Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-122
Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Right Coronary Artery Disease With Spontaneous Dissection
By Yu-Tse Sheih
Presenter
Yu-Tse Sheih
Authors
Yu-Tse Sheih1
Affiliation
Tri-Service General Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-122
Coronary - Complex PCI - Long Lesion
Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction and Right Coronary Artery Disease With Spontaneous Dissection
Yu-Tse Sheih1
Tri-Service General Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 56-year-old male patient presented with exertional chest tightness and accompanying cold sweating that had persisted for one day, starting on September 1, 2024. Past medical history includes hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and type 2 diabetes mellitus.




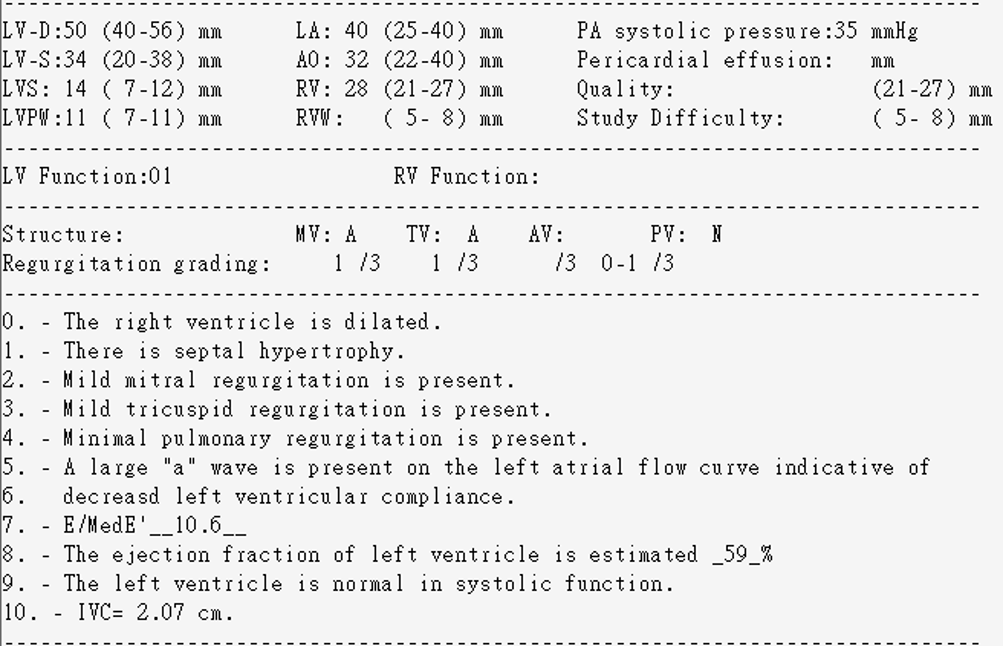
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
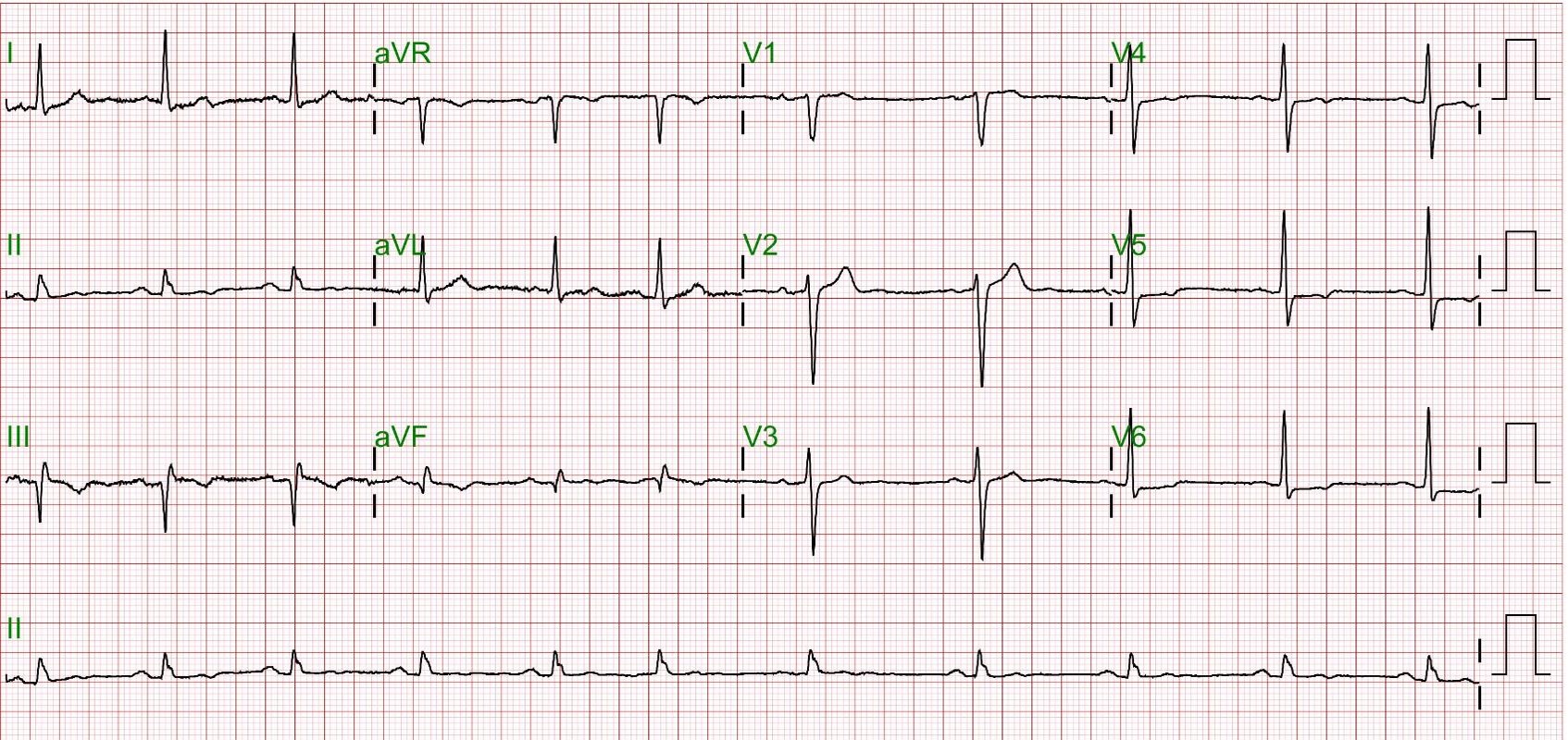
Initial clinical evaluation revealed blood pressure at 105/66 mmHg, heart rate at 82 beats per minute, and oxygen saturation at 97% on room air. The patient had significantly elevated troponin I levels at 17,113 ng/mL, and an ECG showed sinus rhythm with atrial premature complexes (APCs) and a Q wave in leads III/aVF.


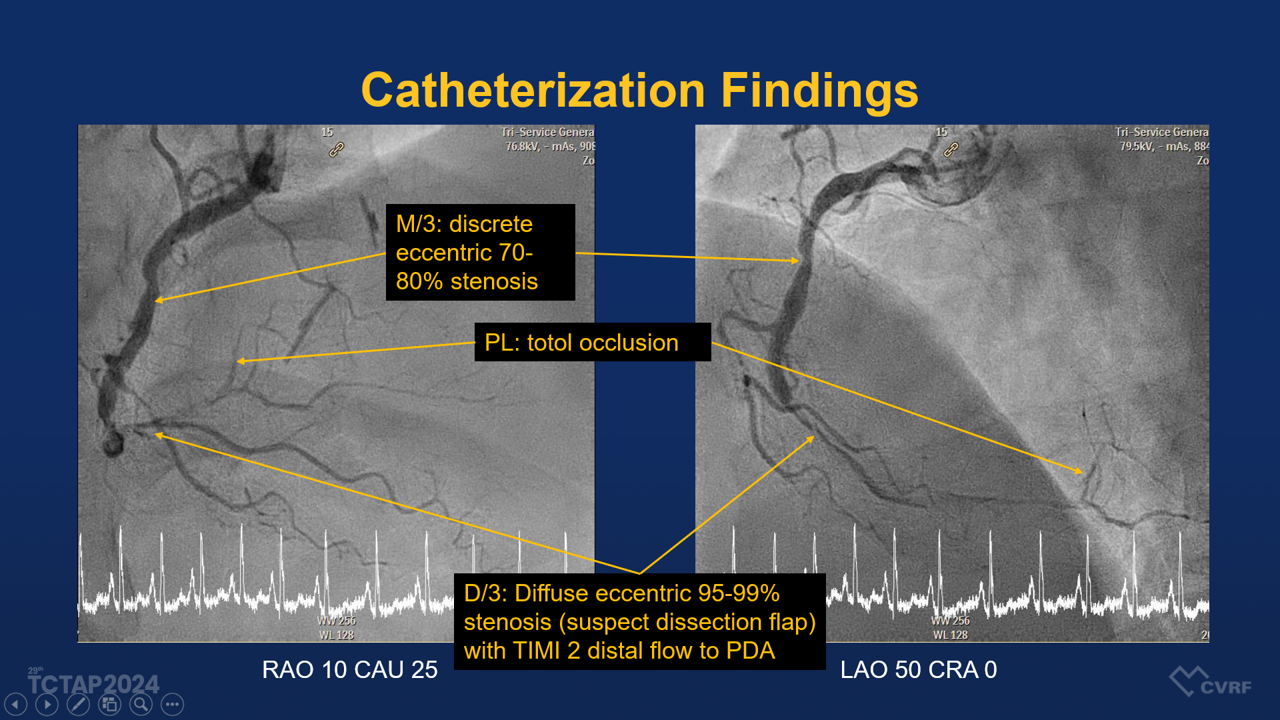
Relevant Catheterization Findings
The patient was diagnosed with a non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (Non-STEMI) and right coronary artery (RCA) disease, complicated by a suspected spontaneous coronary artery dissection (SCAD).
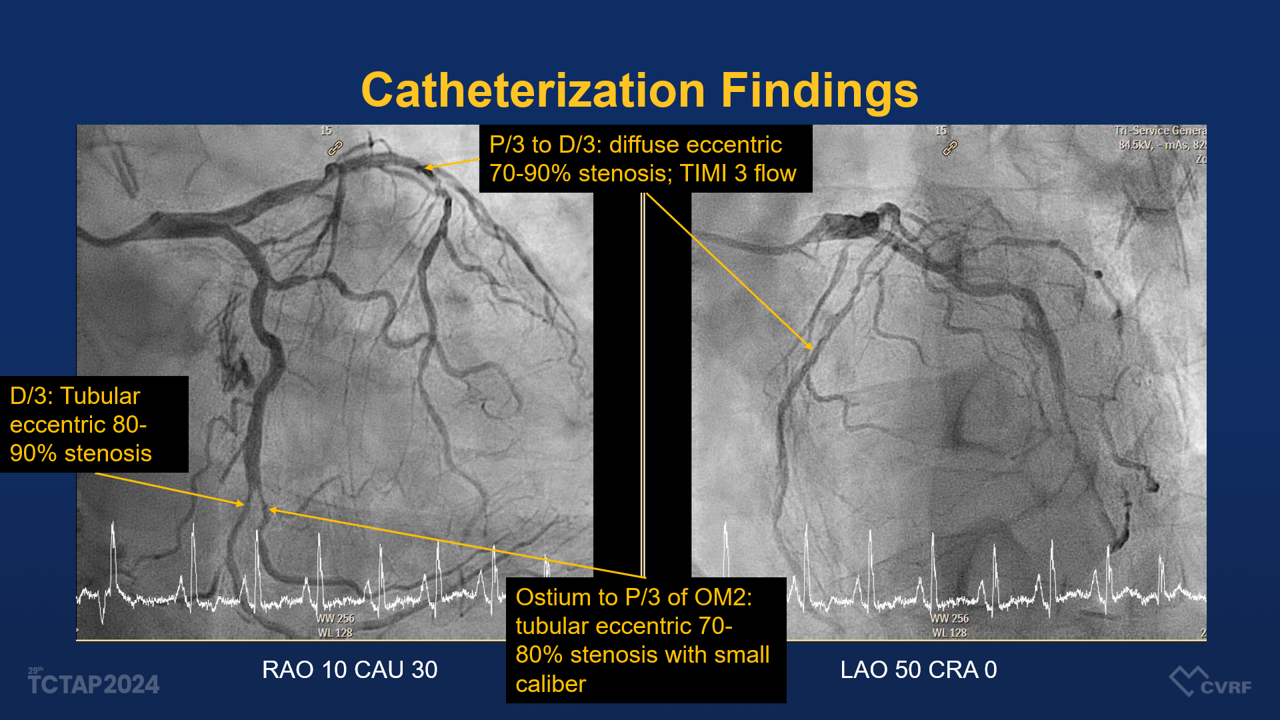


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
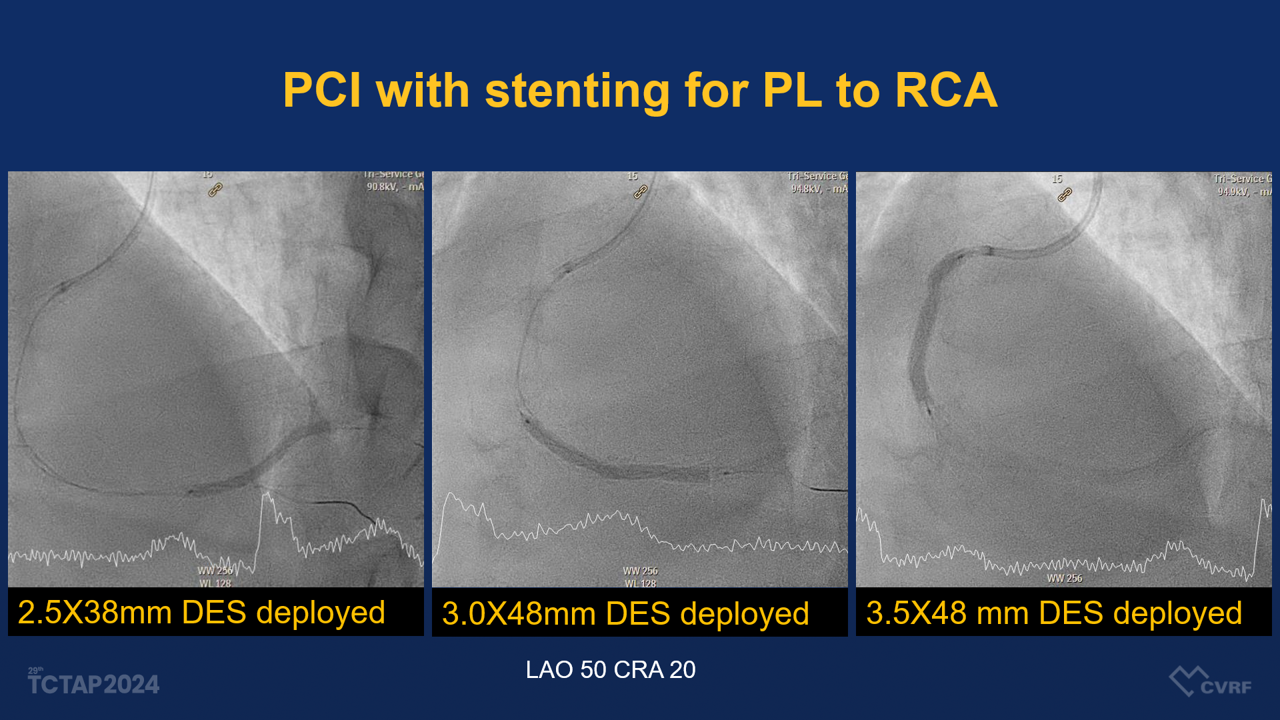
The patient underwent coronary angiography, which demonstrated a diffuse eccentric stenosis of 95-99% in the distal RCA, suspected of having a dissection flap, with TIMI grade 2 distal flow to the posterior descending artery (PDA). A percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) was performed, involving stenting from the middle RCA to the proximal PL (posterolateral branch) using various drug-eluting stents (DES) and balloons, including:
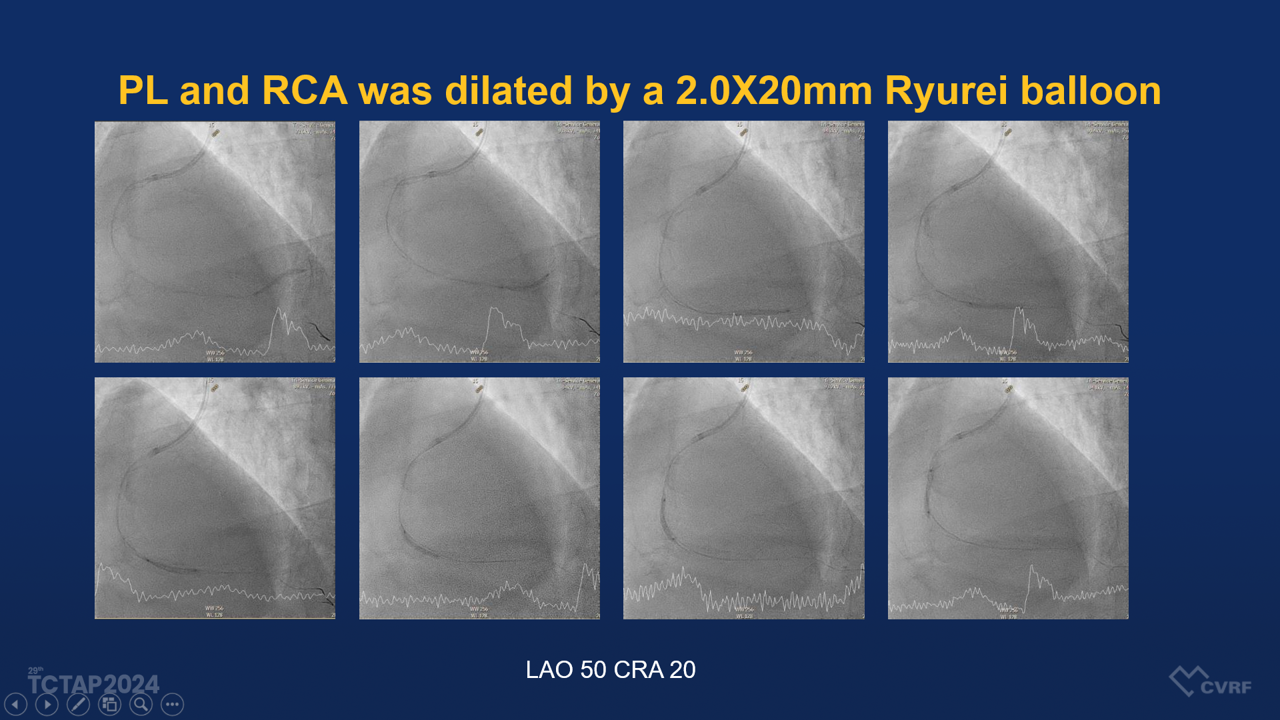
- Guiding catheter: SAL-1 6Fr
- Guide wires: Sion Black and Sion Blue
- Balloon dilation: Ryurei and Accuforce balloons in various sizes
- Stents: 2.5x38mm Onyx, 3.0x48mm Synergy, and 3.5x48mm Xience Xpedition stents


Case Summary
This 56-year-old male presenting with Non-STEMI and spontaneous coronary artery dissection of the distal RCA, with TIMI grade 2 distal flow to the PDA. The patient underwent a challenging PCI that required careful stent placement and management of the dissected lesion. PCI is necessary if the patient’s condition worsens or deteriorating TIMI flow. The use of drug-eluting stents is crucial in stabilizing the dissection, yet the procedure carries inherent risks, such as additional dissection or complications. Success in these procedures is dependent on precise intravascular imaging and meticulous stent deployment to prevent further vessel damage.


