Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-192
Coronary Angioscopic Findings of Biolimus-A9 Coated Stent Deployed for In-Stent Restenosis Lesion
By Taito Nagai
Presenter
taito nagai
Authors
Taito Nagai1
Affiliation
Misato Central General Hospital, Japan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-192
Coronary - Imaging & Physiology - Invasive Imaging (IVUS, OCT, NIRS, VH, etc)
Coronary Angioscopic Findings of Biolimus-A9 Coated Stent Deployed for In-Stent Restenosis Lesion
Taito Nagai1
Misato Central General Hospital, Japan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
Case was 70's female, and she had a history of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation, chronic kidney disease with hemodyalysis. She was diagnosed with angina pectoris and PCI was performed for RCA ostium with drug-eluting stent. Subsequently, in-stent restenosis was occurred repeatedly. Finally Biolimus-A9 Coated Stent was deployed within the stent, and follow up CAG with coronary angioscopy was performed. ECG showed sinus rhythm with inverted T wave of V1-4, and UCG showed normal LV function.

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
At the first procedure, underexpanded stent was deployed without debulking for eccentric calcified plaque of RCA ostium lesion. 1 year and 2 months after the initial procedure, in-stent restenosis due to underexpanded stent was occurred. PCI was performed with drug-coated balloon and another 8 months later, re-restenosis with neointima hyperplasia was occurred.
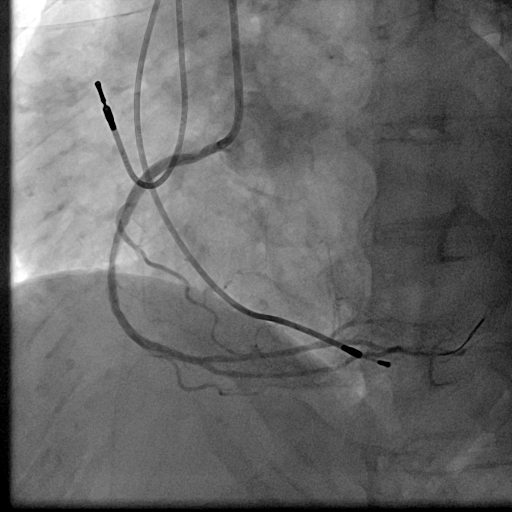
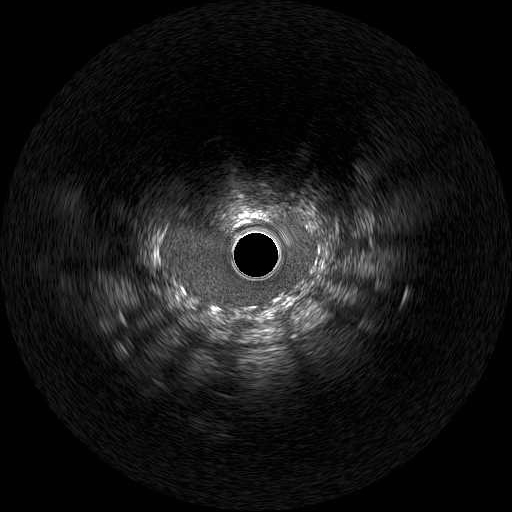
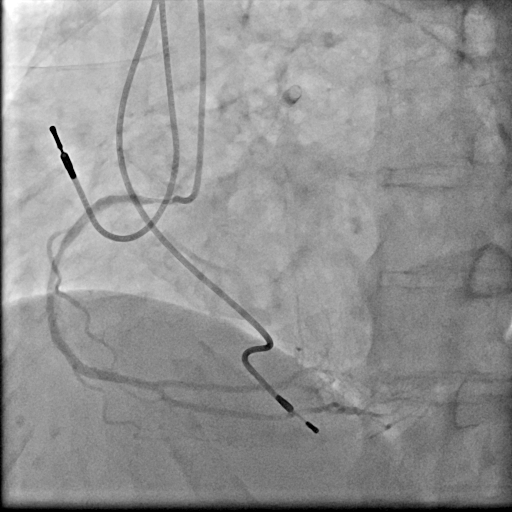



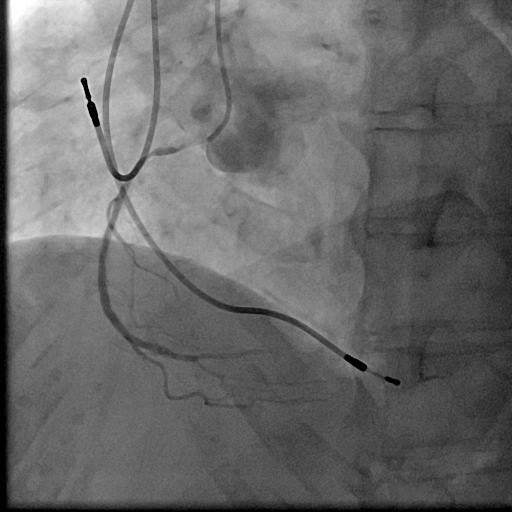
Relevant Catheterization Findings
We used 7Fr JR3.5SH guiding and SION blue ES wire. Wire was easily crossed, and IVUS showed in-stent restenosis with neointimal hyperplasia and underexpanded stent. Long inflation technique using cutting balloon was performed, and Biolimus-A9 coated stent was deployed for in-stent lesion. Post dilation using NC balloon was performed, and procedure was completed. 4 months and 1year and 9 months after the procedure, follow up CAG with coronary angioscopy was performed.
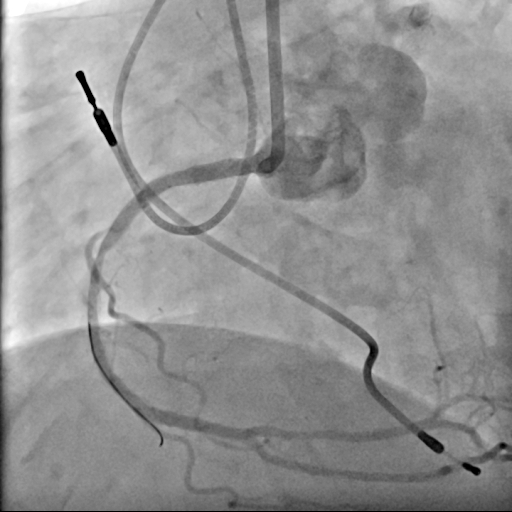
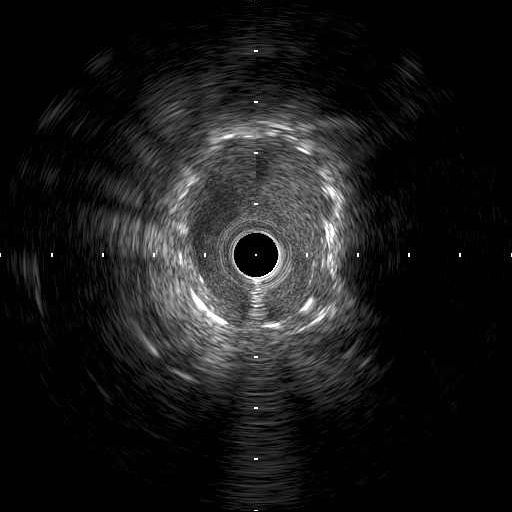


Interventional Management
Procedural Step
1 year and 2 months after the initial procedure using underexpanded stent for eccentric calcified plaque placed at RCA ostium, in-stent restenosis was occurred. PCI was performed with drug-coated balloon and another 8 months later, re-restenosis was occurred. PCI was performed again with Biolimus-A9 coated stent deployed for in-stent lesion. 4 months, and 1 year and 9 months after the stent implantation, CAG was performed with evaluating coronary angioscopy. At the 4 months later, there was no restenosis and we confirmed beginning of neointima coverage for stent strut. At the 1 year and 9 months later, there was also no restenosis, and we confirmed enough and optimal neointimal coverage as vessel healing after stent implantation. Biolimus-A9 coated stent has early drug release system and polymer-free characteristics. The characteristics of the stent may have contributed to get the early smooth and optimal neointimal coverage, and the prevention of malignant cycle of RCA ostium in-stent restenosis.
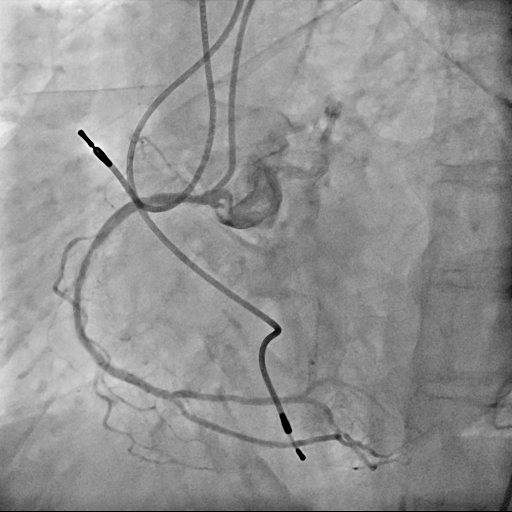

Case Summary
Biolimus-A9 coated stent was deployed for RCA in-stent restenosis lesion, and there was no restenosis at least 2 years after the procedure. The stent may have a possibility of improve the status of in-stent restenosis case with underexpanded stent.


