Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-021
STEMI in the Young: The Deadly Double Infarct Syndrome
By Samrany San, Sokha Chan, Chour Sok
Presenter
Samrany SAN
Authors
Samrany San1, Sokha Chan1, Chour Sok1
Affiliation
Calmette Hospital, Cambodia1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-021
Coronary - ACS/AMI
STEMI in the Young: The Deadly Double Infarct Syndrome
Samrany San1, Sokha Chan1, Chour Sok1
Calmette Hospital, Cambodia1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
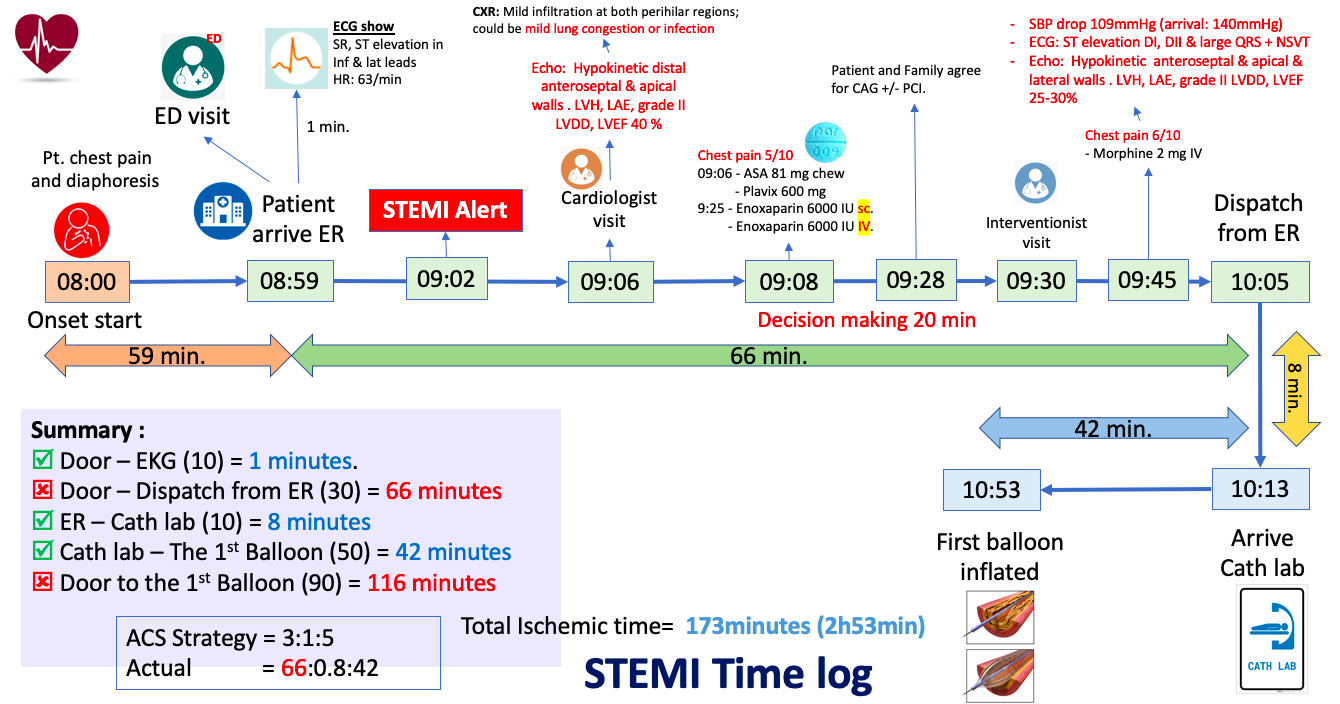
Male, 38 Y.O presenting chest pain for past 1 hour, retrostenal with sweating. His arrival hemodynamic was stable; BP 140/79mmHg, HR: 64bpm, SpO2: 100% in room air. He has unremarkable past medical history beside active smoker. Arrival ECG showed ST elevation DII, aVF, V4-V6 with narrow QRS. 5 minutes later, ECG was changed to ST elevation V1-V3 and q wave in inferio-lateral leads. Bedside ultrasound showed hypokinetic antero-septal and apical with LVEF 40% and grade II LV diastolic dysfunction.
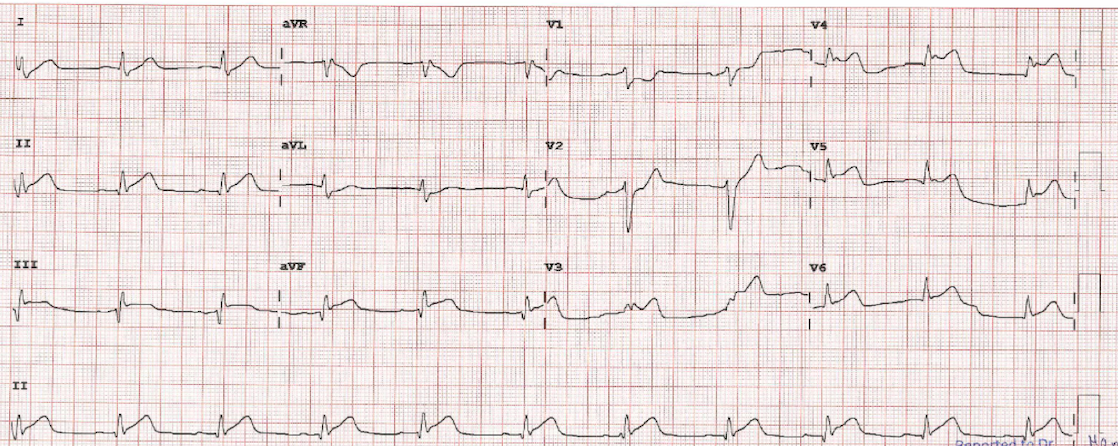


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
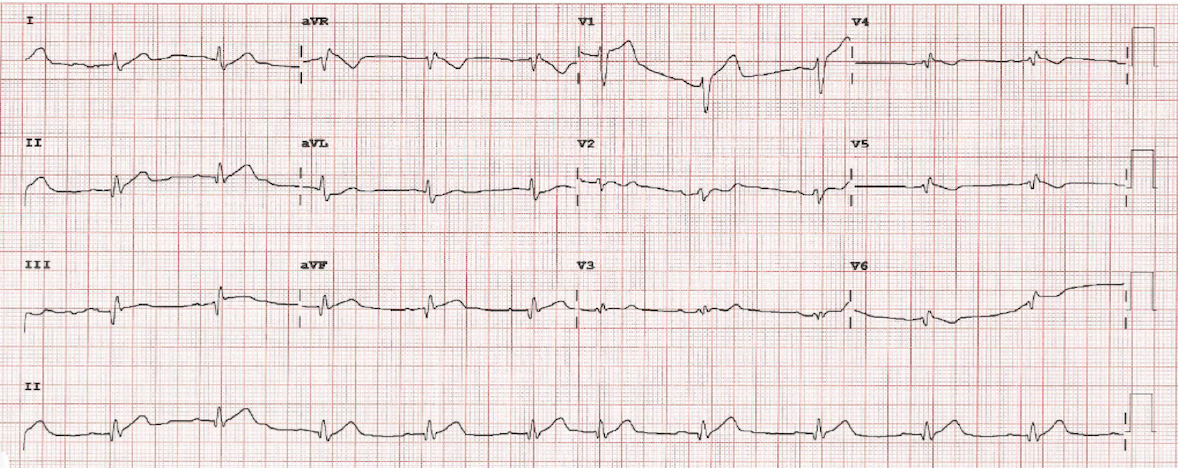
During waiting the decision, he has severe chest pain again. His hemodynamic has changed; SBP drop to 109mmHg with lab results showed lactate 2.9 mmol/l and creatinine 1.02 mg/dl. Base on this modification, his SCAI shock was B. ECG on monitoring showed ST elevation DI, DII and large QRS with non-sustained VT. Bedside heart ultrasound relevant new hypokinetic at lateral wall with LVEF drop to 25-30% and grade II LV diastolic dysfunction. Chest x-ray found mild infiltration at both perihilar.
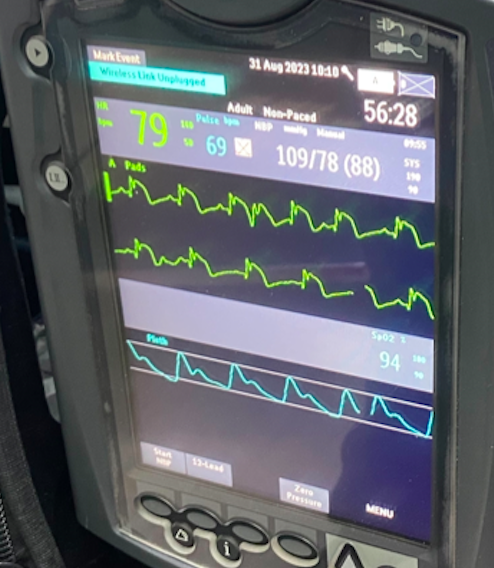
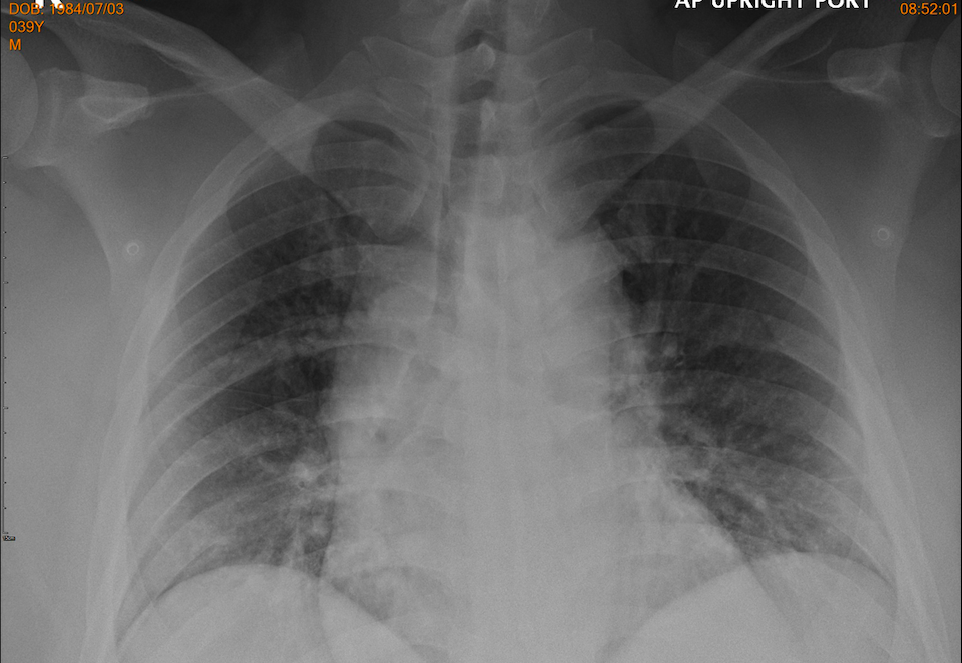



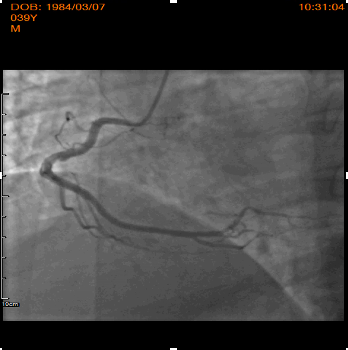
Relevant Catheterization Findings
Emergent coronary angiography was performed using right transradial approach. LVEDP was measured; 22mmHg, hydration 1.5ml/kg/hr was started according to Poseidon protocol. Right coronary artery show non significant lesion, while left system demonstrated total occlusion and sub-occlusion by fresh thrombus to mid LCx and mid LAD respectively. Based on these findings, PCI in the setting of STEMI was performed immediately.
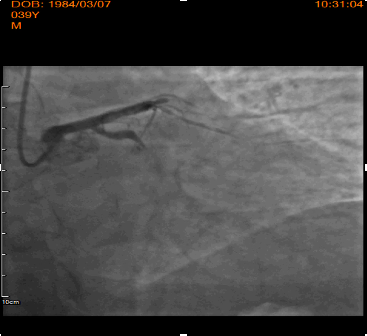
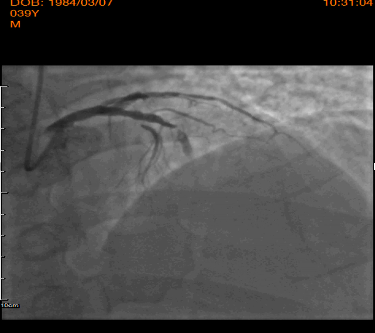



Interventional Management
Procedural Step
After engaged of LM by 6F JL 3.5, LAD lesion was crossed using Whisper MS guidewires. Dues to high thrombus burden, manual aspiration thrombotectomy was performed with Thrombuster aspiration catheter, resulting no thrombus was aspirated. After predilatation (14atm) using 3.0x15mm Sprinter balloon, 4.0x28mm and 4.0x15mmm DES Xience pro were implanted; resulted no-flow distally. After confirmed neither residual stenosis nor distal dissection by distal contrast injection, cocktail of HNF 1000ui and Nitroglycerine 100ug was given repeatedly threefold using Thrombuster catheter to distal coronary; restored TIMI 2-3 flow. Subsequently, PCI of second IRA was performed. After manual aspiration thrombotectomy was performed, resulting in a patent coronary artery with the presence of critical stenosis. 4.0x28mm DES Xience pro was implanted directly with excellent angiographic result and TIMI 3 flow. Post PCI during ICU stay, he developed HF decompensation and Cardiogenic shock. Mechanical circulation support; IABP was inserted to stabilizing hemodynamic. 24hours after restored hemodynamic by IABP, he has persistent lactic acidosis and rhabdomyolysis syndrome. Drug abuse test revealed positive of methamphetamine and cocaine; Methamphetamine intoxication was diagnosed. The patient had complicated by Cardiogenic shock, multi-organs failure, recurrent ventricular tachycardia, and significant deconditioning with against further aggressive treatment and was admitted to a respite a facility.
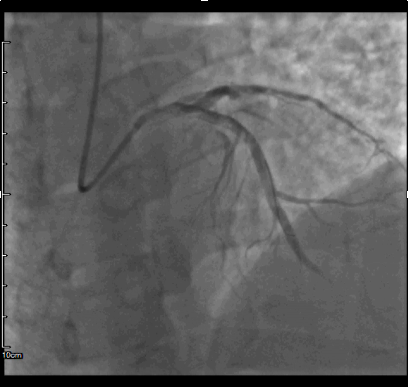
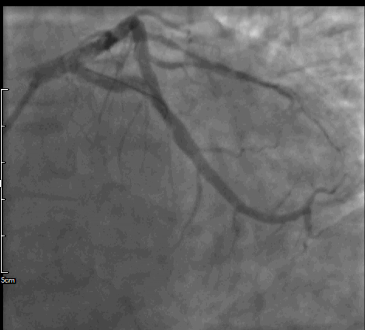
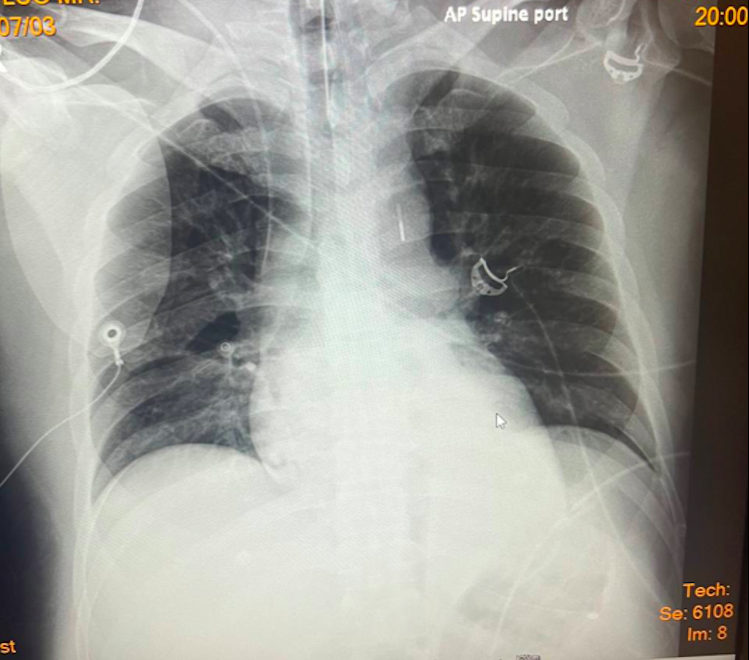



Case Summary
In our case reported a younger man presented the cocaine-induced AMI by double thrombotic occlusion of two major coronary arteries complicated by heart failure, Cardiogenic shock and multi-organs failure. Younger age with rapidly worsen clinical, illegal drug test should be done to help identifier mechanical of lesion and select PCI strategy. SCAI shock classification is mandatory to do in all AMI at admitted and at 24hours to predict the prognosis, identify risk of in-hospital mortality and escalation treatment to optimize outcome.


