation V7, V8, V9. The diagnosis was isolated posterior wall STEMI. Bedsidecardiac ultrasound showed LVEF 50-55% by eyeballestimation with posterior wall akinesia
Relevant Catheterization Findings
CAG was performed via right femoral artery with6 French (Fr) sheath. The diagnostic catheters were JL3.5/6 Fr., JR 4/5Fr.
 CAG_RAOcranial.mp4
CAG_RAOcranial.mp4
 CAG_RAOcaudal.mp4
CAG_RAOcaudal.mp4
 CAG_Spider.mp4
CAG_Spider.mp4
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Guiding: XB 3.0 (6 Fr).
Wire: SION blue to LCX, Runthrough Hypercoat to LAD.
After multiple attempts of manual thrombectomy – no thrombus was obtained.
Manual aspiration via guiding catheter – no thrombus obtained.
Try to open LCX flow with 3.0 balloon – 6 atm.
After predilate LCx, LAD was slow flow. Urgent manual thrombectomy at LAD, only a small red thrombus was obtained. r-TPA (5 mg) was given via guiding catheter immediately.
Systolic BP dropped to 40 mmHg. Patient loss of consciousness and developed sudden cardiac arrest. She was intubated and start CPR: PEA algorithm.
We use AutoPulse to continue CPR and PCI.
Change to 7 Fr system. XB 3.0 (7Fr) guiding. Re-wire LAD and LCX
The second dose of r-TPA (5 mg) was given via guiding catheter.
There was difficult to performed PCI due to excessive movement of heart from AutoPulse.
LMCA, LAD , and LCx were stented with 3.0x15 stents (Step Crush technique).
Post dilated LMCA with NC 4.0. Successful ROSC.
Final angiogram: LAD-TIMI 3 flow, thrombus embolization to mid LCx
IABP was inserted.
CPR summary.
- AutoPulse Time = 40 min
- Defibrillation 200J x 3 times
- Adrenaline = 11 amp
- Amiodarone 150 mg iv
Careful review angiogram after the procedure
- stent LAD embolization to mid LAD
- no LCx stent found
Re CAG 2 week later
IVUS guide optimized LAD stent.
Fluoroscope entire body -cannot find LCX stent. Supra-aortic CT scan was not performed because the patient in unstable condition.
 Slow flow after balloon.mp4
Slow flow after balloon.mp4
 PCI with Autopulse.mp4
PCI with Autopulse.mp4
 Whole body scan.mov
Whole body scan.mov
Wire: SION blue to LCX, Runthrough Hypercoat to LAD.
After multiple attempts of manual thrombectomy – no thrombus was obtained.
Manual aspiration via guiding catheter – no thrombus obtained.
Try to open LCX flow with 3.0 balloon – 6 atm.
After predilate LCx, LAD was slow flow. Urgent manual thrombectomy at LAD, only a small red thrombus was obtained. r-TPA (5 mg) was given via guiding catheter immediately.
Systolic BP dropped to 40 mmHg. Patient loss of consciousness and developed sudden cardiac arrest. She was intubated and start CPR: PEA algorithm.
We use AutoPulse to continue CPR and PCI.
Change to 7 Fr system. XB 3.0 (7Fr) guiding. Re-wire LAD and LCX
The second dose of r-TPA (5 mg) was given via guiding catheter.
There was difficult to performed PCI due to excessive movement of heart from AutoPulse.
LMCA, LAD , and LCx were stented with 3.0x15 stents (Step Crush technique).
Post dilated LMCA with NC 4.0. Successful ROSC.
Final angiogram: LAD-TIMI 3 flow, thrombus embolization to mid LCx
IABP was inserted.
CPR summary.
- AutoPulse Time = 40 min
- Defibrillation 200J x 3 times
- Adrenaline = 11 amp
- Amiodarone 150 mg iv
Careful review angiogram after the procedure
- stent LAD embolization to mid LAD
- no LCx stent found
Re CAG 2 week later
IVUS guide optimized LAD stent.
Fluoroscope entire body -cannot find LCX stent. Supra-aortic CT scan was not performed because the patient in unstable condition.
Case Summary
Follow up:The patient was discharged from hospital. The length of stay was 15 days. LVEF was 51%. She received palliative care for cervical adenocarcinoma. No evidence of stroke or angina pain. She died from end-stage CA cervix seven months later.Learning point:Intracoronary fibrinolysis can use as bailout drug in massive thrombus burden. Automated chest compression machine is helpful for percutaneous coronary intervention during cardiac arrest. PCI with automated CPR- Can use only limited view- Operator should temporarily stop the machine before placing stent- Mechanical force can push deployed stent to improper position, especially when using an undersized stent.


