Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-222
Where There Is a Will, There Is a Way: Balloon Atrial Septostomy as Last Resort Treatment for Advanced Heart Failure
By Ifan Citra, Utojo Lubiantoro
Presenter
Ifan Citra
Authors
Ifan Citra1, Utojo Lubiantoro1
Affiliation
Mitra Keluarga Kelapa Gading Hospital, Indonesia1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-222
Structural - Other Structural Interventions
Where There Is a Will, There Is a Way: Balloon Atrial Septostomy as Last Resort Treatment for Advanced Heart Failure
Ifan Citra1, Utojo Lubiantoro1
Mitra Keluarga Kelapa Gading Hospital, Indonesia1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
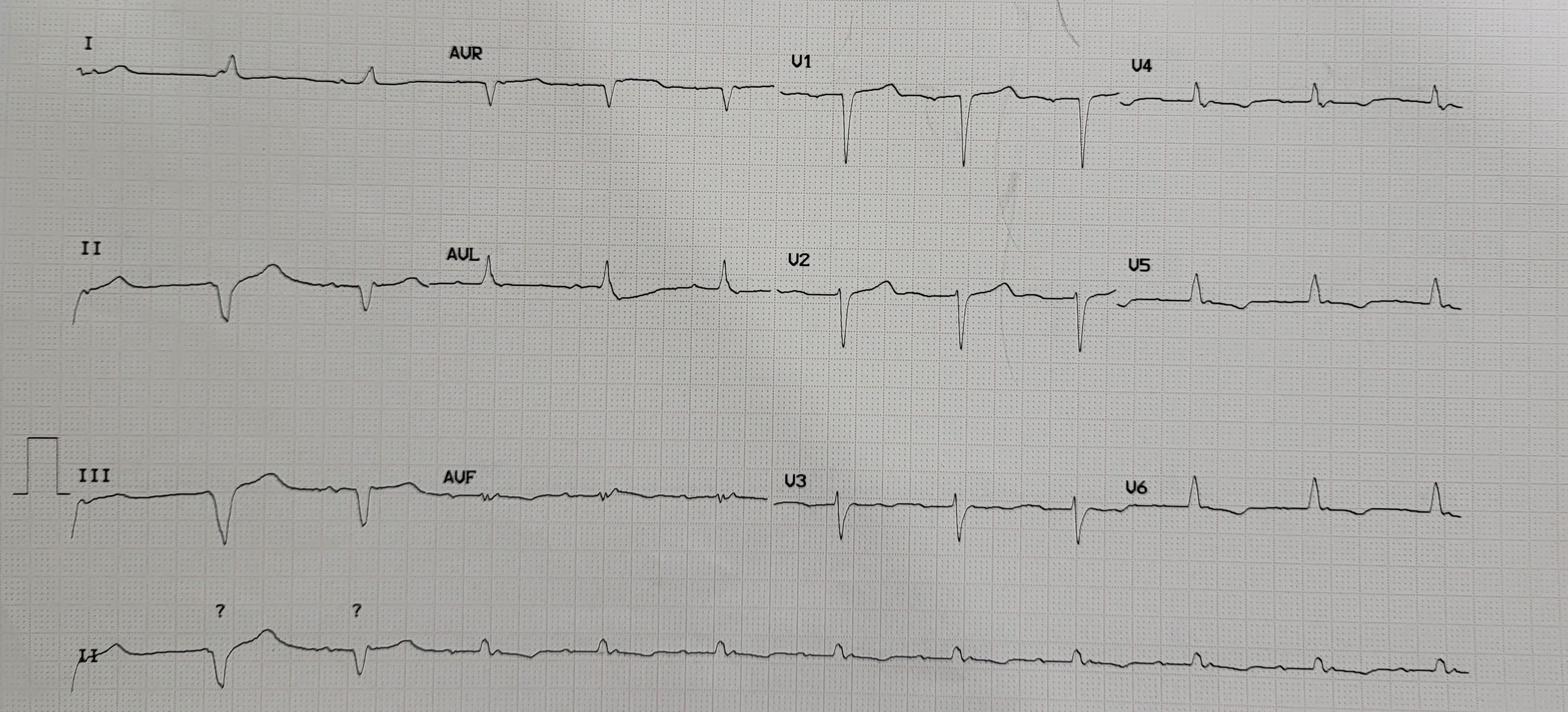
A 78-year-old male with a major complaint of worsening dyspnea since 3 months ago. He had CABG, PCI, and ICD implantation after suffering myocardial infarction 35 years prior. There was an elevated jugular vein pressure and systolic murmur. There was no rales or ankle edema found. He was still in class III NYHA classification even though he was already receiving optimal medical therapy. Electrocardiography (ECG) showed QRS duration of 100 ms, therefore he was not suitable for CRT-D.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Echocardiography showed dilated left atria (LA) and left ventricle (LV). The LV ejection fraction (EF) was 24%, global hypokinetic, grade II diastolic dysfunction. The Interatrial septum (IAS) and interventricular septum were intact without any sign of IAS hypertrophy. Both mild mitral regurgitation (MR) and tricuspid regurgitation (TR) were present. Tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion (TAPSE) was 1.5 cm. Implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) lead was seen in the RV.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Right heart catheterization (RHC) showed pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP) of 19 mmHg, systolic pulmonary artery (PA) pressure of 31 mmHg, systolic RV pressure of 31 mmHg, and systolic RA pressure of 12 mmHg. The patient was diagnosed with advanced heart failure on ICD, coronary artery disease (CAD) post CABG and PCI.
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
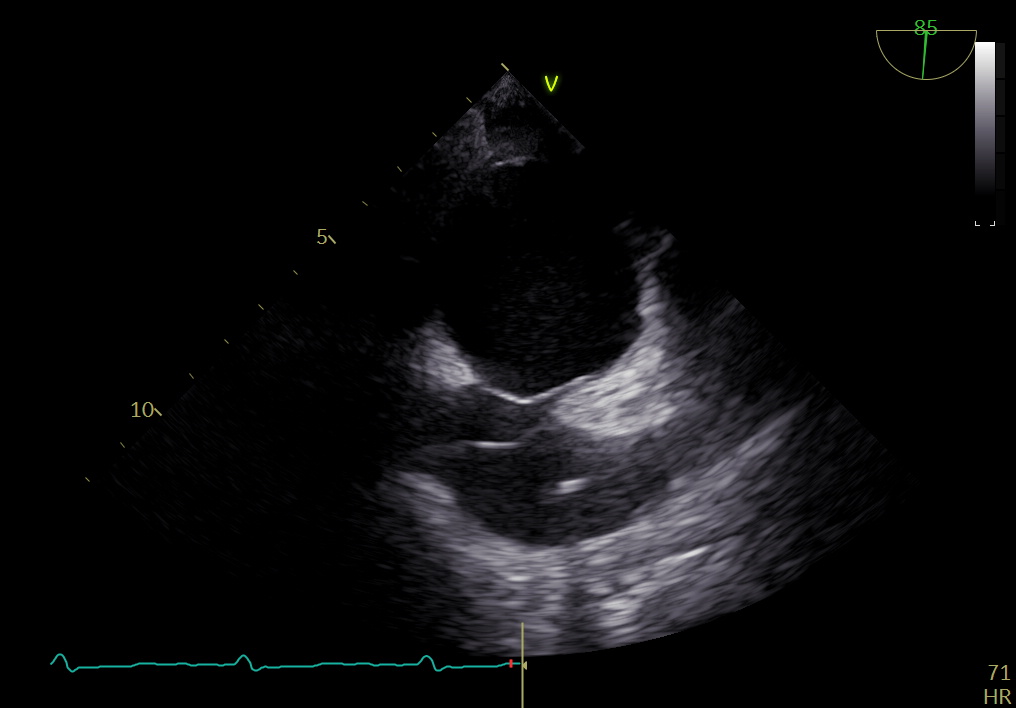
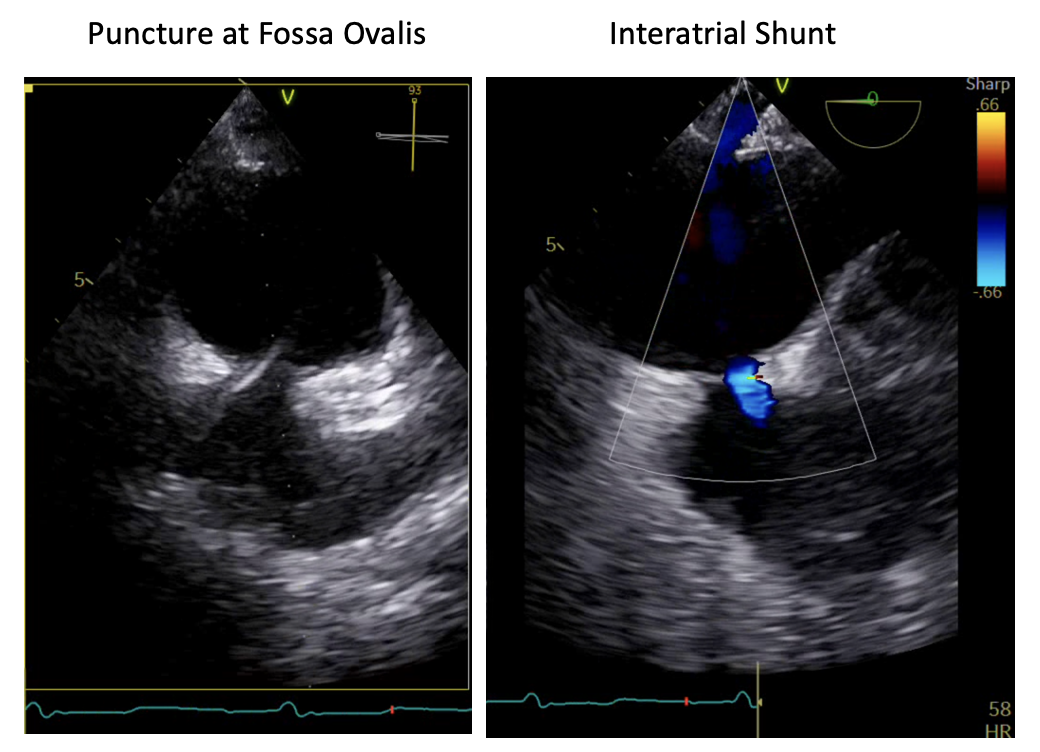
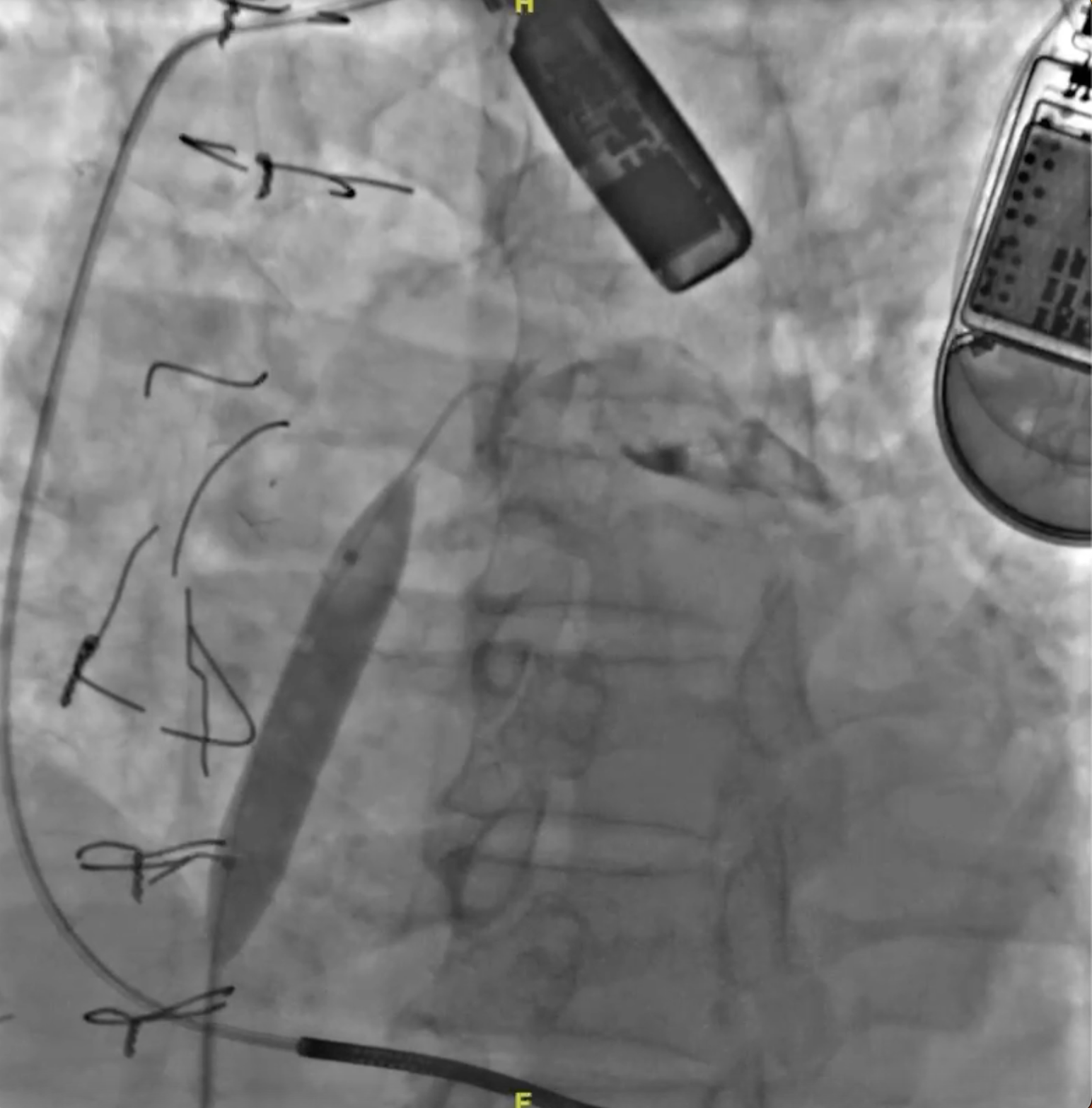
We intended to implant an atrial flow regulator device to create an interatrial shunt to reduce LA pressure and therefore relieve heart failure symptoms. The patient was sedated under general anaesthesia. Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) showed that the interatrial septal was intact, without any atrial septal defect (ASD) or patent foramen ovale (PFO). The septum secundum was thick (lipomatous septum) with a thickness of 11-12 mm. The fossa ovalis was small with the largest diameter of 13 mm. Due to the thick septum secundum, we decided not to perform AFR device implantation because the maximum device size was intended for interatrial septal thickness of 10 mm. Instead of AFR implantation, after careful consideration, we decided to create a small left-to-right interatrial shunting using balloon atrial septostomy (BAS) in this patient as an alternative treatment for heart failure. First, 8 Fr sheath was introduced via the right femoral vein under duplex ultrasound guidance. The transeptal puncture was performed with fluoroscopy and TEE guidance. The atrial septum at fossa ovalis was punctured with a BRK1 needle. The septum was dilated with a 10 mm balloon at 10 atm. Transesophageal echocardiography showed an iatrogenic ASD, left-to-right shunt with a diameter of 2-3 mm. One day after the procedure, he was discharged from the hospital. There was no change in his medication prescription.



Case Summary
Current guidelines do not include interatrial shunting as a part of standard therapy in advanced heart failure. Nevertheless, left-to-right interatrial shunting has been an emerging novel strategy in managing heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. In this patient, we performed balloon atrial septostomy, creating a small left-to-right atrial shunting that could limit increased LA pressure and PCWP during exertion. Further follow-up and evaluation are needed to ensure the treatment goal is achieved.


