Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-174
Empowering High-Risk Revascularization: Impella-Assisted Approach for Ostial Left Main Lesion and Left Anterior Descending Artery Chronic Total Occlusion in Severe Left Ventricular Dysfunction
By Yi-Hsin Hung, Chih-Fan Yeh, Yi-Lwun Ho, Hsien-Li Ko
Presenter
Yi-Hsin Hung
Authors
Yi-Hsin Hung1, Chih-Fan Yeh1, Yi-Lwun Ho1, Hsien-Li Ko1
Affiliation
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-174
Coronary - Hemodynamic Support
Empowering High-Risk Revascularization: Impella-Assisted Approach for Ostial Left Main Lesion and Left Anterior Descending Artery Chronic Total Occlusion in Severe Left Ventricular Dysfunction
Yi-Hsin Hung1, Chih-Fan Yeh1, Yi-Lwun Ho1, Hsien-Li Ko1
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 46-year-old man with hypertension and dyslipidemia presented to the emergency room with a one-month history of worsening exertional dyspnea, orthopnea, and leg edema. He was hemodynamically stable with 98% oxygen saturation on ambient air. Physical examination revealed jugular vein engorgement, bilateral basal crackles, and 2+ pitting edema bilaterally.
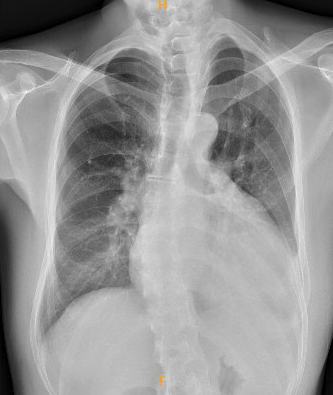

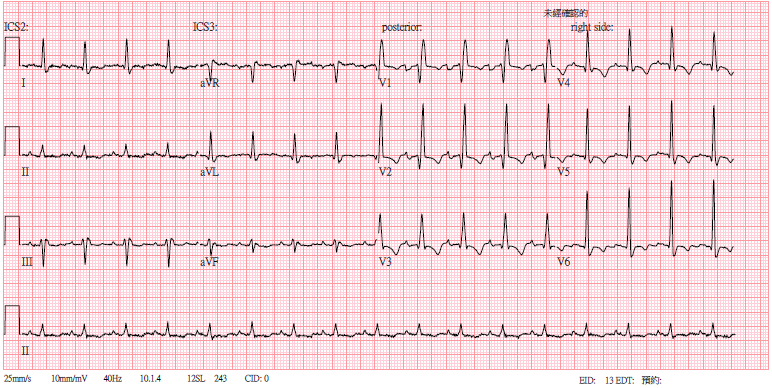
Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Electrocardiogram revealed a right bundle branch block and T-wave inversion in the precordial leads, consistent with the patient’s baseline findings. Echocardiography showed left ventricular ejection fraction of 24%, down from 50% a year ago. Myocardial perfusion imaging indicated resting ischemia with improved redistributive uptake in mid-anterior and inferoseptal wall.
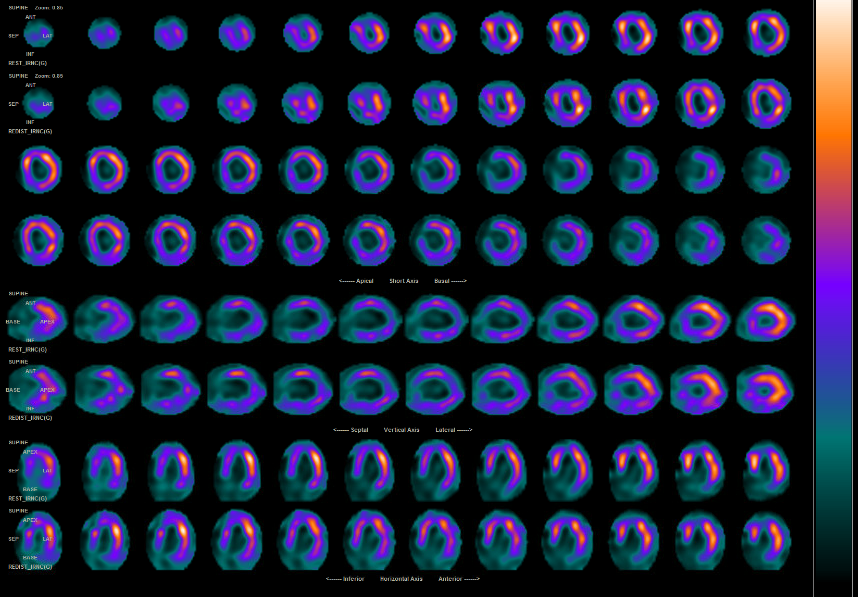


Relevant Catheterization Findings
Coronary angiography revealed a 70% stenosis of the left main (LM) ostium and a stumpless chronic total occlusion (CTO) of the proximal left anterior descending artery (LAD) with collateral supply from the intermediate ramus (IR). The left circumflex artery and right coronary artery were patent. The Syntax score was 32.5. The patient declined coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG).
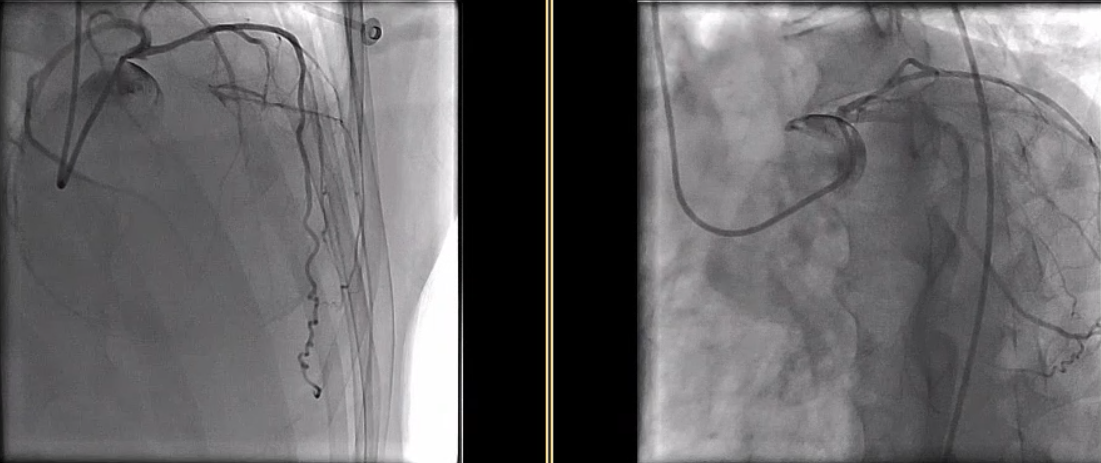
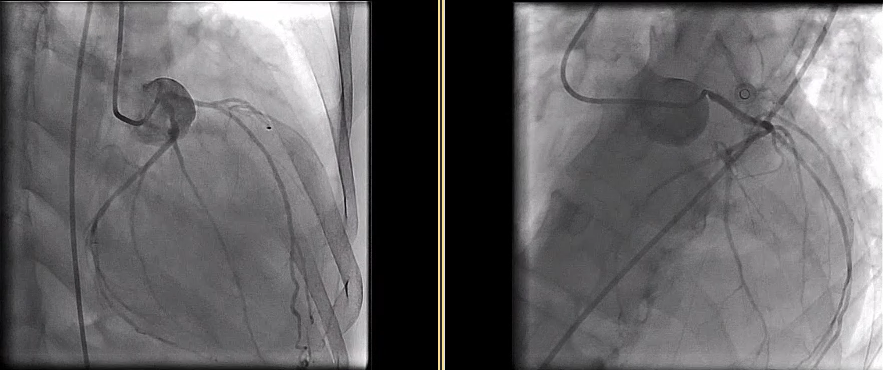



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
A complex high-risk indicated percutaneous coronary intervention (CHIP-PCI) targeting ostial LM and LAD CTO lesions under mechanical circulatory support was planned, with a BCIS-CHIP score of 7. The Impella CP was set up via right femoral artery (RFA). We initially attempted antegrade wiring with ULTIMATE 3 and GAIA II, supported by a Corsair microcatheter. However, this was unsuccessful with ULTIMATE 3 remaining in a false lumen. Additionally, contralateral injection from the IR did not provide sufficient flow to visualize LAD, leading us to switch to retrograde approach. We navigated SOUH 03 through IR collateral and advanced a 150cm Finecross microcatheter for a clear contralateral injection. Subsequently, SOUH 03 was successfully retrograde wired to mid-LAD.
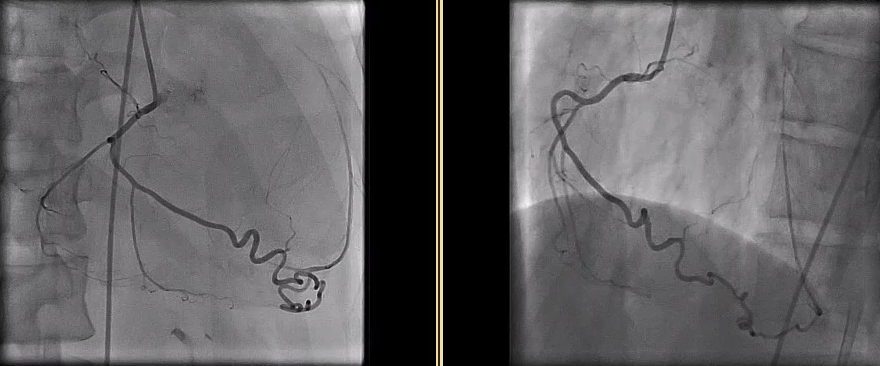
Due to solid plaques in proximal LAD (pLAD) and difficulty advancing through the true lumen, we employed reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde tracking (rev-CART) technique carefully without injuring LM bifurcation, followed by externalization. We assessed LM-LAD with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). A 3.0x38mm drug-eluting stent was deployed from ostial LM to pLAD using Szabo technique, followed by post-dilation based on IVUS findings. Final angiography confirmed satisfactory flow. Throughout the procedure, the patient remained hemodynamically stable. The Impella CP was smoothly removed. The access site was closed with pre-embedded ProGlide, followed by Angioseal.
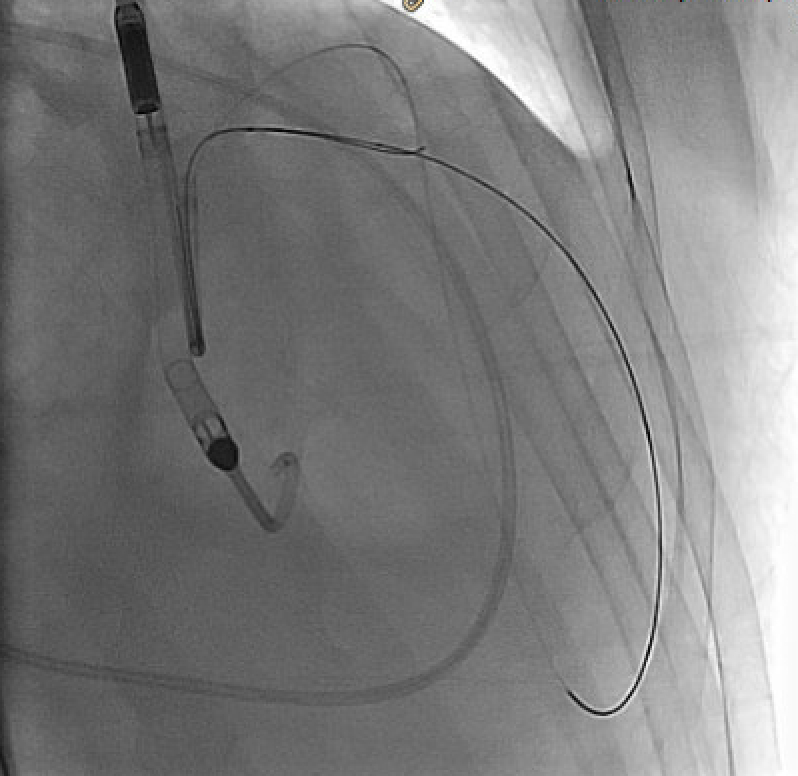
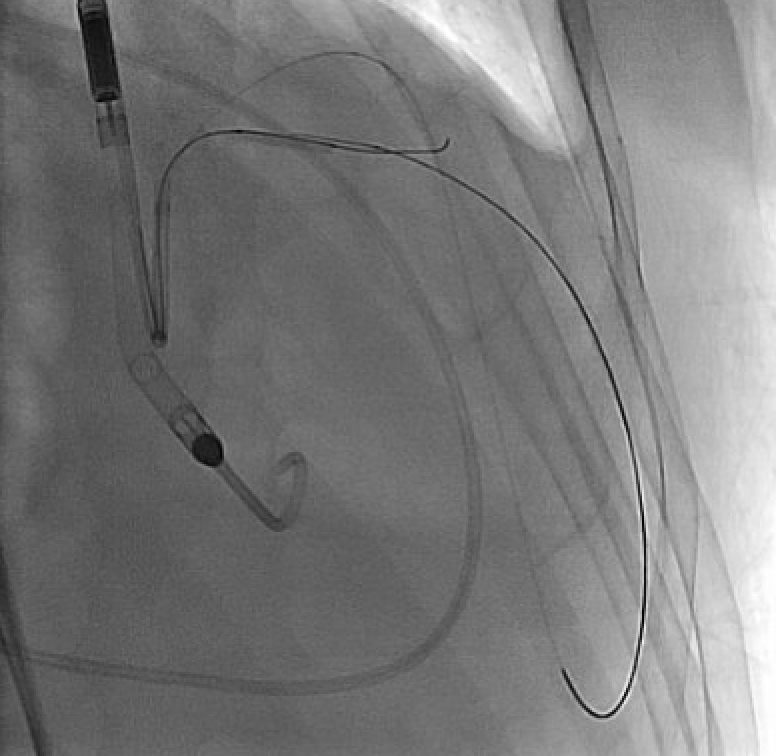
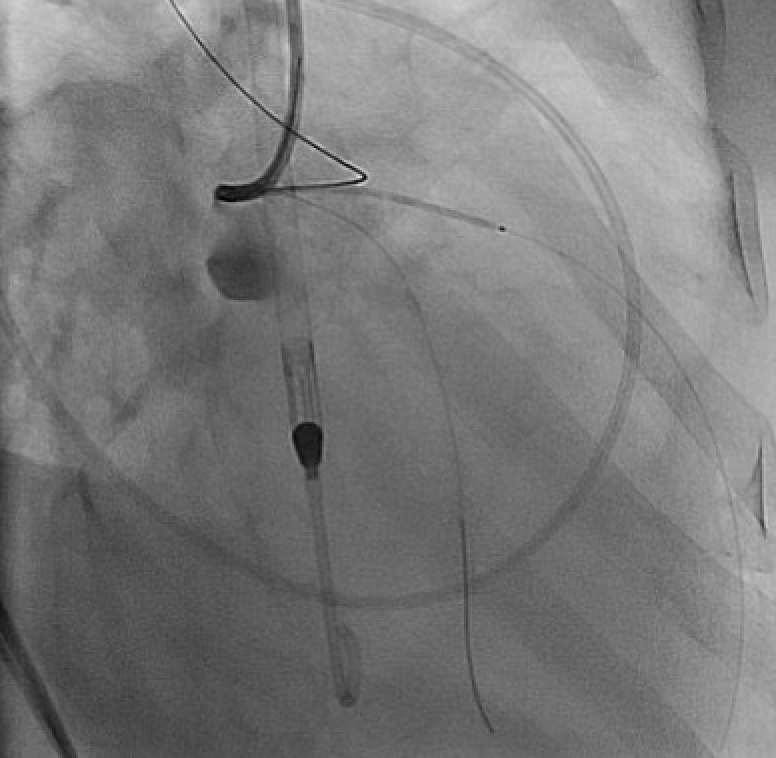
Due to solid plaques in proximal LAD (pLAD) and difficulty advancing through the true lumen, we employed reverse controlled antegrade and retrograde tracking (rev-CART) technique carefully without injuring LM bifurcation, followed by externalization. We assessed LM-LAD with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS). A 3.0x38mm drug-eluting stent was deployed from ostial LM to pLAD using Szabo technique, followed by post-dilation based on IVUS findings. Final angiography confirmed satisfactory flow. Throughout the procedure, the patient remained hemodynamically stable. The Impella CP was smoothly removed. The access site was closed with pre-embedded ProGlide, followed by Angioseal.



Case Summary
With meticulous procedural planning, the Impella device provides a stable environment for CHIP-PCI targeting ostial LM and proximal LAD CTO lesions in a patient with severe left ventricular dysfunction. Retrograde wiring followed by the rev-CART technique inside CTO body enabled successful revascularization of the proximal LAD CTO lesion without compromising the LM bifurcation. Intravascular ultrasound guided the procedure. Then, Szabo technique effectively managed the ostial LM lesion.


