Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-039
Sequential Rotablation for Calcified Tandem RCA Lesions With Guide Extension Assistance
By Sharath Annam, Nitin Naik, Anil Krishna Gundala, Lokanath Seepana
Presenter
Sharath Annam
Authors
Sharath Annam1, Nitin Naik1, Anil Krishna Gundala1, Lokanath Seepana1
Affiliation
Medicover Hospitals, India1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-039
Coronary - Adjunctive Procedures (Thrombectomy, Atherectomy, Special Balloons)
Sequential Rotablation for Calcified Tandem RCA Lesions With Guide Extension Assistance
Sharath Annam1, Nitin Naik1, Anil Krishna Gundala1, Lokanath Seepana1
Medicover Hospitals, India1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
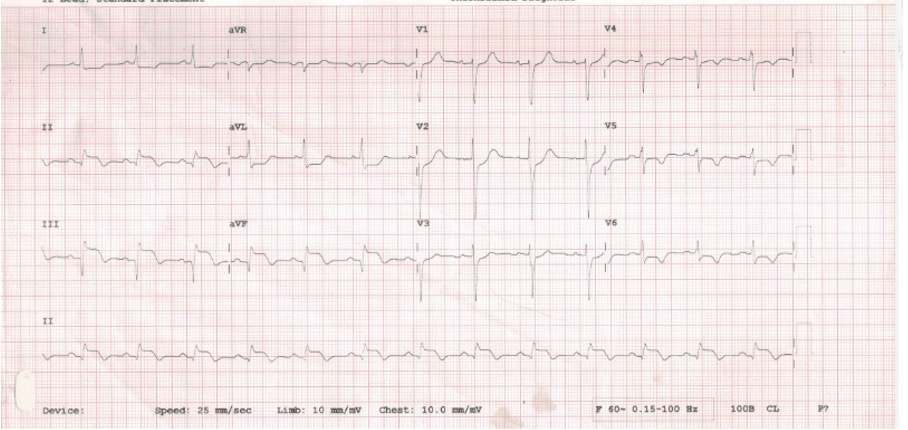
A 68-year-old gentleman with a known history of diabetes mellitus and hypertension had undergone CABG with LIMA to LAD graft in 2019 and now presented with chest discomfort with sweating for 2 days. He was evaluated outside, ECG showed ST and T changes in inferior leads and Echocardiography revealed concentric LVH with hypokinesia of the basal inferior wall.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Coronary angiogram showed patent LIMA to LAD graft mild proximal circumflex disease. The right coronary artery showed proximal 60% calcific stenosis and distal RCA 99% focal calcific lesion with TIMI II distal flow. PCI was attempted but failed due to wire uncrossability of the distal lesion and the inability to deliver devices beyond the proximal lesion. As he had recurrent ACS, he was admitted for PCI of RCA
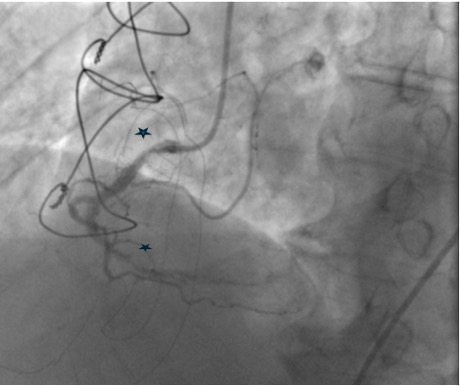

Relevant Catheterization Findings
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Right femoral arterial access was taken with 7F long sheath (45cm) and RCA was engaged with 7F AL 3.5 catheter. We failed to cross proximal lesion with Rinato wire (Asahi Intecc, Japan) but crossed with Fielder XT-R (Asahi Intecc, Japan). We had difficulty in crossing the distal lesion due to inadequate guide support and inability to deliver microcatheter beyond proximal calcific lesion. Proximal lesion was predilated with 2.5 mm NC balloon but the balloon got ruptured. Fielder XTR wire was exchanged with Rota floppy wire (Boston scientific, Japan) with corsair microcatheter (Asahi Intecc, Japan) delivered just beyond proximal lesion. Temporary pacemaker inserted and Rotablation of the proximal RCA lesion was done with 1.5 mm Rota burr. Post proximal lesion modification corsair could be delivered to Distal lesion, and lesion crossed with Ultimate Bros 3 (Asahi Intecc, Japan) followed by de-escalation to Fielder XT-R wire. The proximal lesion was then dilated with 3.5x10mm Wolverine Cutting balloon (Boston Scientific, Ireland) to deliver a 7F Guideliner beyond the proximal lesion for better support to further gear advancement. As 1mm balloon stuck within the distal lesion, grenadoplasty was performed followed by an exchange to rota wire with corsair. Rotablation of distal RCA lesion was done with 1.5 mm burr through guide extension. Further dilatation of distal lesion was done with 3mm IVL balloon followed by stenting with 3.25 x 28 mm drug-eluting stent with good TIMI 111 flow.
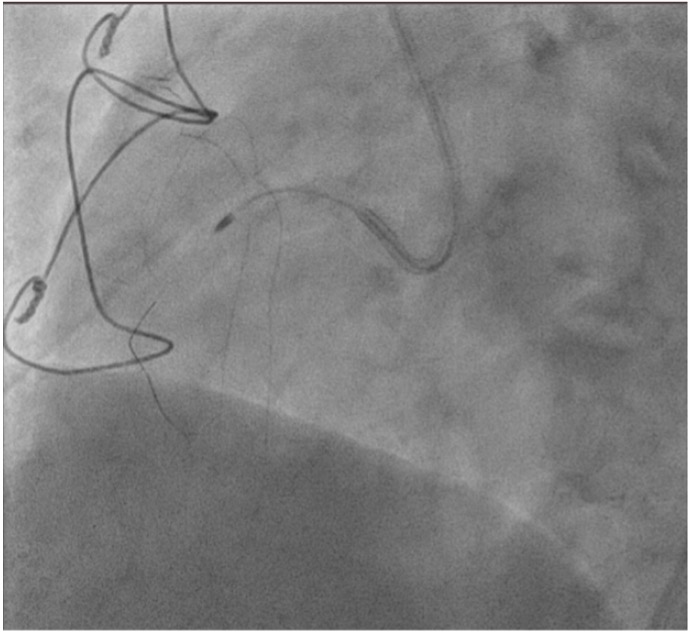
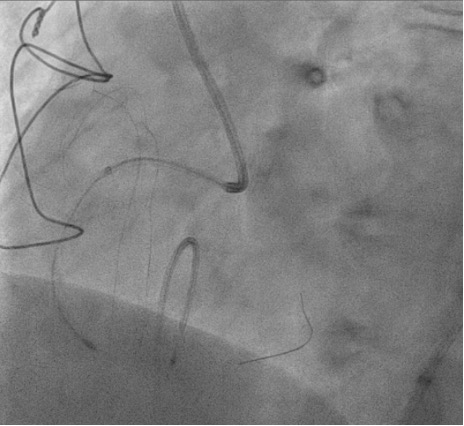
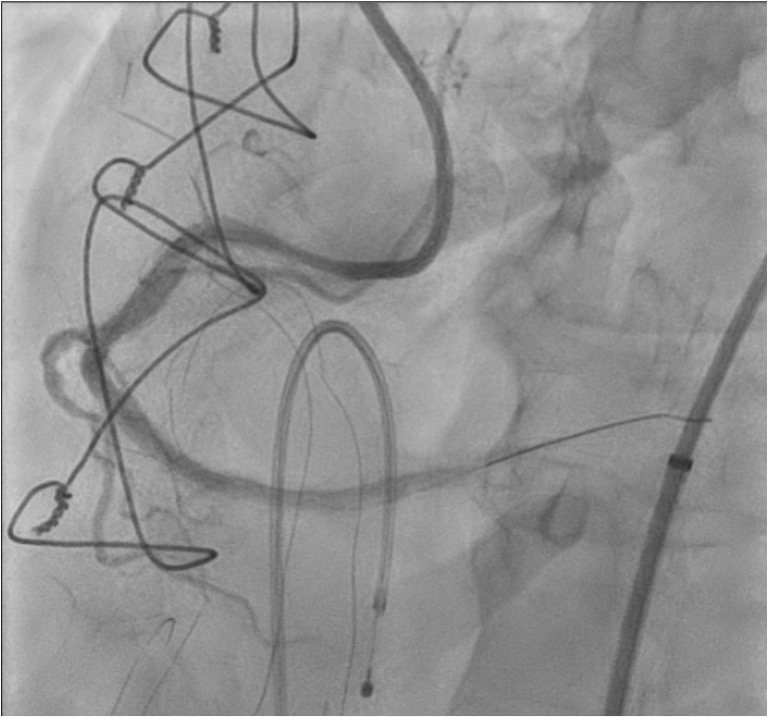



Case Summary
Sequential rotablation can be used in tandem calcified lesions when proximal lesion is obstructing gear delivery beyond. Guide extension facilitates burr delivery to the region of interest and avoids unintentional ablation of vulnerable zones in proximal vessel. Operator must be aware of burr compatibility information and preferred method of burr delivery.


