Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-202
Sudden Hemodynamic Collapse Due to Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Requiring Emergent Septal Ablation After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
By Ryo Arita, Kentaro Hayashida, Tomonari Moriizumi, Juri Iwata, Akiyoshi Kajino, Shingo Sakata, Toshinobu Ryuzaki, Hikaru Tsuruta, Hideyuki Shimizu, Masaki Ieda
Presenter
Ryo Arita
Authors
Ryo Arita1, Kentaro Hayashida1, Tomonari Moriizumi1, Juri Iwata1, Akiyoshi Kajino1, Shingo Sakata1, Toshinobu Ryuzaki1, Hikaru Tsuruta1, Hideyuki Shimizu1, Masaki Ieda1
Affiliation
Keio University Hospital, Japan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-202
Structural - Aortic Valve Intervention - Complex TAVR
Sudden Hemodynamic Collapse Due to Left Ventricular Outflow Tract Obstruction Requiring Emergent Septal Ablation After Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Ryo Arita1, Kentaro Hayashida1, Tomonari Moriizumi1, Juri Iwata1, Akiyoshi Kajino1, Shingo Sakata1, Toshinobu Ryuzaki1, Hikaru Tsuruta1, Hideyuki Shimizu1, Masaki Ieda1
Keio University Hospital, Japan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
An 89-year-old woman without any medical history was referred to our hospital due to shortness of breath on exertion (NYHA class III). Her height was 143 cm, and her weight was 43 kg. The blood pressure was 125/85 mmHg, the heart rate was 75 bpm, and the oxygen saturation was 98 %. She had a systolic murmur on cardiac auscultation. Clinical Frailty Score was 4, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality was 12.2 %.
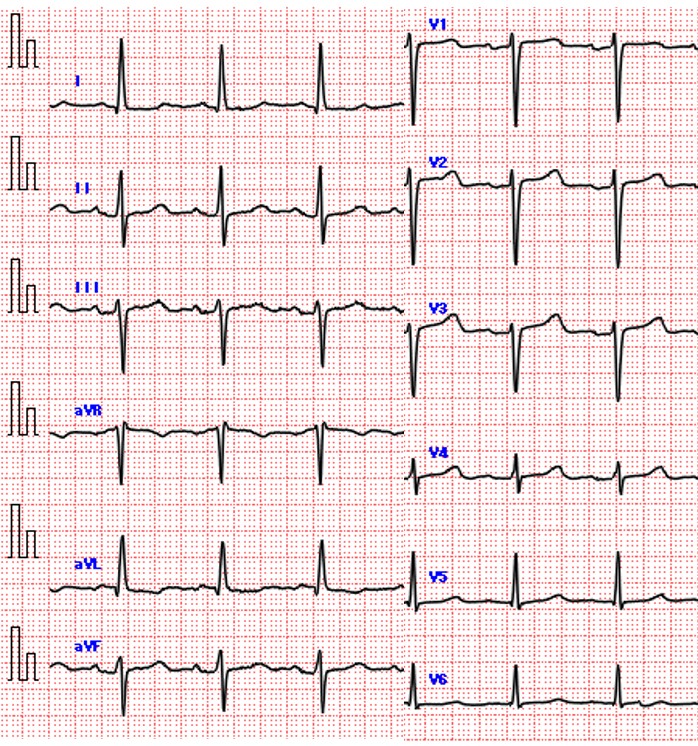

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Pre-procedural transthoracic echocardiogram revealed very severe aortic stenosis (peak flow velocity: 6.5 m/s and mean pressure gradient: 100 mmHg). The left ventricular ejection fraction was 60 %. Accelerated blood flow was observed in the left ventricular outflow tract, but no significant pressure gradient was detected. Computed tomography showed that the annulus area was 396.1 mm2, perimeter was 73.6 mm. There was severe calcification on the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT).
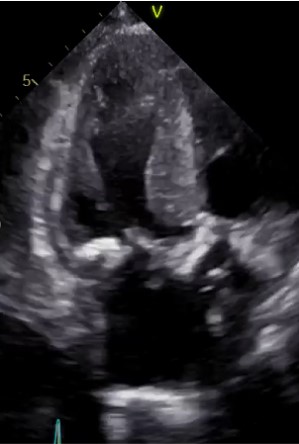
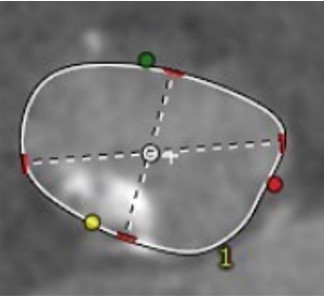


Relevant Catheterization Findings
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
We decided to perform transfemoral transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) with Evolut FX 26 mm valve because of the LVOT calcification. After valve implantation, the patient developed sudden hemodynamic collapse due to LVOT obstruction with accelerated blood flow of 4 m/s, and severe mitral regurgitation (MR) with systolic anterior motion (SAM). After continuous intravenous noradrenaline administration and right ventricular pacing with a temporary pacemaker, the hemodynamic status was temporally stabilized.Despite of administration of bisoprolol 5 mg and cibenzoline 200 mg after the procedure, the hemodynamics was unstable due to worsening LVOT obstruction and MR with SAM, which led to worsening heart failure. Therefore, we decided to perform percutaneous transluminal septal myocardial ablation (PTSMA) on 2 post operative days.After septal ablation by injection of ethanol into the first, second, and third septal branches, the hemodynamics immediately stabilized with resolution of LVOT obstruction and SAM with decrease of pressure gradient of 10 mmHg. Permanent pacemaker implantation was required for complete atrioventricular block with continuation of oral bisoprolol 5 mg and cibenzoline 200 mg. Finally, the patient was discharged walking independently.One year after TAVR, despite of unplanned discontinuation of all medication due to patient’s low compliance, follow-up echocardiogram showed no recurrence of LVOT obstruction, and electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm.
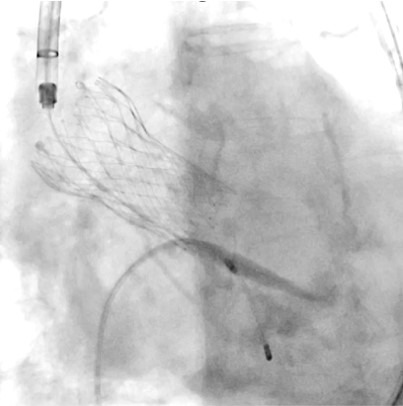
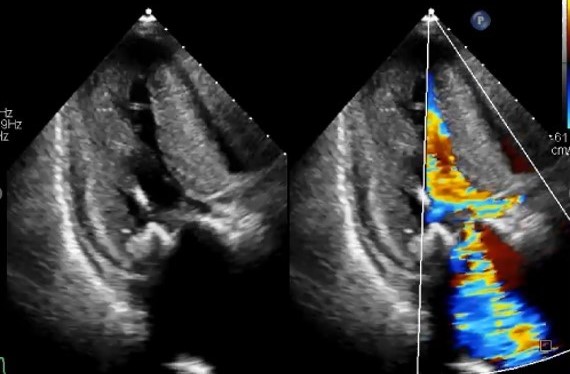
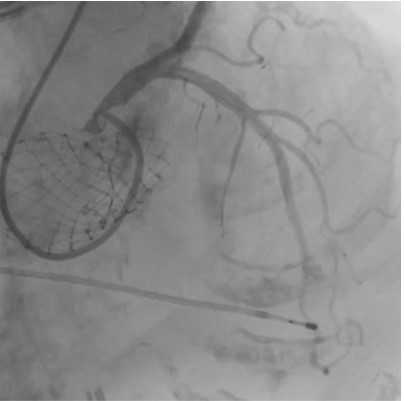



Case Summary
We experienced a case of sudden hemodynamic collapse due to LVOT obstruction requiring emergent septal ablation after TAVR. Sometimes prediction of this complication is difficult, and meticulous screening to avoid this catastrophic complication is important. Multidisciplinary approach including intensive medical treatment and invasive catheter-based treatment should be provided. Spontaneous regression provides us insight into the mechanism of LVOT obstruction complicating with aortic stenosis.


