Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2021 Virtual. Below are accepted ones after thoroughly reviewed by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to explore your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion!
TCTAP A-020
Presenter
Oyunkhand Buyankhishig
Authors
Khuyag Batmyagmar1, Oyunkhand Buyankhishig1, Bum-Erdene Batbayar2, Surenjav Chimed3, Lkhagvasuren Zundui3
Affiliation
Intermed Hospital, Mongolia1, First State Central Hospital, Mongolia2, Third State Central Hospital, Mongolia3
View Study Report
TCTAP A-020
Bifurcation/Left Main Diseases and Intervention
Prognostic Impact of Residual SYNTAX Score After Successful Percutaneous Coronary Intervention of Left Main Coronary Artery Bifurcational Stenosis
Khuyag Batmyagmar1, Oyunkhand Buyankhishig1, Bum-Erdene Batbayar2, Surenjav Chimed3, Lkhagvasuren Zundui3
Intermed Hospital, Mongolia1, First State Central Hospital, Mongolia2, Third State Central Hospital, Mongolia3
Background
Left main coronary artery (LMCA) bifurcational stenosis is considered as a complex coronary artery disease (CAD) and successful percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) ofLM bifurcational stenosis could substantially decrease total SYNTAX score. However, the impact of residual SYNTAX score after successful PCI of LMbifurcational stenosis on long-term patient prognosis is unknown.
Methods
We chose patients with LMCA bifurcational stenosis who successfully treated by PCI. SYNTAX score was calculated before and after PCI. Cox proportional hazard regression analysis and Kaplan-Meier curve were used to estimate the relationship between residual SYNTAX score and all-cause mortality after PCI of LM bifurcational stenosis.
Results
A total of 78 patients with LM bifurcational stenosis were chosen (mean age60±11, 81% male). Pre-procedural median SYNTAX score was significantly decreased after successful PCI of LMCA bifurcational stenosis (28±9.2 vs. 2±3.1,p<0.001). After adjustment of age, gender, and Medina classification, post-procedural residual SYNTAX score was not associated with all-cause mortality in the long term (HR=1.01, 95% CI 0.82-1.25, p=0.918). Also Kaplan-Meier curve estimation didn’t show a significant difference between patients with residual SYNTAX score 0 and ≥ 1 (Figure 1).
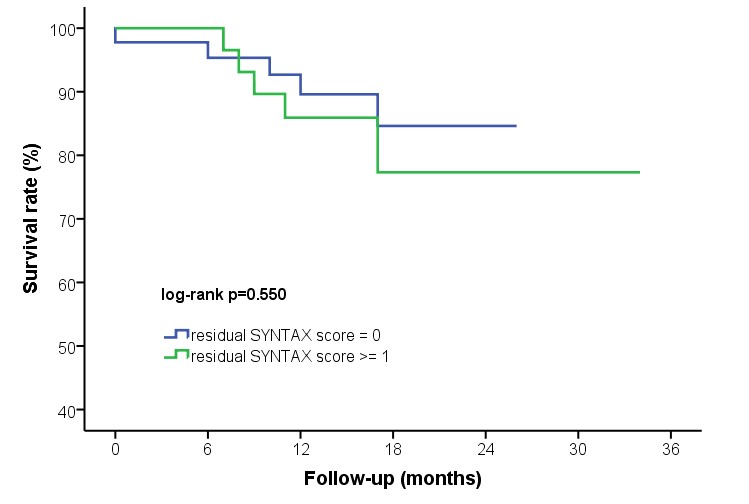

Conclusion
Successful PCI of LMCA bifurcational stenosis substantially decreases total SYNTAX score. Residual SYNTAX score after PCI of LMCA bifurcational stenosis is not related to long-term patient prognosis.


