Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-134
Complex Calcified Coronary Lesion Treated with ROTAtripsy: From Complication to Optimal Outcome
By Habibullah Moghal, Ponnusamy Shunmuga Sundaram
Presenter
Habibullah Moghal
Authors
Habibullah Moghal1, Ponnusamy Shunmuga Sundaram1
Affiliation
Velammal Medical College, India1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-134
Coronary - Complication Management
Complex Calcified Coronary Lesion Treated with ROTAtripsy: From Complication to Optimal Outcome
Habibullah Moghal1, Ponnusamy Shunmuga Sundaram1
Velammal Medical College, India1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 70-year-old male with a long history of hypertension and diabetes presented with dyspnea and palpitations over the past four months. His coronary angiography revealed distal Left Main (LM) disease, triple vessel disease, and severe stenosis in the left anterior descending (LAD), circumflex (LCX), and right coronary artery (RCA). Despite being recommended for coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), the patient opted for high-risk percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
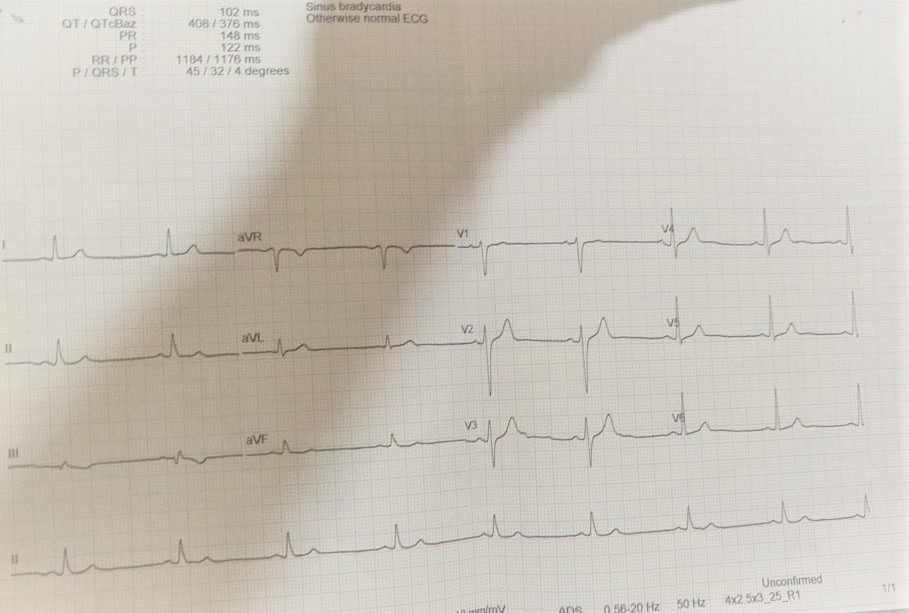

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Blood parameters-NormalTroponin I-NegativeEKG: Sinus bradycardia with no significant ST-T changes.Echocardiography: Left ventricular hypertrophy, preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF of 62%), no regional wall motion abnormalities.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
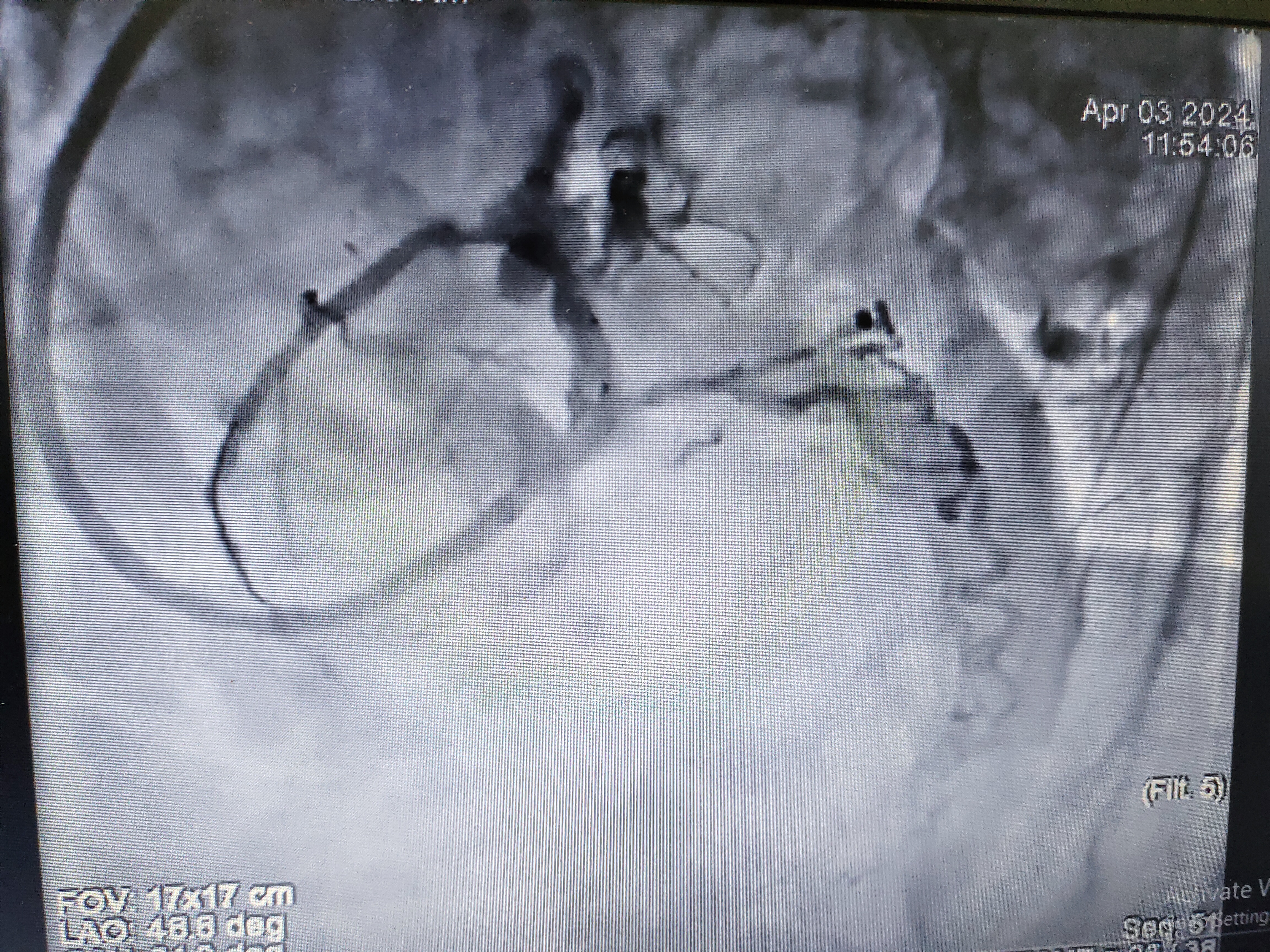
Left Main: 70% stenosis in the shaft and distal LM.LAD: Type III vessel with 90% stenosis in the proximal to mid segment, and two tandem lesions in the distal LAD (99% stenosis each).LCX: Non-dominant, with 40% stenosis at the ostial region and 50% stenosis at the major obtuse marginal (OM) branch.RCA: Dominant, with 90% calcific stenosis in the proximal segment.
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
Procedure Setup:A 7FR EBU 3.5 guide catheter was used to access the Left Coronary Artery (LCA).A Runthrough wire was exchanged with a rotawire using a microcatheter.
Pre-procedural Imaging: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) revealed a long, diffusely calcified lesion in the LAD with both superficial and deep calcifications in the mid and ostial segments.
RotaBurr and Ballooning:A 1.5mm Rota Burr was used for calcium modification.Pre-dilatation was performed with a 3.5 x 15mm Scoreflex balloon in the mid LAD.IVL (Intravascular Lithotripsy) with a 3.5 x 10mm balloon was employed for calcium modification in the osteo-proximal LAD.
Complication: After IVL, a Grade II perforation occurred during osteo-proximal dilatation with the balloon.
Management of Complication:The perforation was sealed using a 3.25 x 26mm Graft Master covered stent after prolonged balloon tamponade.The mid LAD was stented with a 2.75 x 20mm Promus Premier DES, and the LM to LAD segment was stented with a 3.5 x 24mm SYNERGY DES at 11 atm.
Post-Procedure Optimization:Post dilatation was performed using NC (non-compliant) balloons (3.75 x 12mm and 4.5 x 12mm) to achieve optimal stent expansion.Post-procedure OCT confirmed no dissection or malapposition.TIMI III flow was achieved, and the final result was satisfactory with excellent vessel expansion.
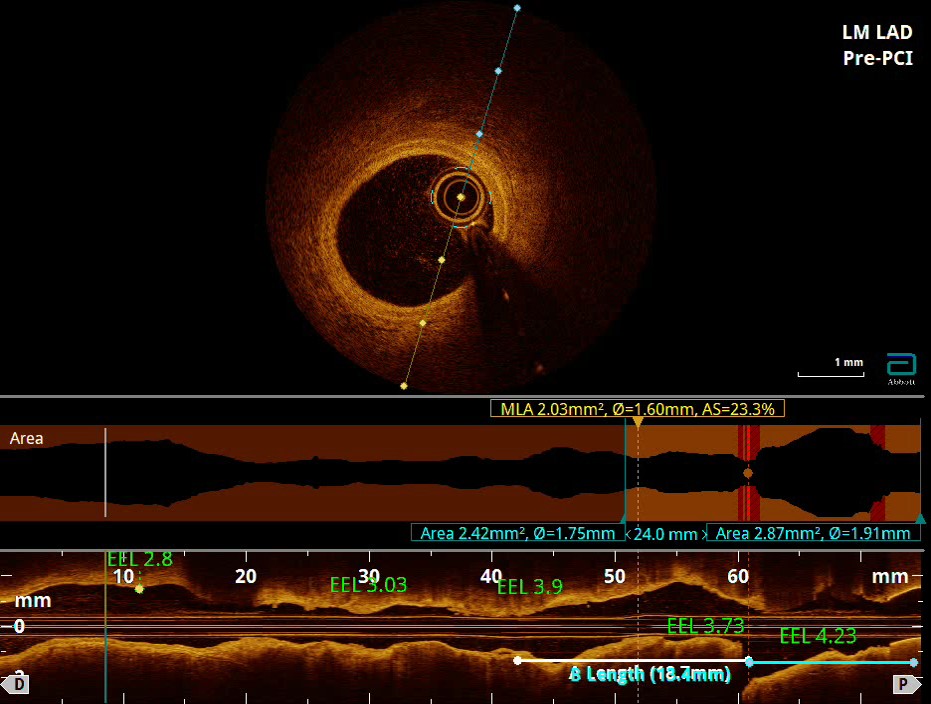
Pre-procedural Imaging: Optical coherence tomography (OCT) revealed a long, diffusely calcified lesion in the LAD with both superficial and deep calcifications in the mid and ostial segments.
RotaBurr and Ballooning:A 1.5mm Rota Burr was used for calcium modification.Pre-dilatation was performed with a 3.5 x 15mm Scoreflex balloon in the mid LAD.IVL (Intravascular Lithotripsy) with a 3.5 x 10mm balloon was employed for calcium modification in the osteo-proximal LAD.
Complication: After IVL, a Grade II perforation occurred during osteo-proximal dilatation with the balloon.
Management of Complication:The perforation was sealed using a 3.25 x 26mm Graft Master covered stent after prolonged balloon tamponade.The mid LAD was stented with a 2.75 x 20mm Promus Premier DES, and the LM to LAD segment was stented with a 3.5 x 24mm SYNERGY DES at 11 atm.
Post-Procedure Optimization:Post dilatation was performed using NC (non-compliant) balloons (3.75 x 12mm and 4.5 x 12mm) to achieve optimal stent expansion.Post-procedure OCT confirmed no dissection or malapposition.TIMI III flow was achieved, and the final result was satisfactory with excellent vessel expansion.


Case Summary
This case demonstrates the successful management of a complex, heavily calcified coronary lesion using advanced techniques like Rotablation and intravascular lithotripsy (IVL). Despite encountering a Grade-II perforation during balloon dilatation, timely intervention with balloon tamponade and a covered stent led to a favorable outcome. Post-dilatation ensured optimal stent expansion, and OCT confirmed no dissection or malapposition. This case underscores the significance of advanced tools, meticulous planning, and readiness for complications in high-risk PCI.


