Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-238
Fish and CHIP: Concurrent Percutaneous Left-Ventricular Thrombus Retrieval and Complex Coronary Intervention With Hemodynamic Support
By Jonathan X Fang
Presenter
Jonathan X Fang
Authors
Jonathan X Fang1
Affiliation
Henry Ford Hospital, USA1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-238
Endovascular - Thrombus Removal Devices and Techniques
Fish and CHIP: Concurrent Percutaneous Left-Ventricular Thrombus Retrieval and Complex Coronary Intervention With Hemodynamic Support
Jonathan X Fang1
Henry Ford Hospital, USA1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
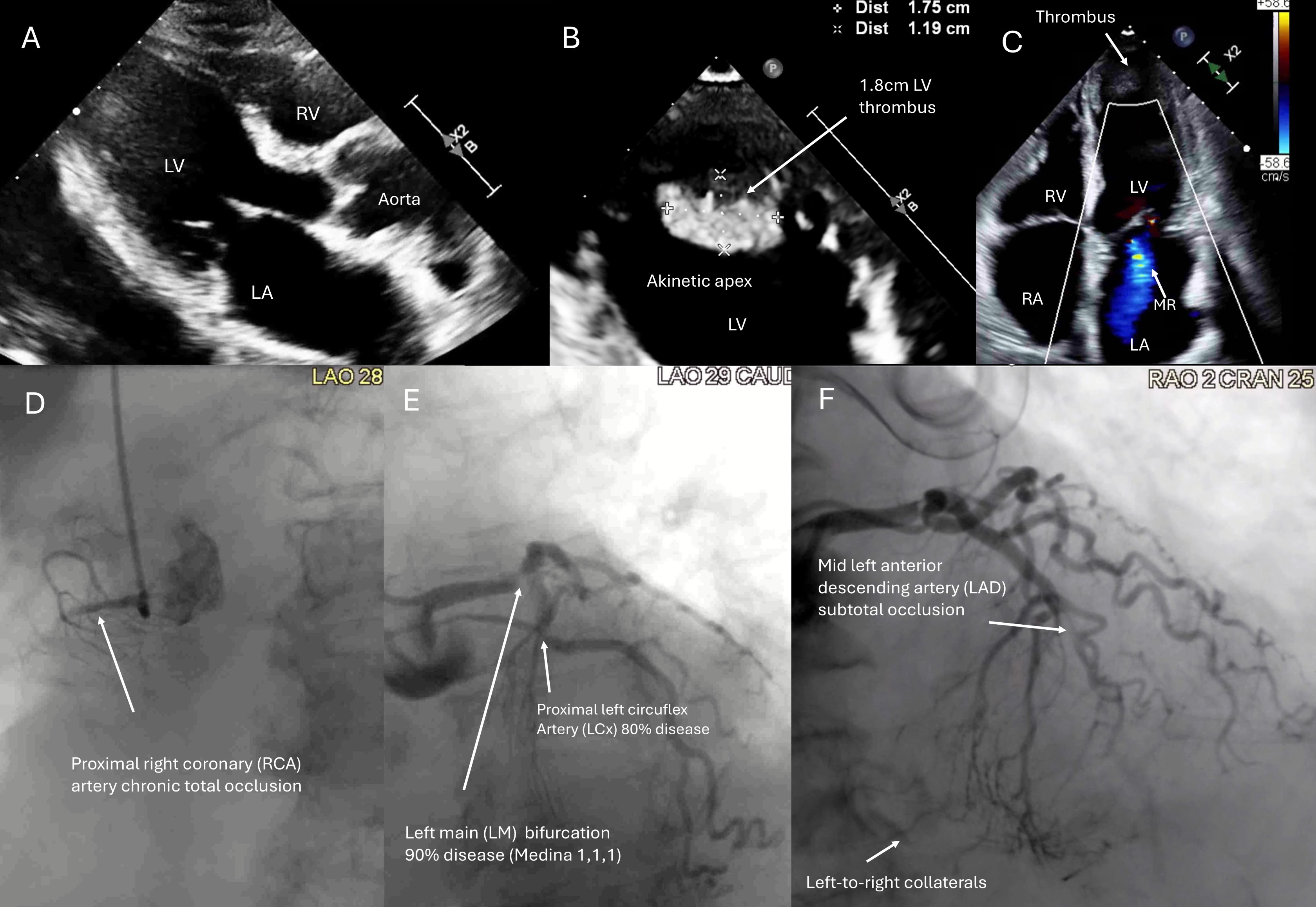
A77-year-old female with ACS, LM-triple vessel disease, LVEF 20% and a 1.8cm LVT(Figure 1), with prohibitive surgical risk and cardiac index of 1.5 L/min/m2on inotropic support, was offered percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) withconcurrent thrombus aspiration with the AngioVAC system (AngioDynamic, USA) perheart team decision.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
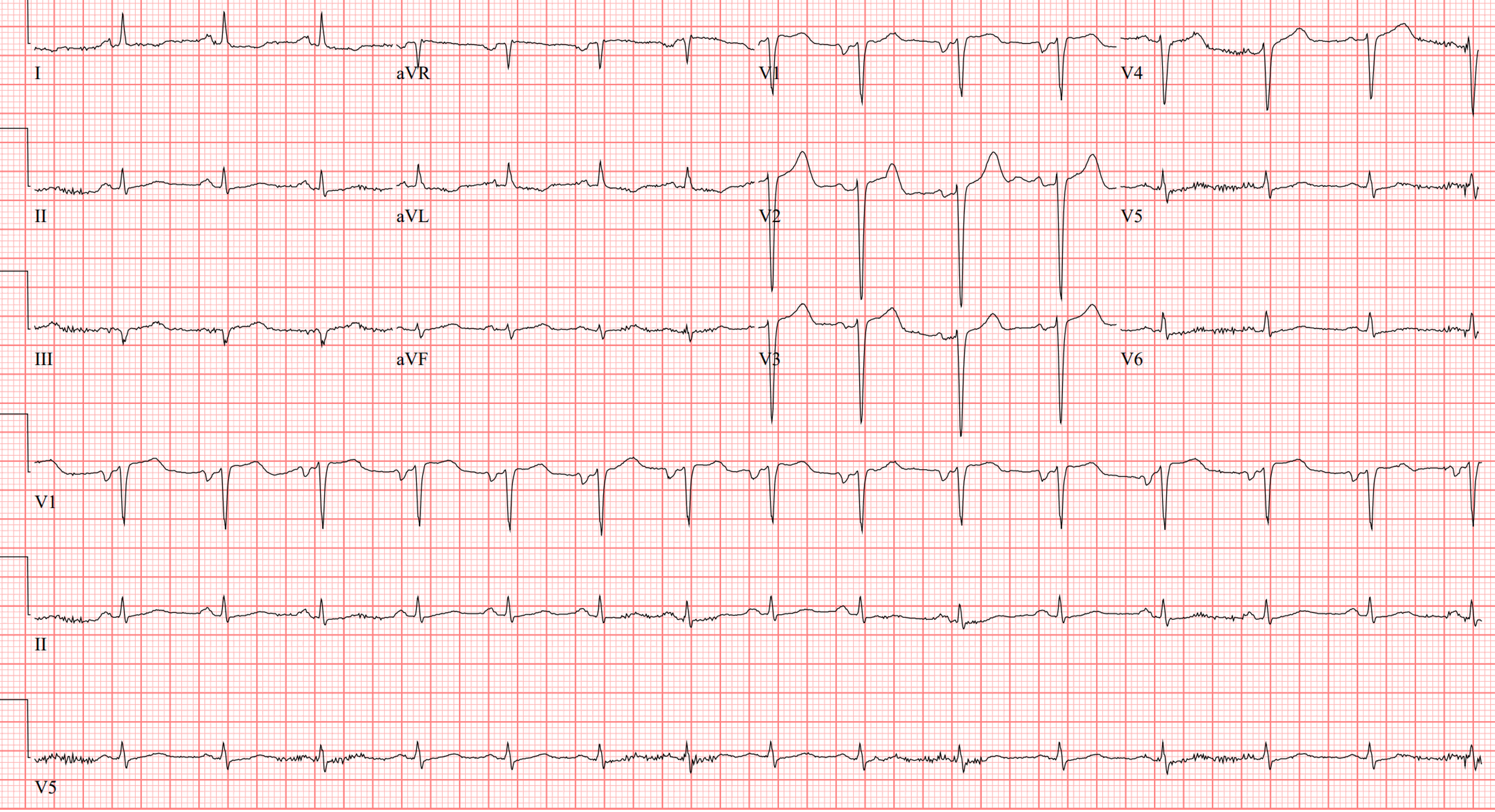
ECG: TWI I, V5-V6, late precordial R transitionEcho: LVEF 20%. Apical aneurysm. 1.8 LV apical thrombus. Moderate mitral regurgitatino
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Elevated filling pressures. RA 10mmHg PA 52/12mmHg mean 32mmHg, PCWP 28mmHgFick Cardiac output/index 2.6 / 1.5 Coronary arteriogram: LM bifurcation medina 1,1,1 diseasemLAD subtotal occlusionpLCx 70-80% calcified lesionpRCA CTO, left-to-right collaterals

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
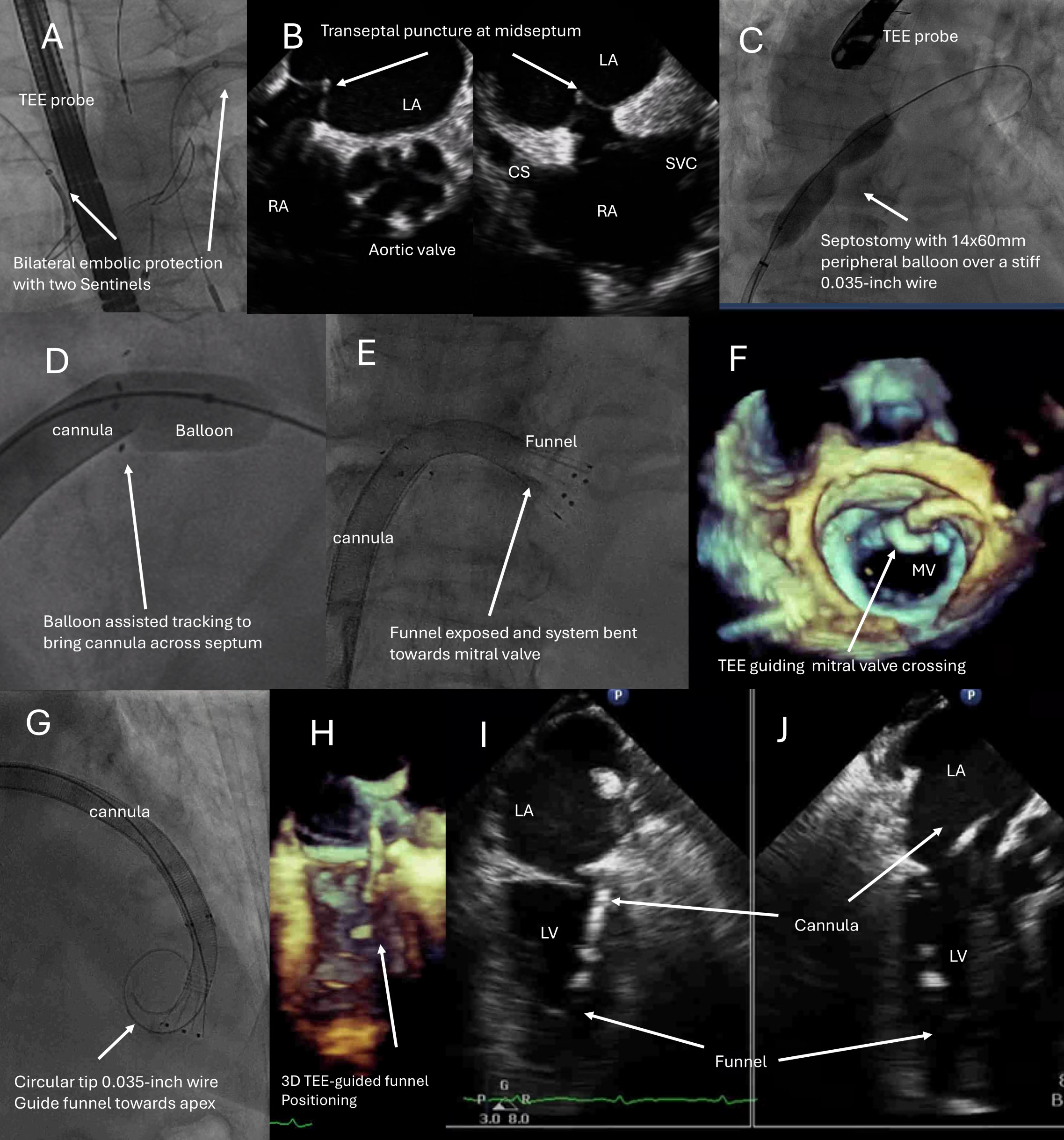
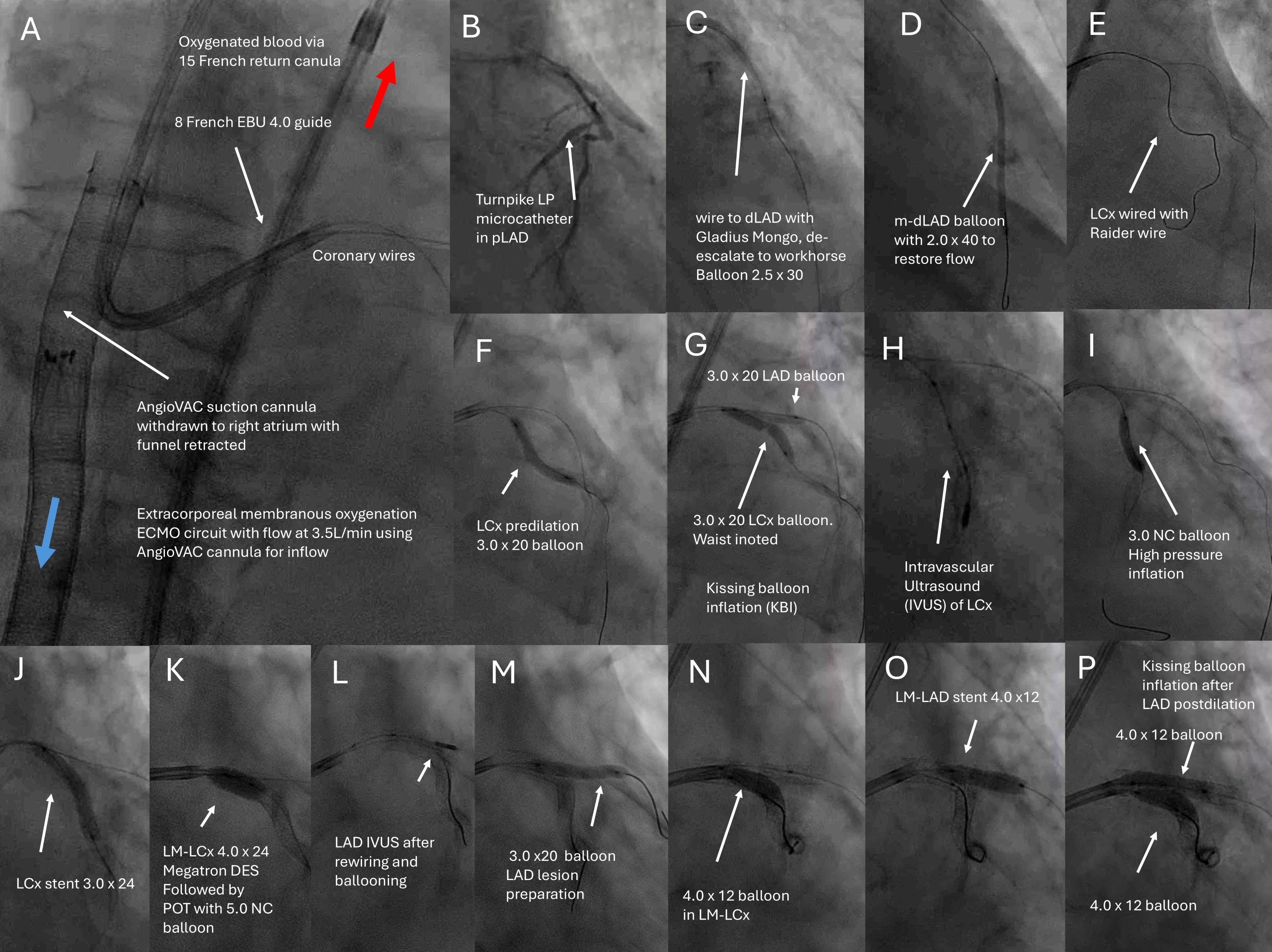
Right femoral vein access with a 26-French sheath with hemostatic valve (DrySeal, Gore Medical USA) preclosed with two proglides (Abbott Cardiovascular, USA) was obtained. Biradial accesses were used for cerebral embolic protection (figure 2, panel A). Transeptal puncture(B) and septostomy(C) followed by balloon-assisted tracking(D) brought a 22 French AngioVAC cannula into the left atrium (E), followed by mitral valve crossing to reach the LV apex via a Confida wire(G-I) (Medtronic, USA), followed by thrombectomy, all under transesophgeal echocardiography(TEE) guidance (H-J). Blood was returned through an oxygenator into a 15 French cannula place in 16 French Dryseal sheath via right femoral artery access preclosed with proglides. After thrombectomy, the suction cannula was pulled back into the right atrium with the funnel retracted. At a flow rate of 3.5 liters-per-minute , it served as a venoarterial-extracorporeal memebraneous oxygenation(VA-ECMO) circuit(figure 3, panel A). Complex high-risk indicated PCI (CHIP) was performed via left femoral artery access to left anterior descending artery(LAD), left circumflex artery(LCx) and LM bifurcation (B-P) with good result on final angiogram (figure 4, panel A). Contrast echocardiography showed no further LV thrombus (B) and unchanged mitral regurgitation (C) after the thrombus was fished out (D). The patient recovered and was discharged
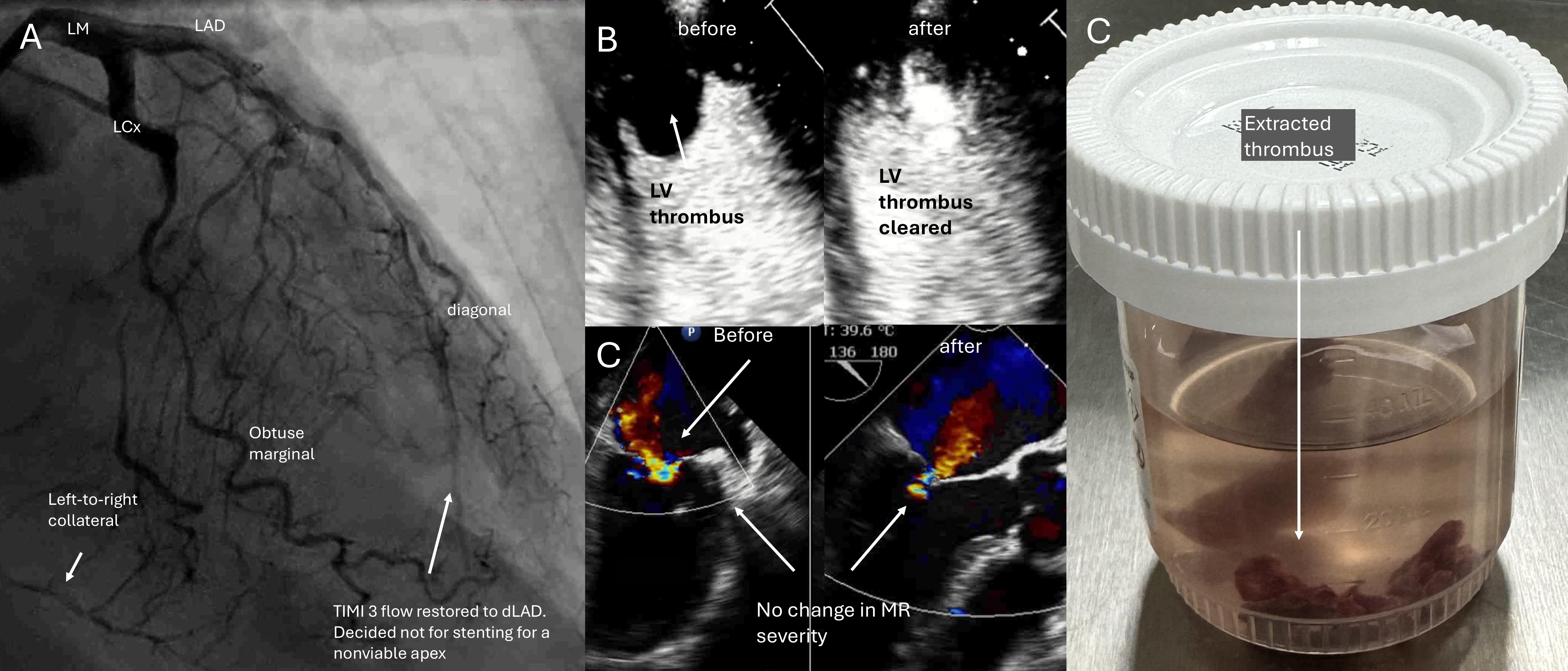



Case Summary
Acutecoronary syndrome(ACS) with concurrent left main bifurcation disease, reduced leftventricular ejection fraction(LVEF) and left-ventricular thrombus(LVT) is achallenging situation where the microaxial flow pump for supporting coronaryintervention is contraindicated owing to embolic risk.


