Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP C-212
Redo-TAVR in a Patient With Bicuspid Aortic Valve Stenosis and Infective Endocarditis
By Huan Chiu Lin, Chun-Ting Liu, Yung-Tsai Lee, Tien-Ping Tsao, Wei Hsian Yin
Presenter
Huan Chiu Lin
Authors
Huan Chiu Lin1, Chun-Ting Liu1, Yung-Tsai Lee1, Tien-Ping Tsao1, Wei Hsian Yin1
Affiliation
Cheng Hsin General Hospital, Taiwan1,
View Study Report
TCTAP C-212
Structural - Aortic Valve Intervention - Valve in Valve TAVR
Redo-TAVR in a Patient With Bicuspid Aortic Valve Stenosis and Infective Endocarditis
Huan Chiu Lin1, Chun-Ting Liu1, Yung-Tsai Lee1, Tien-Ping Tsao1, Wei Hsian Yin1
Cheng Hsin General Hospital, Taiwan1,
Clinical Information
Patient initials or Identifier Number
Relevant Clinical History and Physical Exam
A 72-year-old man, who had undergone TAVR with a Medtronic Evolut R transcatheter heart valve in 2017 for type 1 bicuspid aortic stenosis, was admitted to our intensive care unit seven years later with symptoms of functional class III heart failure. Physical exam showed bilateral lower lung rales breathing sounds, and bilateral lower limb pitting edema.


Relevant Test Results Prior to Catheterization
Transesophageal echocardiography revealed severe aortic regurgitation due to THV leaflet perforation following untreated infective endocarditis, along with a preexisting paravalvular leak caused by the calcified raphe of the type 1 bicuspid aortic valve.Given the patient’s deteriorating clinical status despite inotropic support, and after three negative blood cultures and five weeks of antibiotic treatment, the heart team decided to proceed with transcatheter treatment.
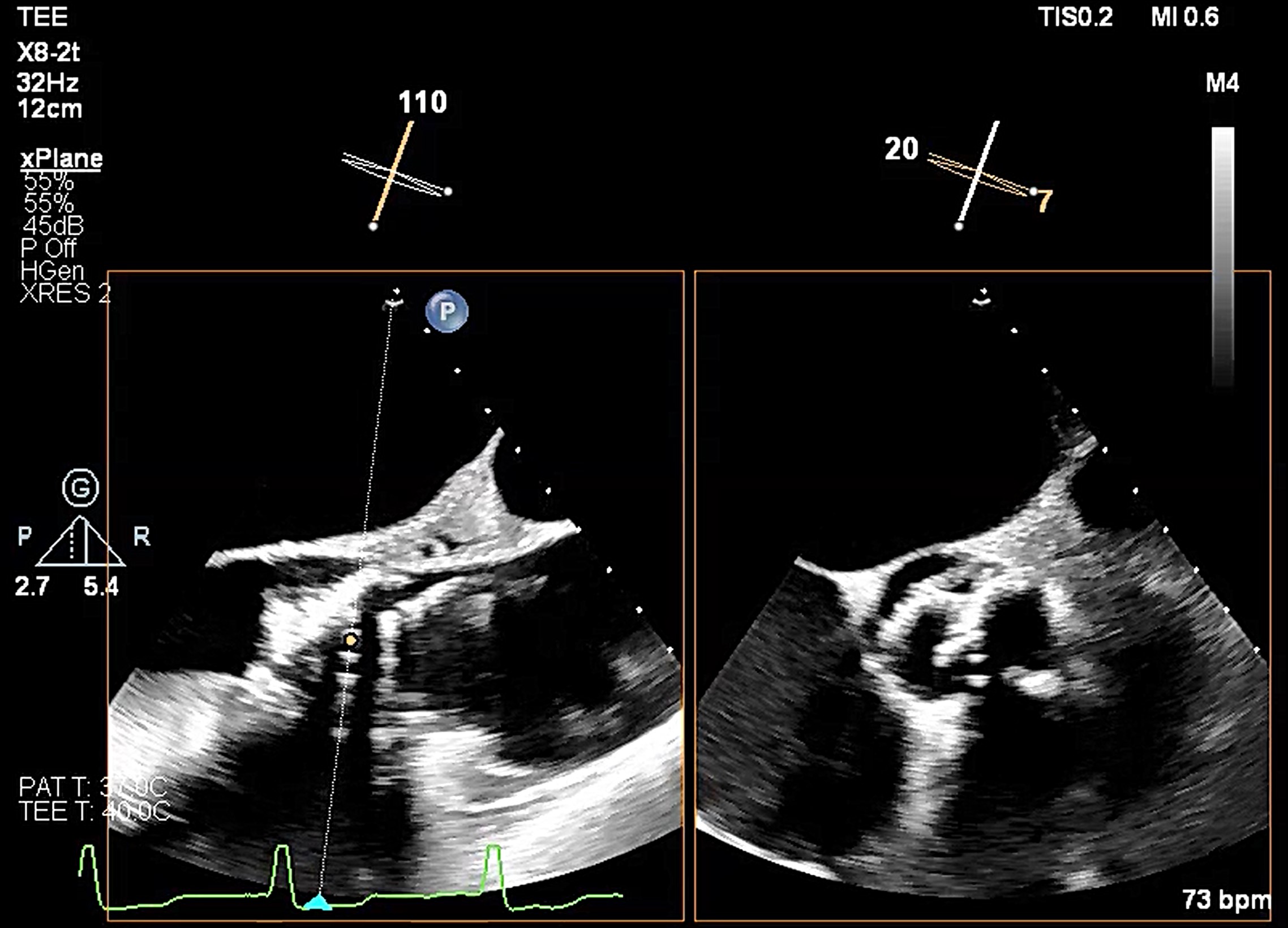
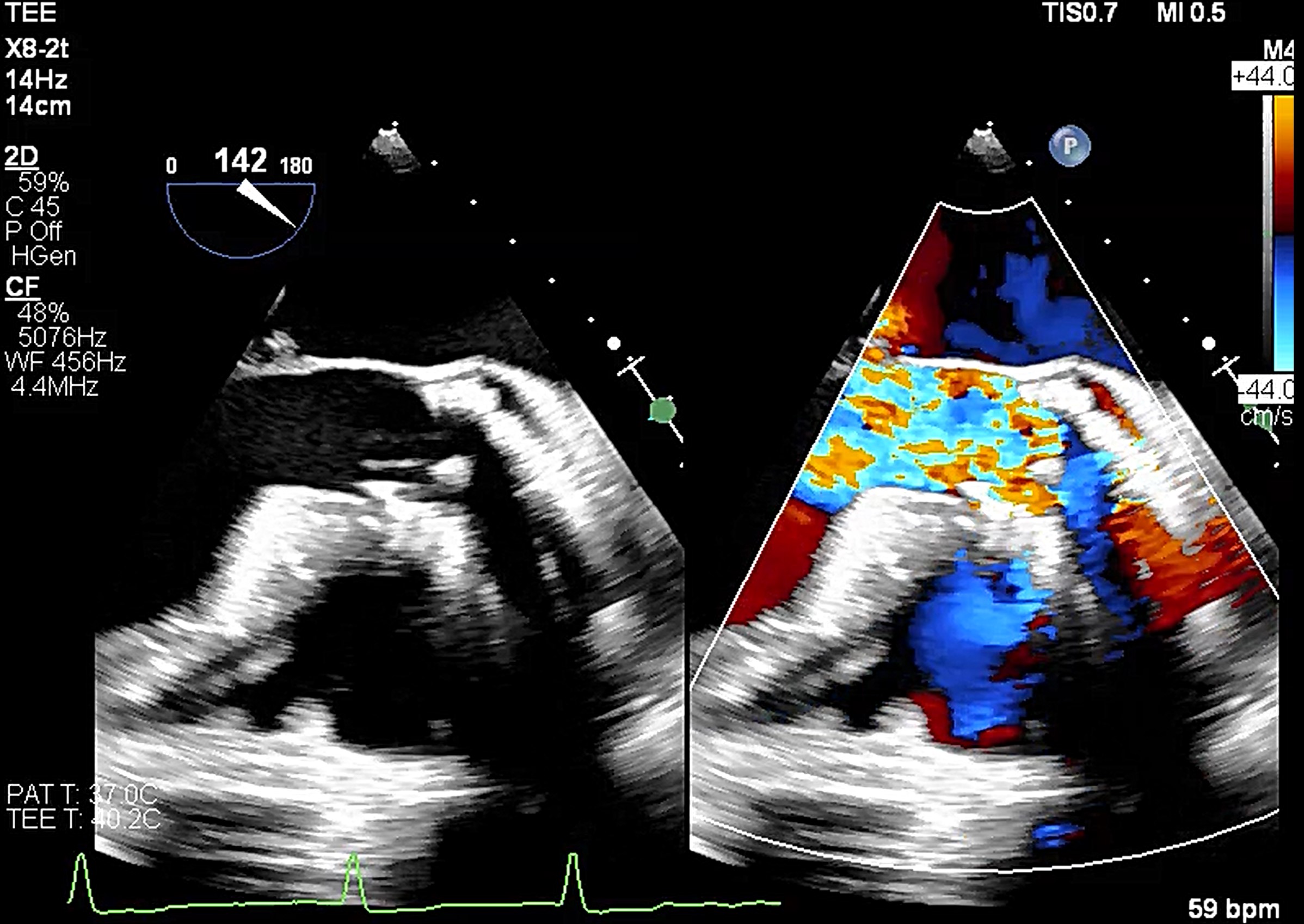
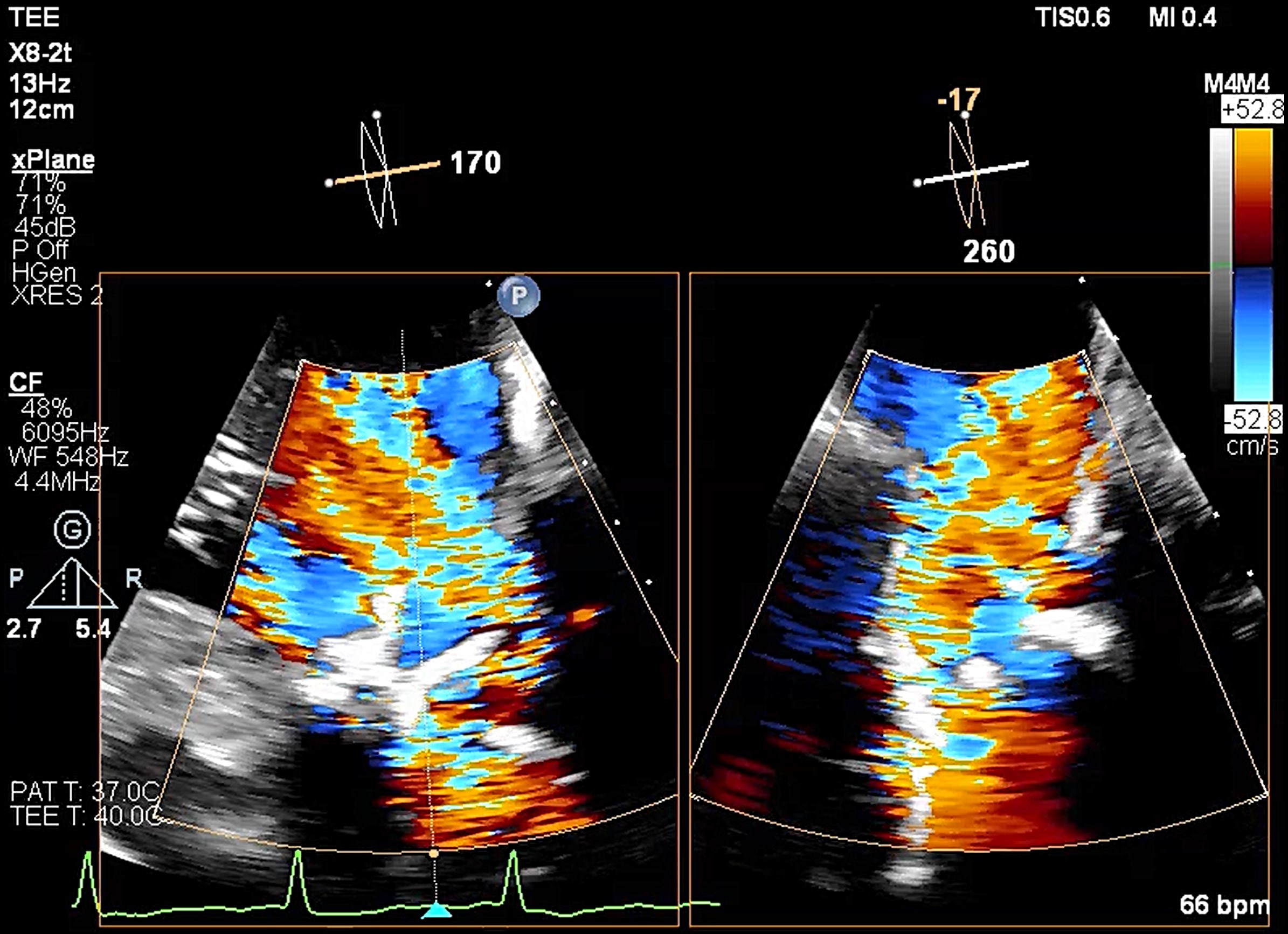



Relevant Catheterization Findings
He underwentTAVR with a Medtronic Evolut R 29mm transcatheter heart valve in 2017 for type 1bicuspid aortic stenosis.
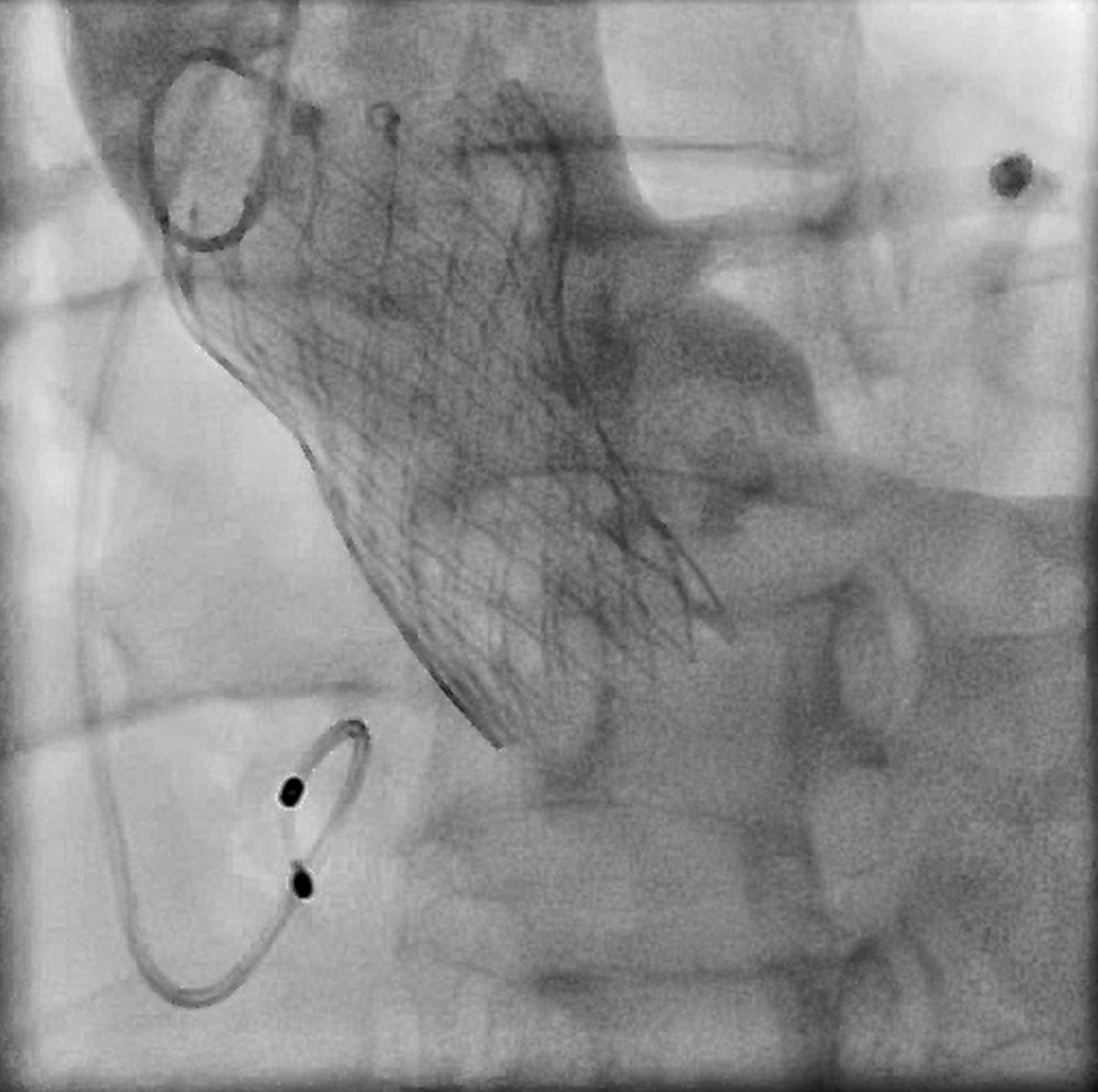

Interventional Management
Procedural Step
A combined procedure including transcatheter closure of paravalvular leak and redo-TAVR, was performed under general anesthesia with transesophageal echocardiographic guidance.1. Bilateral approach via left femoral artery(8Fr non-kinking sheath), right femoral artery(16Fr E-sheath).2. We used a Terumo guide wire accompanied with AL/5F diagnostic catheter to cross the defect of paravalvular leak.3. MP/7F guide catheter accompanied with 6 x 40mm Mustang balloon crossed the paravalvular leak defect by using balloon assisted tracking technique.4. Wire exchanged to Confida super-stiff wire.5. Amplatzer Vascular Plug II 9-12mm occluder was deployed successfully under TEE guidance. 6. TEE showed paravalvular leak downgrade to mild. There was no nearby structure damage, no new pericardial effusion, nor coronary obstruction.7. An Extra-small Safari super-stiff wire was placed in the left ventricle.8. A 23mm Sapien 3 valve was deployed successfully with 1cc overfill.9. The paravalvular leak and valvular AR both sealed successfully, with only minimal paravalvular leak remain.10. The transvalvular mean pressure gradient was 9mmHg, and the valve functioned well.
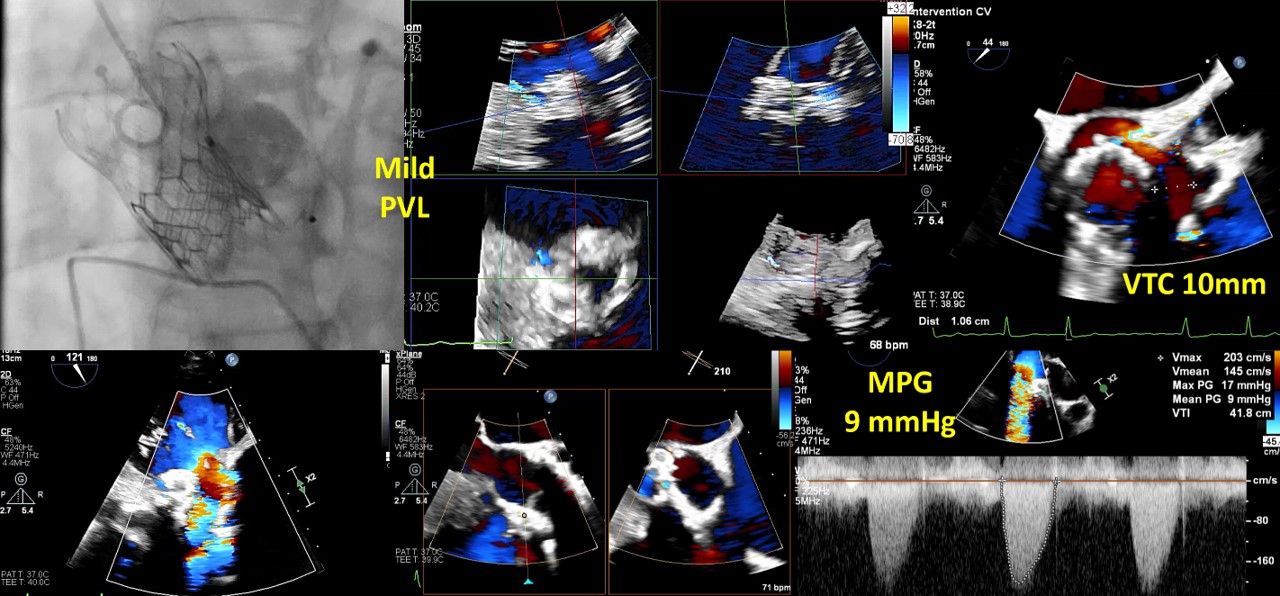

Case Summary
This case report highlights a successful percutaneous closure of a paravalvular leak using an Amplatzer Vascular Plug, followed by a TAVR-in-TAVR intervention in the same procedure. This approach effectively managed a severe THV failure induced by infective endocarditis, which was complicated by severe valvular regurgitation and a paravalvular leak with hemodynamic instability.


