Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-215
Advanced Transeptal Optimization for Mitral Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Repair (M-TEER) in Patients With Post Atrial Septal Defect Closure Device: Case Report
By Varistha Phetcharakupt, Krissada Meemook, Tawai Ngernsrirakul, Thinnakrit Sasiprapha, Surakiat Leelasithorn
Presenter
Varistha Phetcharakupt
Authors
Varistha Phetcharakupt1, Krissada Meemook1, Tawai Ngernsrirakul1, Thinnakrit Sasiprapha1, Surakiat Leelasithorn1
Affiliation
Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-215
Structural - Mitral Valve Intervention - TEER
Advanced Transeptal Optimization for Mitral Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Repair (M-TEER) in Patients With Post Atrial Septal Defect Closure Device: Case Report
Varistha Phetcharakupt1, Krissada Meemook1, Tawai Ngernsrirakul1, Thinnakrit Sasiprapha1, Surakiat Leelasithorn1
Ramathibodi Hospital, Thailand1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
An 84-year-old female with symptomatic severe MR presented with dyspnea and heart failure, classified as NYHA class III. She had past medical history of AF and ASD which underwent transcutaneous ASD device closure eight years prior (26 mm Amplatzer closure device). Despite optimized medication, patient still had symptom.
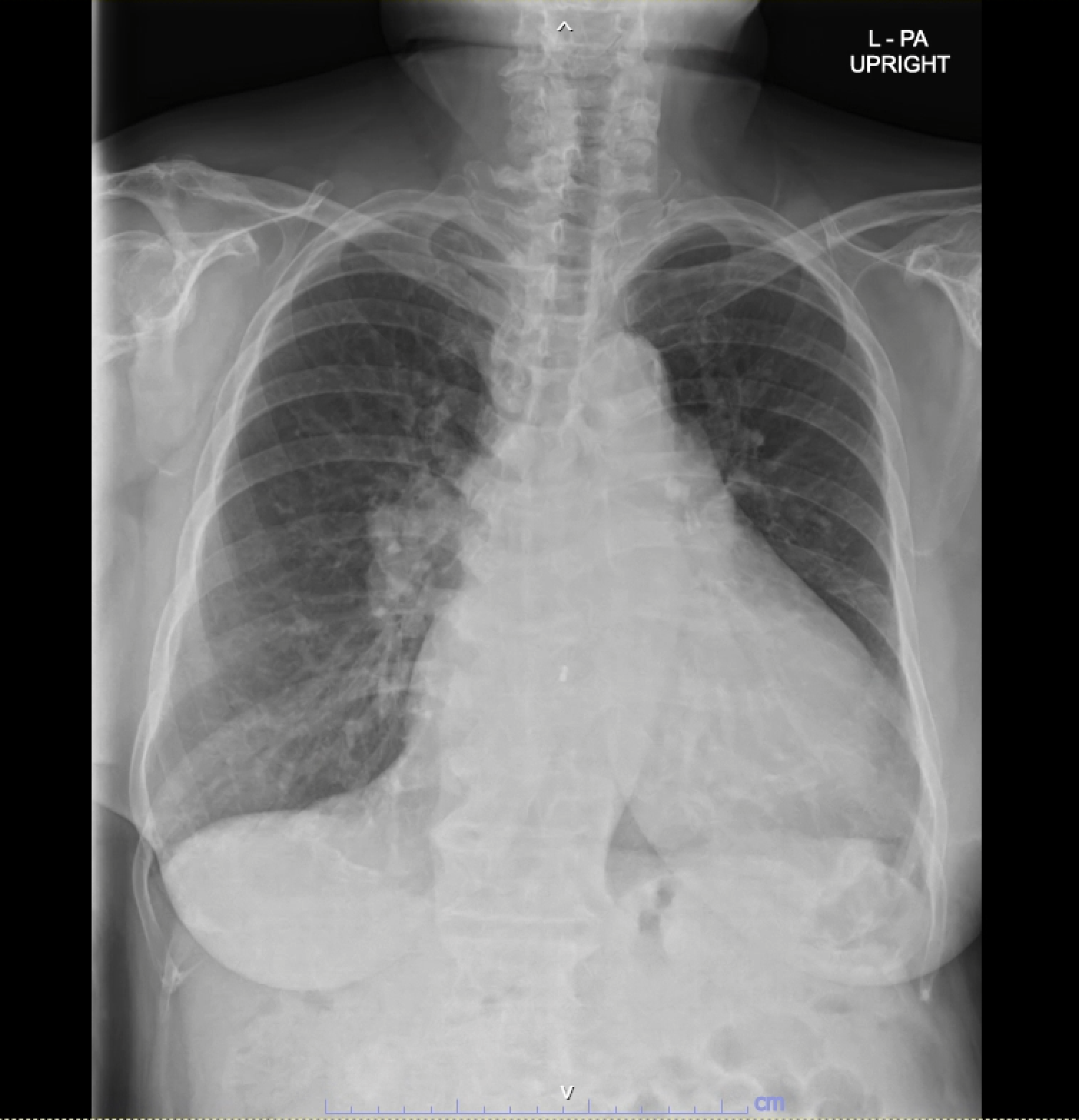
Due to high risk for surgery (Euroscore II was 3.8 % and STS score was 8.0 %),our interdisciplinary heart team decided to perform M-TEER.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
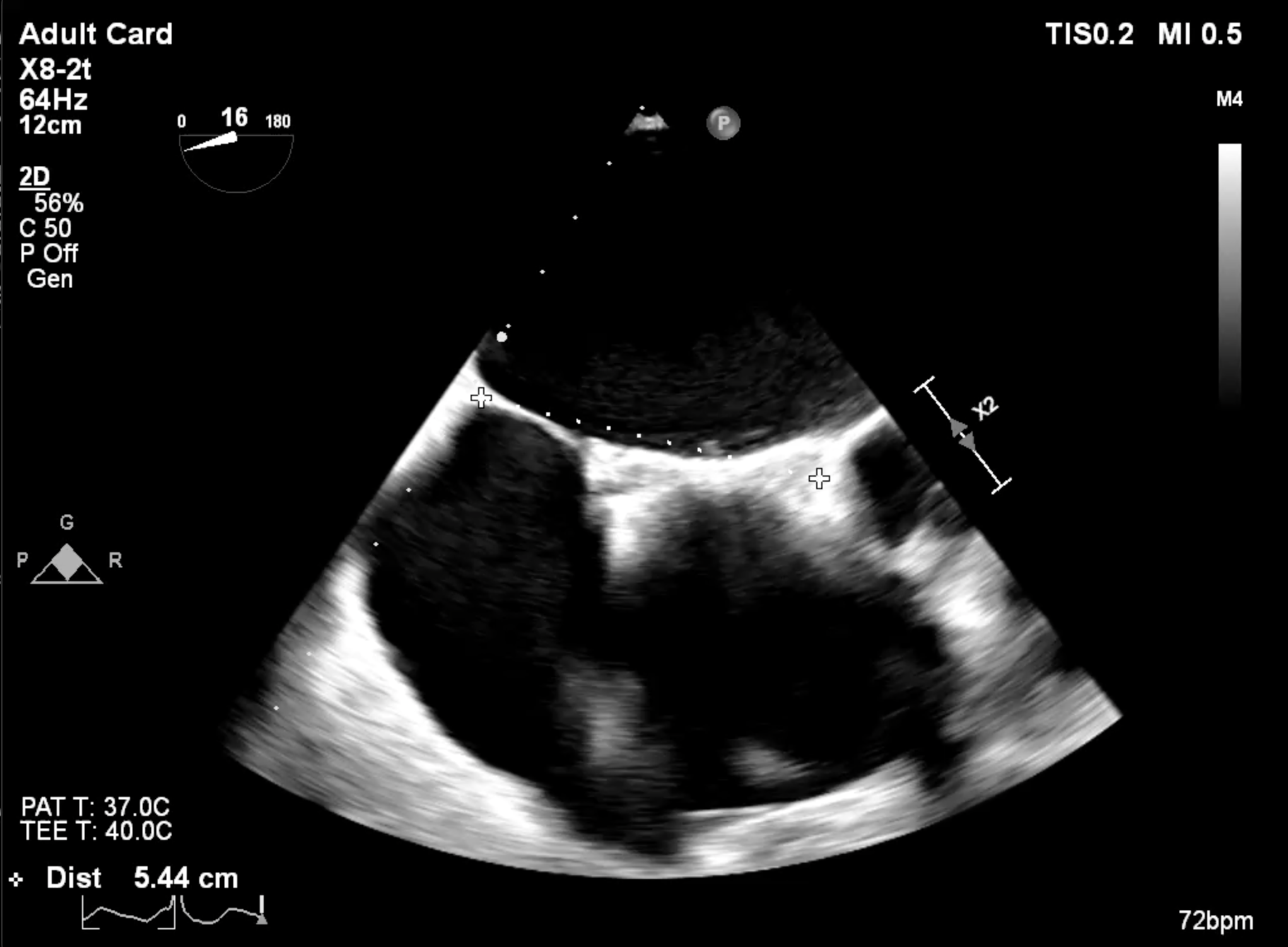
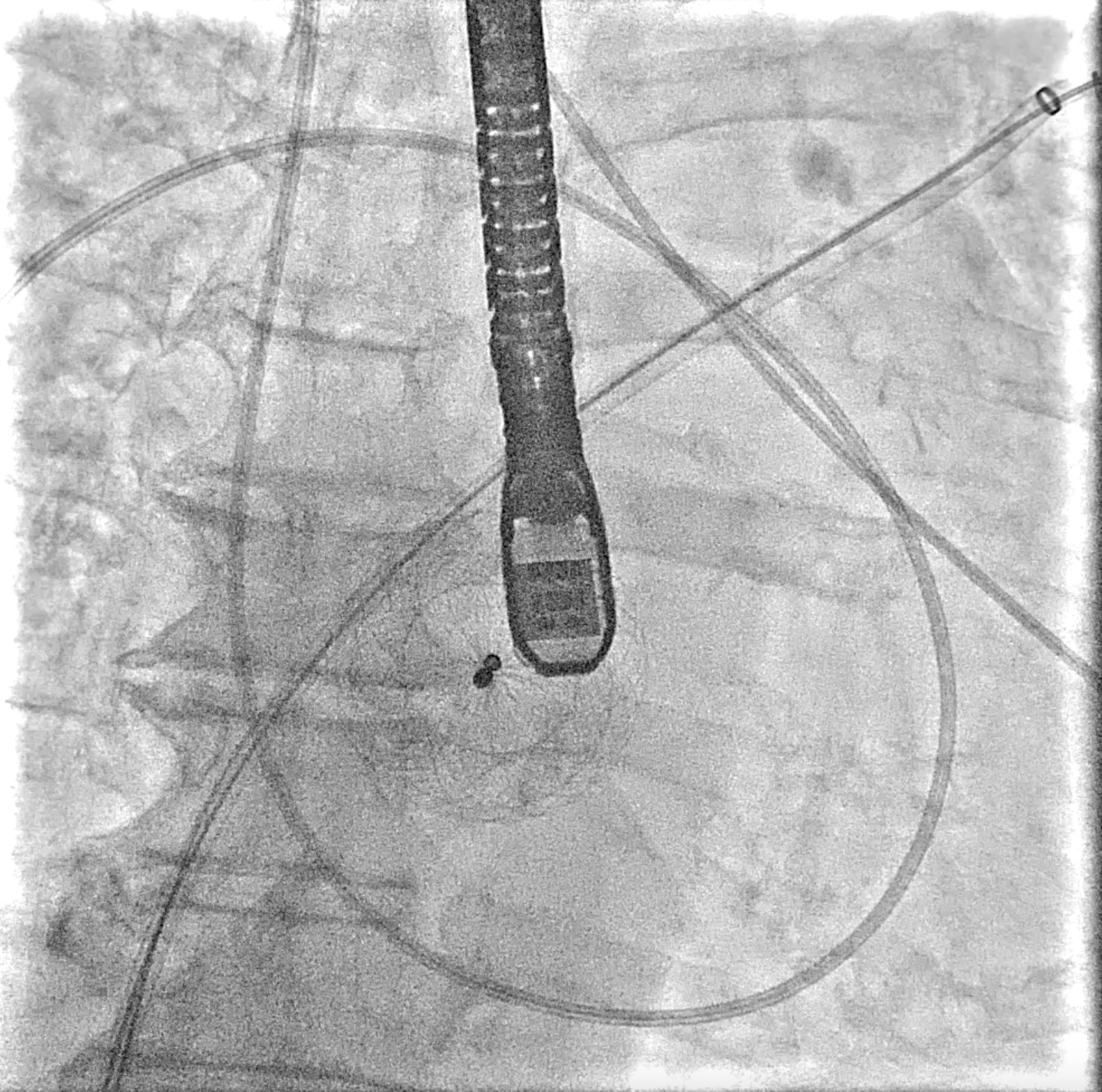
Echocardiography : showed severe MR from flail P1 segment adjacent to lateral commissure with rupture cordae tendineae, P1 length was 7.7 mm. The ASD device was well seated and no color Doppler flow across the device. The interatrial septum had no space of anterior rim and had space at posterior rim apart from the ASD deviced for 5 mm for septal puncture.
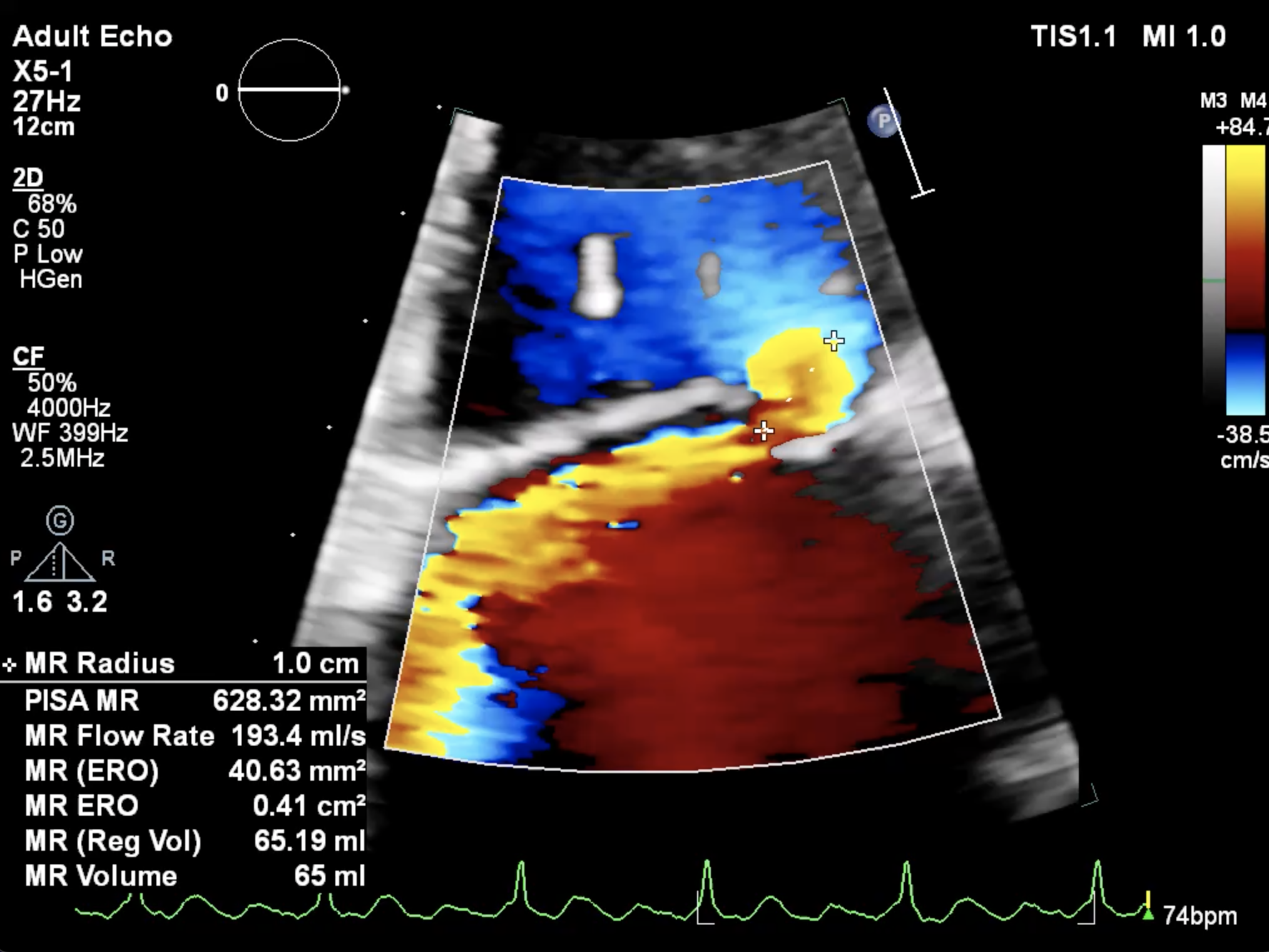
Hemodynamic parameter showed post capillary pulmonary hypertension (MPAP 29 mmHg, PCWP 21 mmHg).


Relevant Catheterization Findings
Interventional Management
Procedural Step
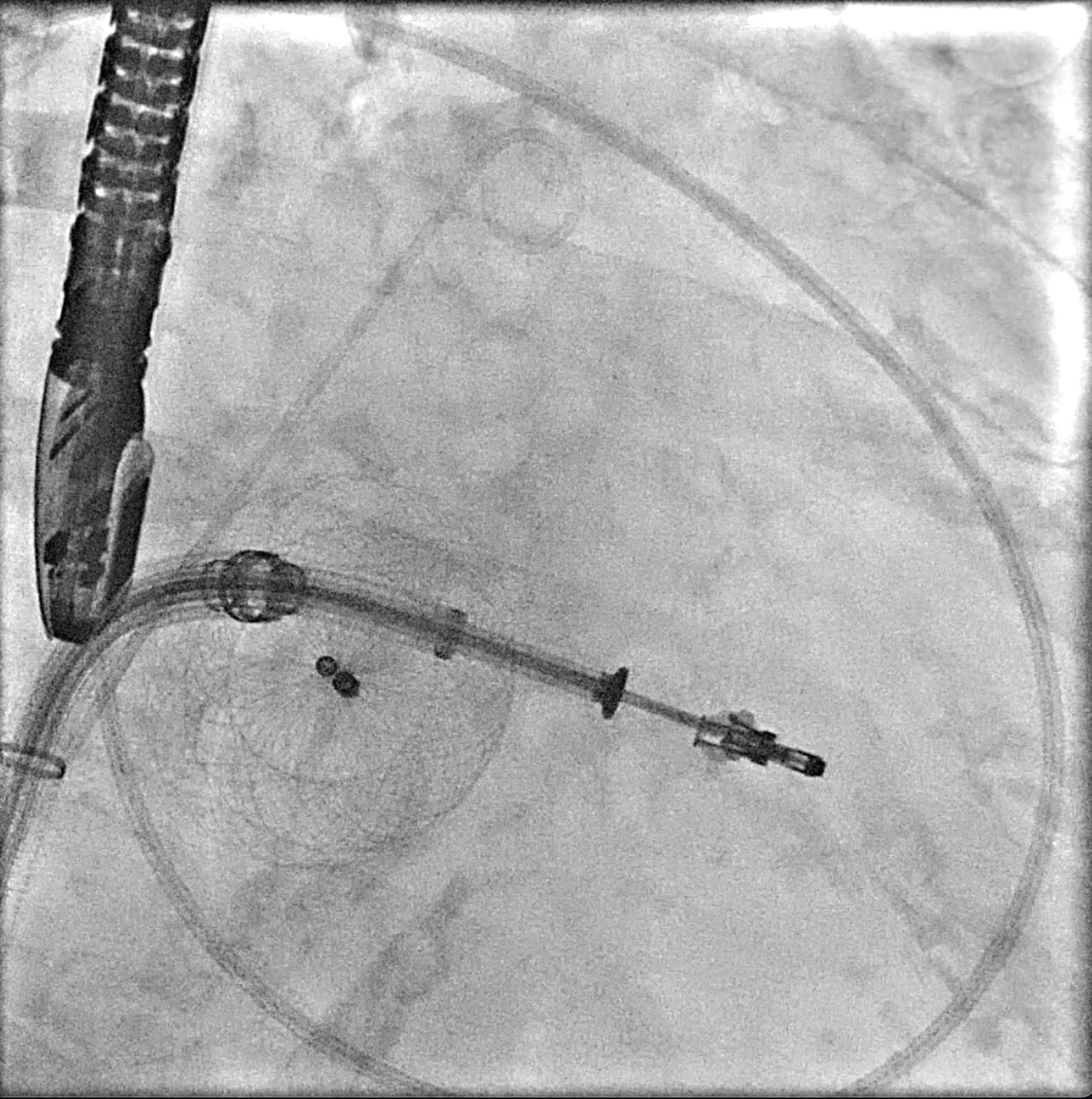
Under general anesthesia, a transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) probe was advanced for imaging guidance. Venous access was obtained via the right femoral vein with 16F Ultimum sheath and preclosure technique with proglide.
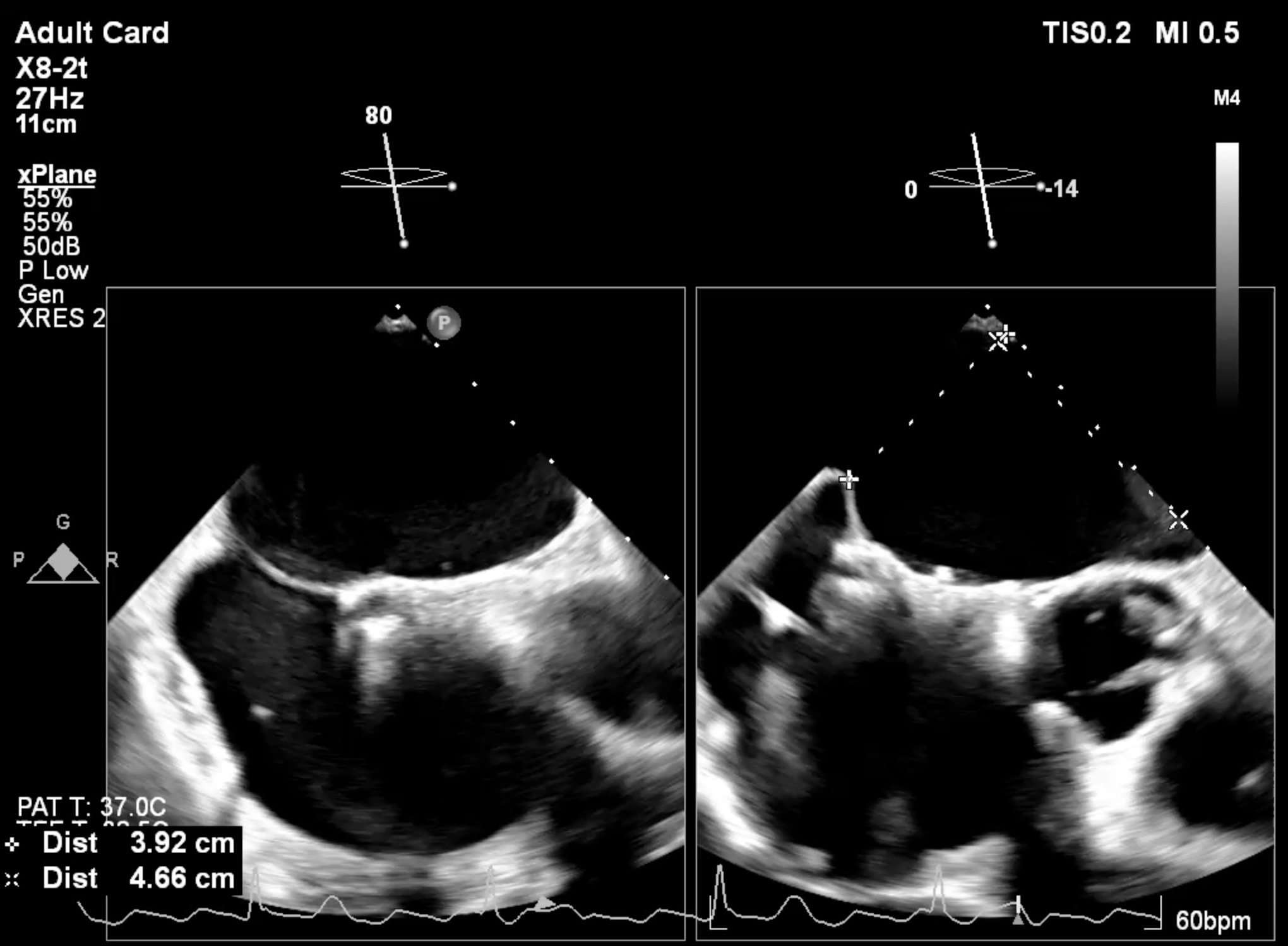



Case Summary
The Mitral valve Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge repair (M-TEER) in patient with an ASD closure device might be challenge due to the complexity of transeptal approach.This condition required careful consideration between puncturing though the device, which may lead to significant residual defect or device deformity and performing a transeptal puncture adjacent to the ASD device, which may result in a high puncture location and difficulty in catheter manipulation. However, even with a suboptimal transeptal puncture (too high or too low), M-TEER procedure can be adjusted by using advanced clip steering to modify height. Therefore, we prefer to puncturing approach outside the device.


