Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-162
Complication Management: Cover Stent as an Effective Option for Coronary Pseudoaneurysm
By Yu-Ching Chien, Yen-Lien Chou
Presenter
Yu-Ching Chien
Authors
Yu-Ching Chien1, Yen-Lien Chou1
Affiliation
Tri-Service General Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-162
Coronary - Complication Management
Complication Management: Cover Stent as an Effective Option for Coronary Pseudoaneurysm
Yu-Ching Chien1, Yen-Lien Chou1
Tri-Service General Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 58-year-old male with a known history of coronary artery disease (CAD) involving three-vessel disease underwent a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with 6 stents in the right coronary artery, 1 stent in the left anterior descending artery, and 1 stent in the left circumflex artery. The result of his last cardiac catheterization final angiography showed TIMI 3 flow without complications. More than 4 months after the procedure, he presented with intermittent chest pain.

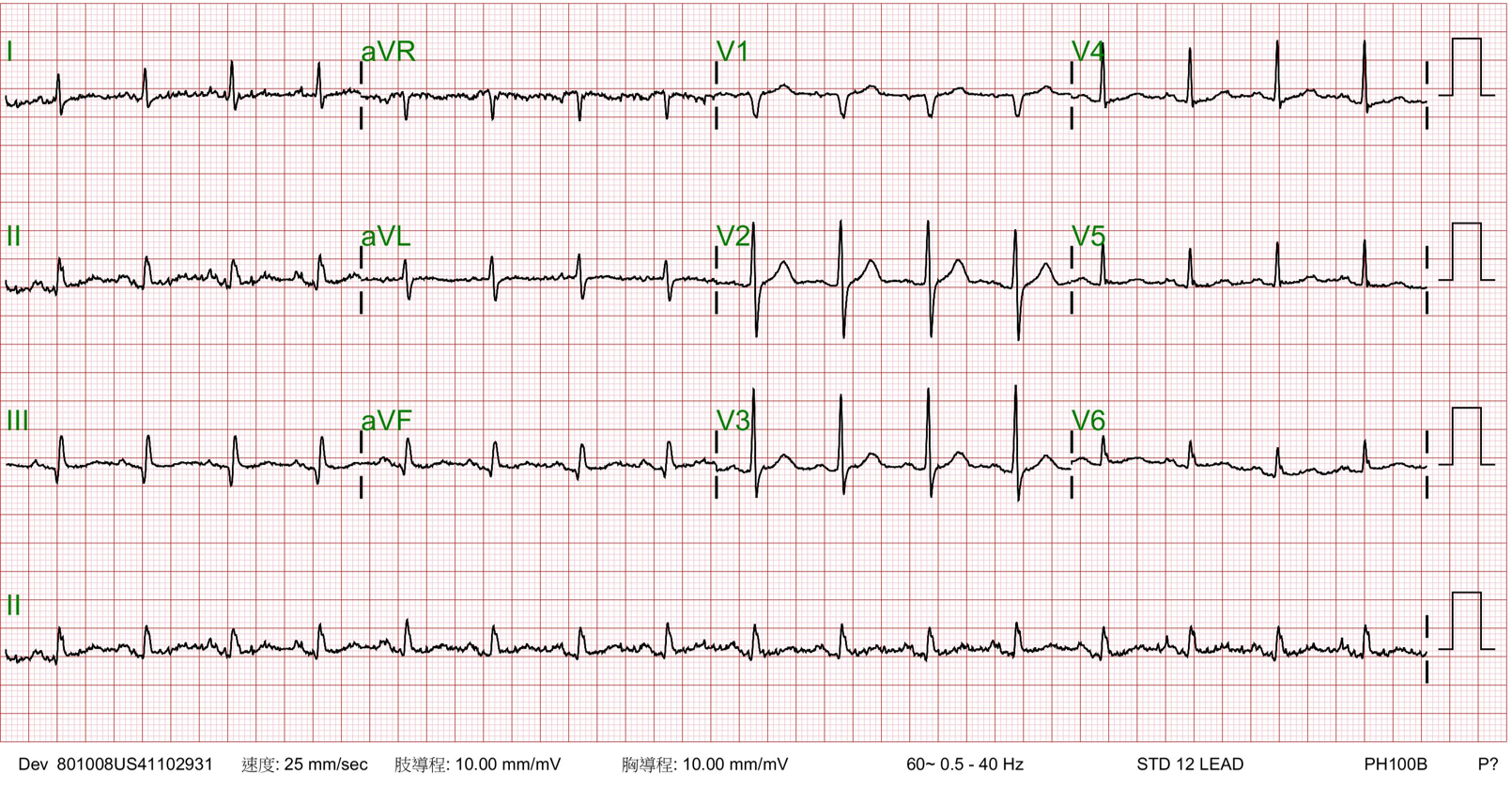
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Echocardiography showed normal ejection fraction. His ECG showed Sinus rhythm and Q wave in inferior leads.

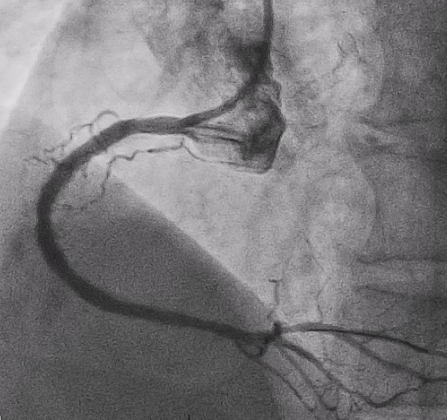
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Subsequent coronary angiography identified a pseudoaneurysm in the right coronary artery (RCA), without any evidence of extravasation.
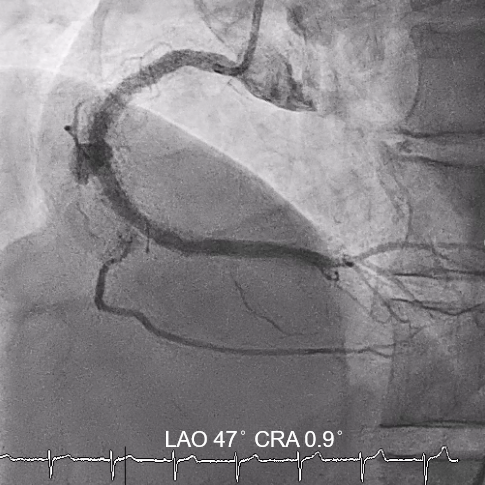
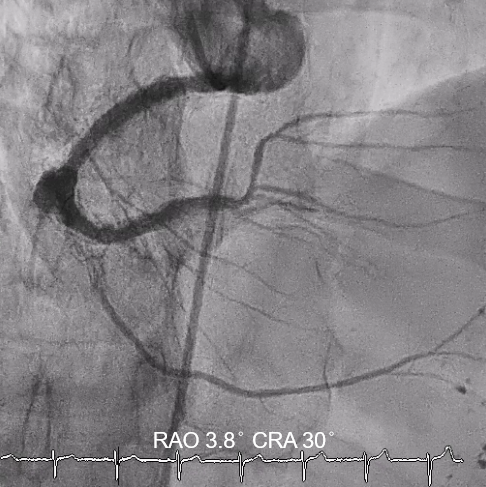


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
In this coronary catheterization procedure, a guidewire was used to cross the lesion and advanced to the posterolateral branch (PL). An intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) examination was conducted, revealing a pseudoaneurysm in the mid-right coronary artery (m-RCA). To cover the pseudoaneurysm, a 3.5 x 16 mm cover stent was deployed in the m-RCA at a pressure of 16-18 atmospheres for 15-20 seconds, repeated twice. Subsequently, the cover stent was further post-dilated with a 3.75 x 15 mm non-compliance balloon at 18-20 atmospheres for 10 seconds, also performed twice. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) was then performed, showing a post-dilation stent MSA of 7.40 mm² with good apposition and expansion. The cover stent was additionally dilated with a 4.0 x 30 mm drug-eluting balloon (DEB) at 6 atmospheres for 60 seconds. The final angiography demonstrated TIMI grade 3 flow without any extravasation.
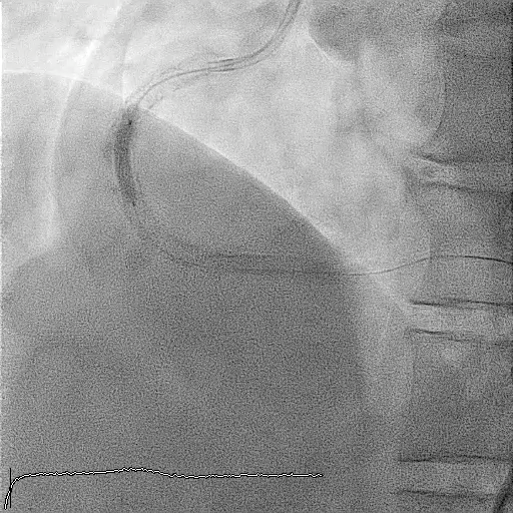
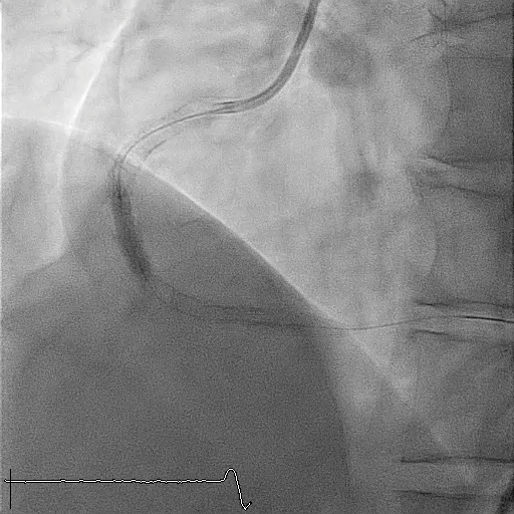
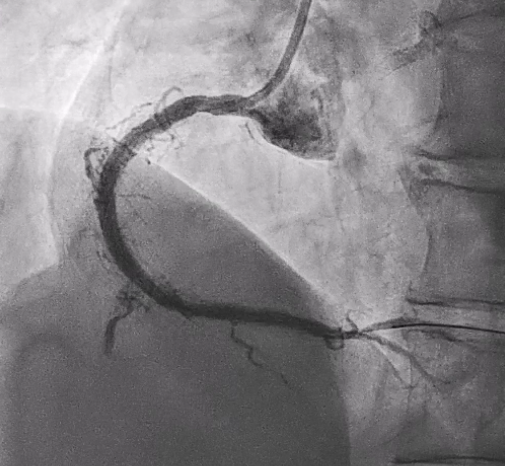



Case Summary
Post-intervention angiography demonstrated improved blood flow in the affected artery. The RCA pseudoaneurysm was effectively sealed, and subsequent imaging confirmed appropriate stent placement. The use of IVUS and OCT allowed for optimal sizing and placement, leading to a successful outcome.
This case demonstrates that cover stents are a valuable tool in treating coronary pseudoaneurysms, with advanced imaging techniques improving procedural outcomes. Optimal stent deployment is critical in minimizing complications and ensuring long-term vessel patency.
This case demonstrates that cover stents are a valuable tool in treating coronary pseudoaneurysms, with advanced imaging techniques improving procedural outcomes. Optimal stent deployment is critical in minimizing complications and ensuring long-term vessel patency.


