Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-051
Drug Coated Balloon (DCB) Enhanced Modified Jailed Balloon Technique in a Double Bifurcation Lesion in the Setting of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction - A Novel Technique for Simplifying Complex Bifurcation Lesions
By Wee Meng Ng, Alimi Ahmad Hatib, Eran Sim, Fahim Jafary
Presenter
Wee Meng Ng
Authors
Wee Meng Ng1, Alimi Ahmad Hatib1, Eran Sim1, Fahim Jafary1
Affiliation
Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-051
Coronary - Complex PCI - Bifurcation
Drug Coated Balloon (DCB) Enhanced Modified Jailed Balloon Technique in a Double Bifurcation Lesion in the Setting of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction - A Novel Technique for Simplifying Complex Bifurcation Lesions
Wee Meng Ng1, Alimi Ahmad Hatib1, Eran Sim1, Fahim Jafary1
Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 59-year-old man with poorly controlled diabetes and peripheral vascular disease (PVD) presented with anterior ST-elevation myocardial infarction and ongoing chest pain. He was in cardiogenic shock and acute decompensated heart failure, requiring intravenous norepinephrine. The extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) team declined intervention due to his PVD. He was urgently taken to the cardiac catheterization lab for further management.
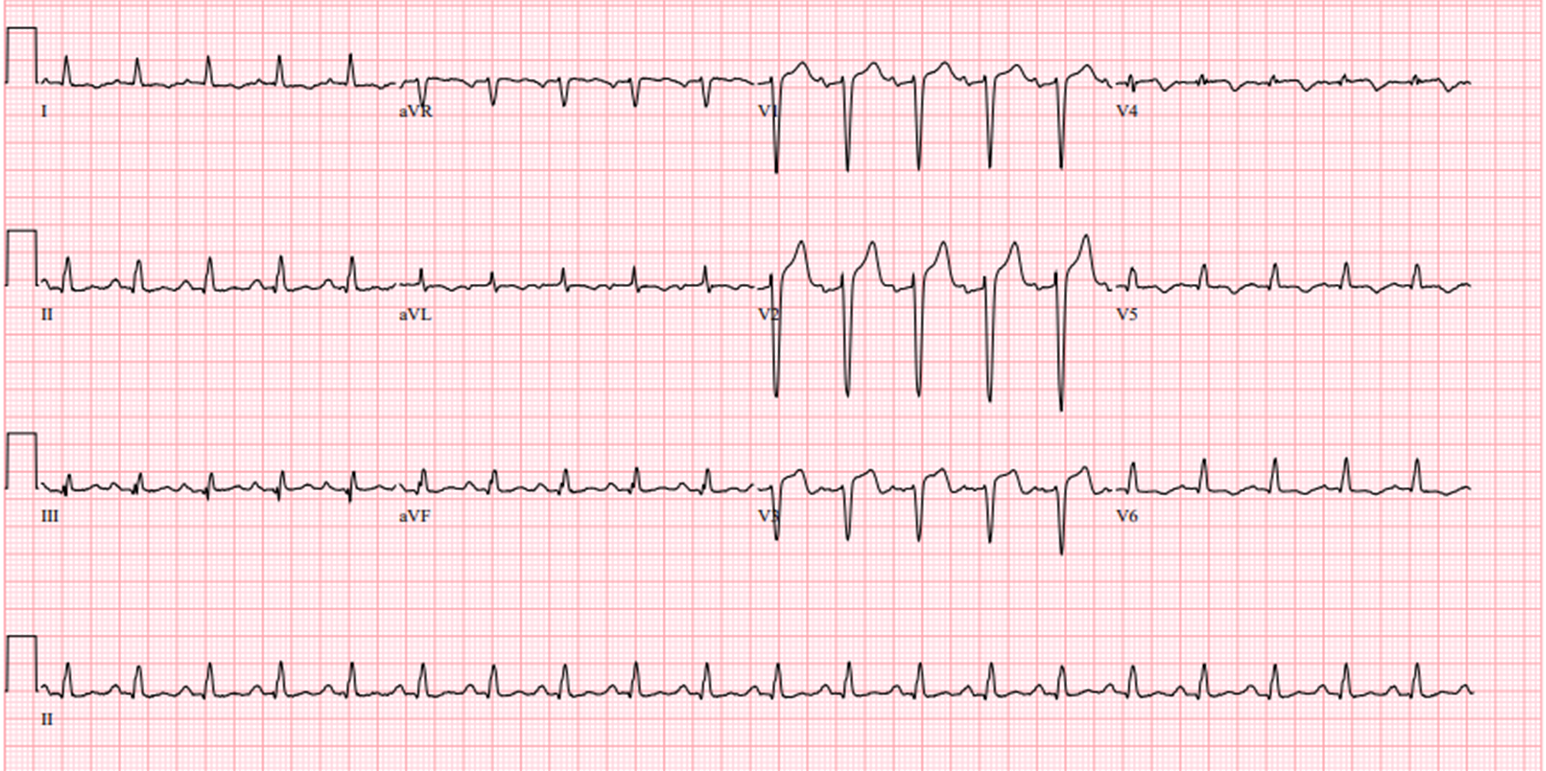

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed anterior ST-segment elevations. Chest XR showed bilateral infiltrates. Lactate levels were elevated, and arterial blood gases showed hypoxemia and severe metabolic acidosis, prompting intubation. Bedside echocardiogram showed a severely reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of 20%. An intra-aortic balloon pump (IABP) was inserted emergently via the right femoral artery. Clinical impression: anterior STEMI with cardiogenic shock and acute pulmonary edema

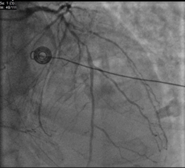
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Angiography revealed left main triple vessel disease, with severe LAD involvement at the LCX and D1 bifurcation, and a chronic total occlusion (CTO) of the RCA. The LCX had severe ostio-proximal disease.
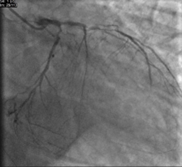



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
We aimed for revascularization of the LM-LAD using a modified approach. Despite initially considering a double-stent strategy, we opted for a drug-coated balloon (DCB) enhanced modified jailed balloon (JB) technique to maintain patency of the side branches (LCX and D1).
First, LAD and D1 were predilated. After adequate modification, the D1 was treated with a 2.0 DCB. A 3.0 drug-eluting stent (DES) was deployed across the mid-LAD with a 2.0 compliant balloon as the JB across the D1 ostium. Following inflation of the JB, the LAD stent was deployed, and simultaneous deflation of both balloons was performed. Patency of both main and side branches was confirmed.
We applied a similar technique to the LM-LAD/LCX bifurcation. The ostio-proximal LCX was treated with a 3.0 DCB, followed by deployment of a 3.5 stent from the LM to the LAD. A 3.0 JB was used across the LCX ostium, and LAD post-dilation was achieved with a 3.5 NC balloon. Final proximal optimization with a 4.0 NC balloon ensured good stent expansion, carina maintenance, and side branch patency.
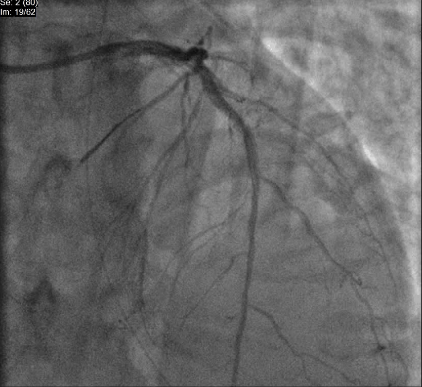
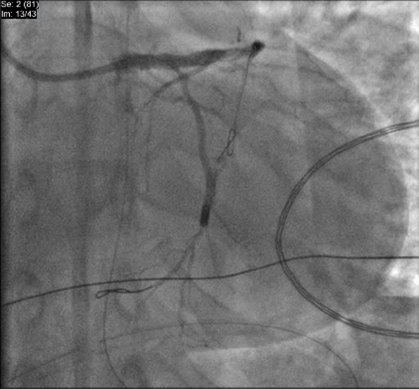
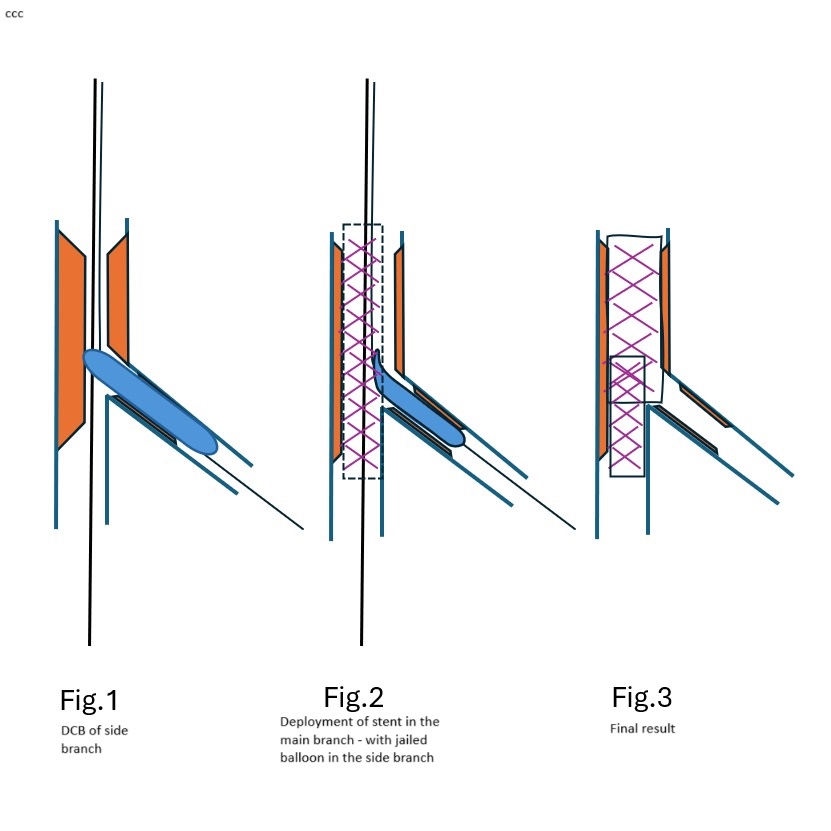
Case Summary
The DCB-enhanced modified jailed balloon technique is a novel, feasible strategy for bifurcation lesions, preserving side branch patency without an upfront two-stent approach. This method reduces procedural time, simplifies the intervention, and minimizes stent material use, making it advantageous in critically ill patients. Further studies with long-term follow-up are needed to validate these preliminary findings.


