Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-213
Role of Photon-Counting Computed Tomography in Detecting High-Risk Unstable Angina Patient: A Case Report
By Duc Chinh Nguyen, Thi Quynh Huong Tran, Hoang Dil Mai, Duc Cam Tran, Duong Quoc Anh Nguyen, Chi Cuong Tran
Presenter
Hoang Dil Mai
Authors
Duc Chinh Nguyen1, Thi Quynh Huong Tran1, Hoang Dil Mai1, Duc Cam Tran1, Duong Quoc Anh Nguyen1, Chi Cuong Tran1
Affiliation
Can Tho Stroke International Services General Hospital, Vietnam1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-213
Structural - Imaging - Computed Tomography
Role of Photon-Counting Computed Tomography in Detecting High-Risk Unstable Angina Patient: A Case Report
Duc Chinh Nguyen1, Thi Quynh Huong Tran1, Hoang Dil Mai1, Duc Cam Tran1, Duong Quoc Anh Nguyen1, Chi Cuong Tran1
Can Tho Stroke International Services General Hospital, Vietnam1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 57-year-old man with hypertension. 6 months before admission, photon-counting computed tomography showed 30% RCA I stenosis. He was given aspirin, atorvastatin, metoprolol succinate, and felodipin. 2 weeks before admission, he had multiple angina episodes at rest. On admission, he had a heart rate of 79 beats per minute, blood pressure of 160/100 mmHg. Other physical checkup was unremarkable. ECG showed sinus rhythm, no raised ST segment, and mildly inverted T waves in V5, V6, and aVL.
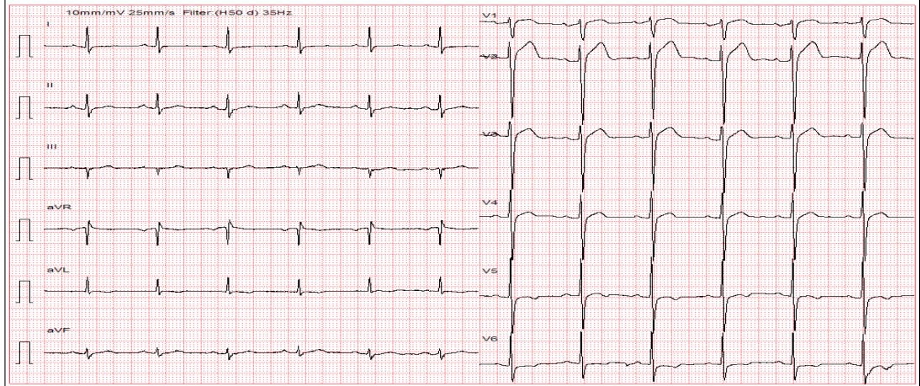
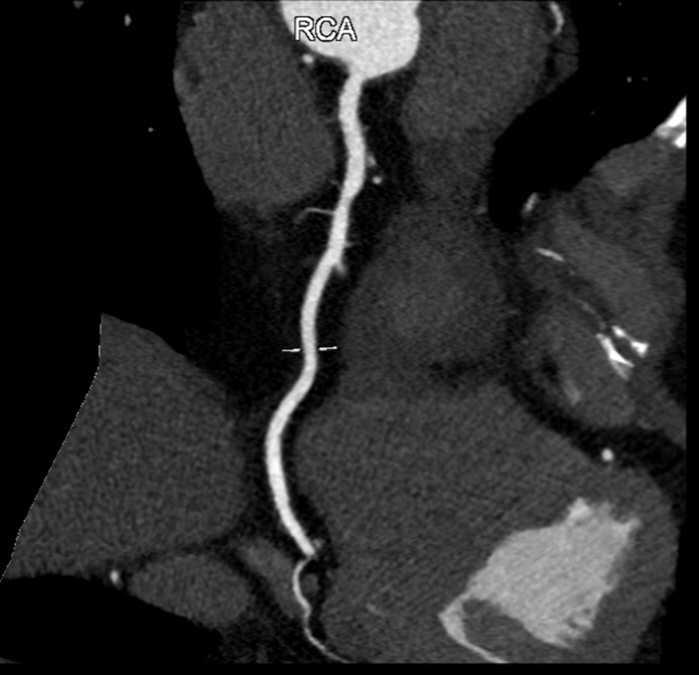


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
hs-troponin I was 6.1 pg/mL (< 15.6 pg/mL), HbA1C of 5.8%, eGFR of 77.88 mL/min/1.73 m2 (> 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), LDL-C of 1.8 mmol/L (was 2.35 mmol/L 6 months before), AST of 31 U/L, ALT of 41 U/L. Echocardiography showed a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction of 62%, no sign of dilatation or thick wall, and no abnormal regional wall motion. PCCT showed 35% stenosis of LAD II (not significant changed), 30% stenosis of RCA I and 80% stenosis of RCA III.
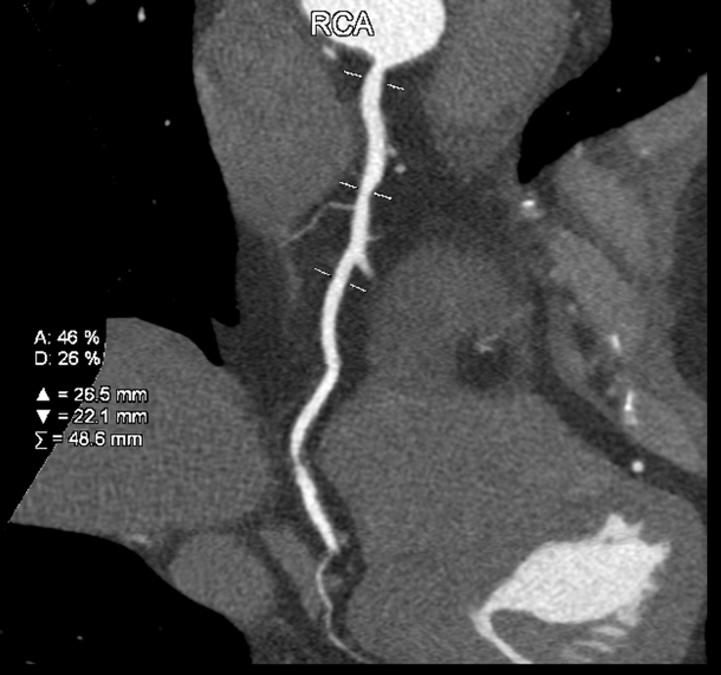
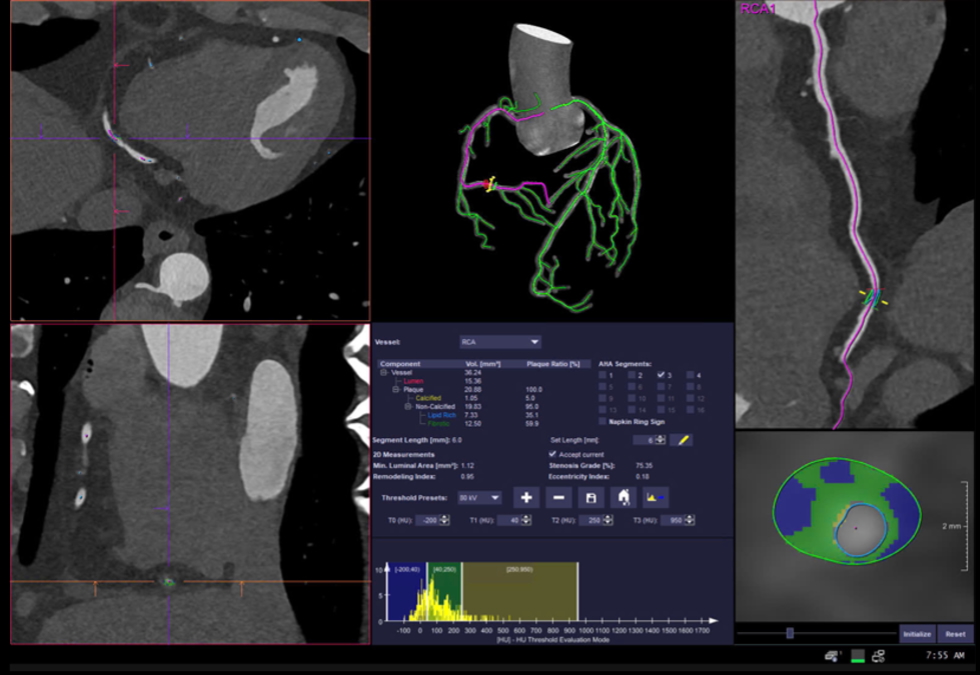


Relevant Catheterization Findings
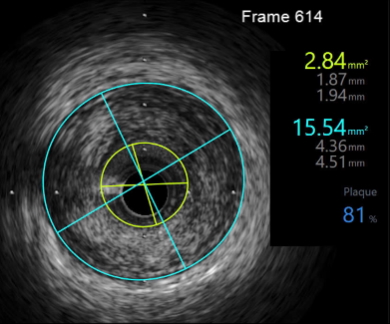
IVUS at the time showed showed 90 degree of endothelial dissection from 0h to 3h position along RCA III, with a maximum plaque burden of 81% with a MSA of 2.84 mm2.


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
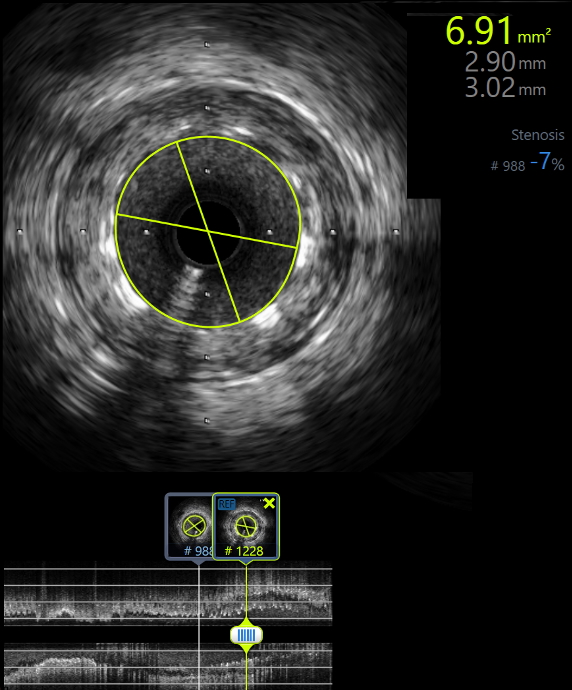
The intervention was made based on the indication of unstable angina refractory to medical treatment and a dissected lesion in RCA III on intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). We placed a 3.0 x 18 mm drug-eluting stent in RCA III and then we used an NC balloon 3.0 x 15 mm for post dilatation. IVUS was conducted after intervention to ensure optimal intervention, which revealed no edge dissection. The lumen cross-sectional area was 6.91 mm2 and was 93% of the distal lumen reference. RCA flow was TIMI 3.

Case Summary
The combination of photon-counting computed tomography and intravascular ultrasound is new and promising. PCCT can play a role in closely monitoring the plaque development in chronic chest pain patients. IVUS will then be used for lesion confirmation and intervention guidance. We believe this approach will result in a gain in net specificity and work in patients’s favor. This combination will improve diagnostic accuracy, provide a practical way for intervention guidance, and check for optimal intervention results. This approach can solve the disadvantages of traditional computed tomography and coronary angiography.


