Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-093
Expect the Unexpected: IVUS-Guided Intervention for Chronic Total Occlusion In-Stent Restenosis
By Nancy Virginia, Kai Soon Liew, Huan Yean Kang, Chai Yih Tan, Kenneth Kay Leong Khoo, Prabahkar Subramaniam, Mohd Khairi Othman, Saravanan Krishinan, Kantha Rao Narasamuloo, Chee Tat Liew, Dharmaraj Karthikesan
Presenter
Nancy Virginia
Authors
Nancy Virginia1, Kai Soon Liew1, Huan Yean Kang1, Chai Yih Tan1, Kenneth Kay Leong Khoo1, Prabahkar Subramaniam1, Mohd Khairi Othman1, Saravanan Krishinan1, Kantha Rao Narasamuloo1, Chee Tat Liew2, Dharmaraj Karthikesan1
Affiliation
Hospital Sultanah Bahiyah, Malaysia1, Hospital Pantai, Malaysia2,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-093
Coronary - Complex PCI - CTO
Expect the Unexpected: IVUS-Guided Intervention for Chronic Total Occlusion In-Stent Restenosis
Nancy Virginia1, Kai Soon Liew1, Huan Yean Kang1, Chai Yih Tan1, Kenneth Kay Leong Khoo1, Prabahkar Subramaniam1, Mohd Khairi Othman1, Saravanan Krishinan1, Kantha Rao Narasamuloo1, Chee Tat Liew2, Dharmaraj Karthikesan1
Hospital Sultanah Bahiyah, Malaysia1, Hospital Pantai, Malaysia2,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 45-year-old male had a history of anterior myocardial infarction (MI) in 2018 for which thrombolysis and subsequent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with a 3.0 x 48 mm drug-eluting stent (DES) was performed to left anterior descending (LAD) artery. His risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) were hypertension, dyslipidemia and ex-smoker. He was recently admitted for an unstable angina.
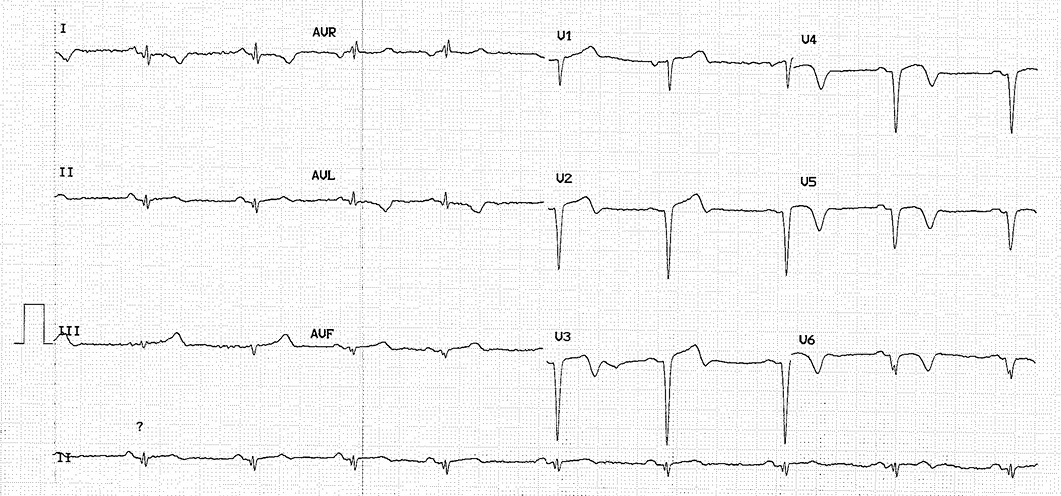

Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Electrocardiogram (ECG) showed sinus rhythm with old anterior MI. Cardiac contractility was still good with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) 68%. Laboratory results showed normal renal function.
Relevant Catheterization Findings
The coronary angiogram revealed chronic total occlusion (CTO) in-stent restenosis (ISR) in the LAD stent, along with moderate disease in the distal left circumflex artery (LCX). The CTO, over 20 mm long, presented with a blunt stump and calcification (J-CTO score =3).
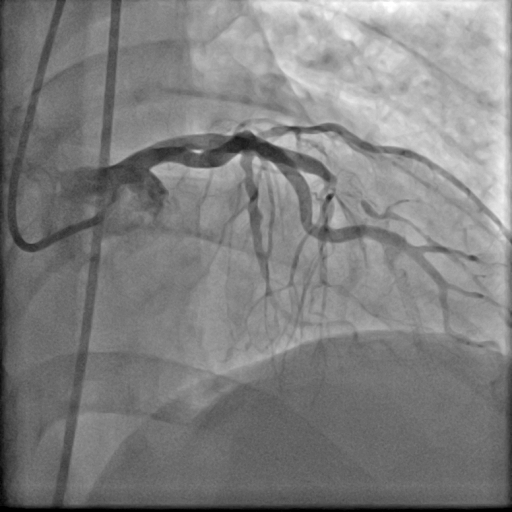
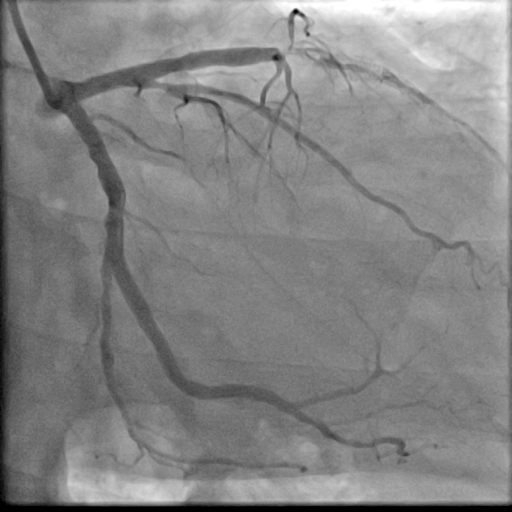
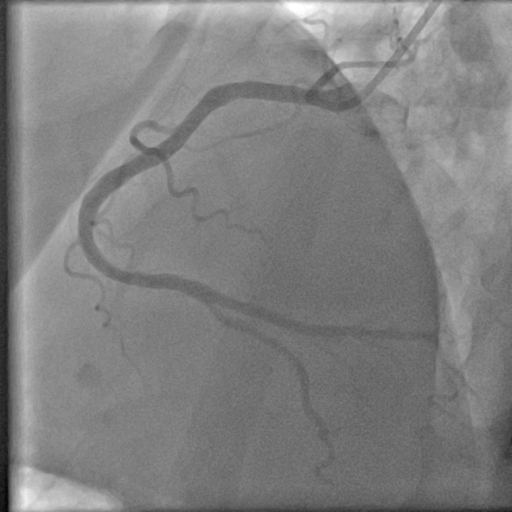



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
PCI was performed via right femoral artery using an EBU 3.5 guiding catheter, with contralateral injection from the right radial artery. Crossing the CTO was challenging and necessitated a wire escalation technique. Attempts with Fielder XT-R, Gaia Next 2, Ultimate Bros 3, and Gaia Next 3 were unsuccessful, with the latter entering a false lumen. Poor retrograde channels from the right coronary artery (RCA) precluded this option. The proximal CTO cap was crossed using a 3D-wiring technique with a Conquest Pro wire which went to the diagonal branch. Using the side branch anchor technique, Gladius wire was able to cross the distal part of the CTO. Intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) displayed a heavy plaque burden and subintimal tracking proximal to the old stent. After lesion preparation, IVUS check revealed a significant portion of the wire was subintimal. For this reason, rewiring was done with a Gladius wire using a slipstream technique. Lesion was further prepared and treated with two drug-coated balloons (DCB). The area proximal to the old stent was stented with a DES. The final IVUS showed good stent apposition, although a dissection flap remained. The final angiogram confirmed TIMI 3 flow with a non-flow-limiting dissection. The patient’s symptoms improved, and he was discharged the next day, with a follow-up angiogram planned in 9-12 months.
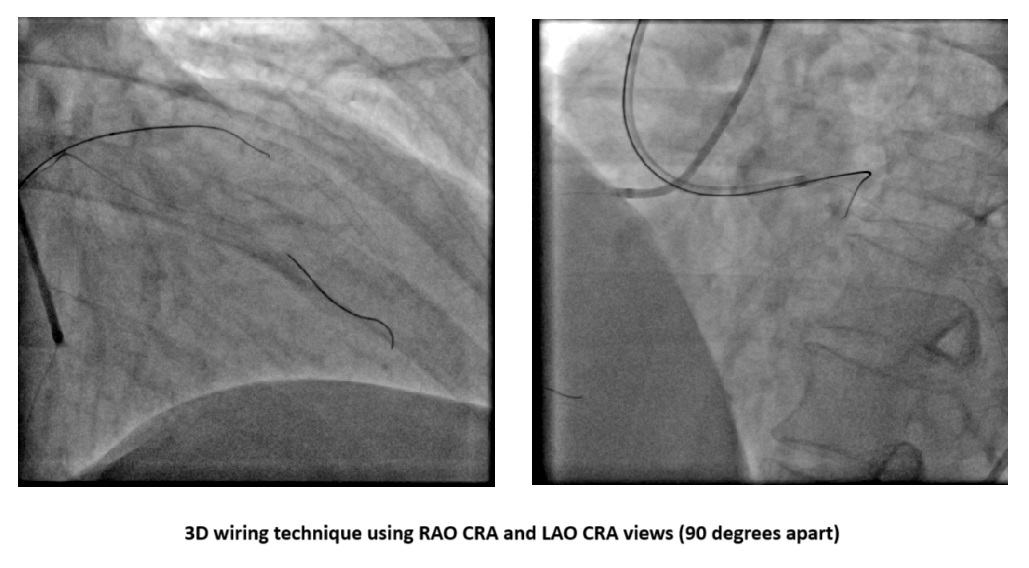
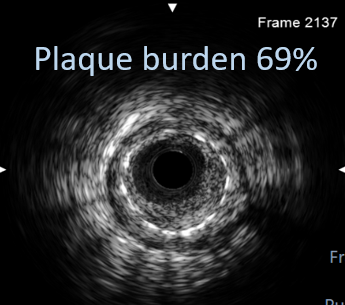
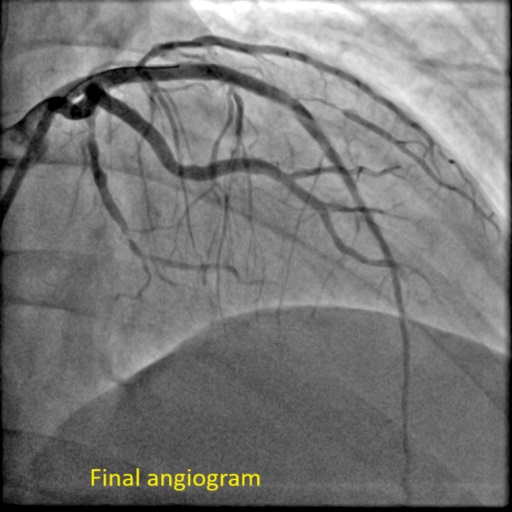



Case Summary
CTO lesions are highly unpredictable, necessitating the use of multiple techniques for successful intervention. Intracoronary imaging is invaluable during CTO ISR interventions to confirm wire position, assess lesions and previous stents, and evaluate preparation, stent expansion, and apposition.


