Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-039
Assessing the Real-World Clinical Outcomes of AgentTM (Boston Scientific) Drug-Coated Balloon (DCB) for Coronary Angioplasty Among Patients With and Without Diabetes - A Retrospective Cohort Study
By Ruth Sim, Vireender Kaur, Jas Min Tan, Clement Lim, Callix Wong, Gim Hooi Choo, Kim Tan, Lawrence Hon Wah Chan, Suren Thuraisingham, David Chew, Rosli Bin Mohd Ali, Al Fazir Bin Omar, Khiam Yan Goh, Jayakhanthan Kolanthaivelu, Chee Yoong Foo, Tamil Selvan Muthusamy
Presenter
Jayakhanthan Kolanthaivelu
Authors
Ruth Sim1, Vireender Kaur1, Jas Min Tan1, Clement Lim2, Callix Wong2, Gim Hooi Choo3, Kim Tan3, Lawrence Hon Wah Chan3, Suren Thuraisingham3, David Chew3, Rosli Bin Mohd Ali3, Al Fazir Bin Omar3, Khiam Yan Goh3, Jayakhanthan Kolanthaivelu3, Chee Yoong Foo3, Tamil Selvan Muthusamy3
Affiliation
IQVIA Malaysia, Malaysia1, Boston Scientific Asia Pacific, Singapore2, Cardiac Vascular Sentral Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia3
View Study Report
TCTAP A-039
DES/BRS/DCB
Assessing the Real-World Clinical Outcomes of AgentTM (Boston Scientific) Drug-Coated Balloon (DCB) for Coronary Angioplasty Among Patients With and Without Diabetes - A Retrospective Cohort Study
Ruth Sim1, Vireender Kaur1, Jas Min Tan1, Clement Lim2, Callix Wong2, Gim Hooi Choo3, Kim Tan3, Lawrence Hon Wah Chan3, Suren Thuraisingham3, David Chew3, Rosli Bin Mohd Ali3, Al Fazir Bin Omar3, Khiam Yan Goh3, Jayakhanthan Kolanthaivelu3, Chee Yoong Foo3, Tamil Selvan Muthusamy3
IQVIA Malaysia, Malaysia1, Boston Scientific Asia Pacific, Singapore2, Cardiac Vascular Sentral Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia3
Background
This study evaluates the effects of DCB on restenosis (assessed by cardiac computerized tomography and coronary angiogram) and clinical outcomes in ischaemic heart disease (IHD) patients with and without diabetes, given the unique lesion characteristics in diabetic patients, including diffuse atherosclerosis, longer lesions, negative remodeling, and small vessel disease.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study in Malaysia from 2019 to 2023. The study included adult IHD patients treated with AgentTM (Boston Scientific) paclitaxel-coated DCB. Primary outcomes assessed were restenosis and immediate angiographic success post-DCB procedure. Outcomes were compared between patients with and without diabetes. Additionally, we performed a nested case-control analysis within the diabetic subgroup with angiographic reassessments, to examine factors potentially associated with restenosis, including diabetes control, lesion characteristics and patient characteristics.
Results
This analysis included 1157 patients (58.3% with diabetes) who underwent 1194 DCB procedures for 1641 lesions. Diabetic patients were older and had higher rates of hypertension, chronic renal failure, heart failure, and myocardial infarction, with less family history of premature cardiovascular disease. They showed elevated serum creatinine, reduced left ventricular ejection fraction, lower total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein, and haemoglobin levels, and required more antihypertensives and glucose-lowering medications. They also had longer durations since prior coronary artery bypass grafting, and a higher rate of prior percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Their lesions were less frequently located at side branches, more commonly in-stent restenosis (ISR), more calcified, and had a lower balloon-to-artery ratio. Among 502 lesions with angiographic reassessment (median follow-up : 396 days), restenosis occurred in 16.9% (number of lesions with restenosis=91) of the overall population, 23.0% (number of lesions with restenosis=66) in diabetic patients, 9.9% (number of lesions with restenosis=25) in non-diabetic patients (p-value < 0.05). Angiographic success was achieved in 98.2% of lesions, 6.7% of lesions required bailout stenting due to dissection or had suboptimal results, and minimal post-DCB cardiovascular complications (5.2%) were observed, with no significant differences between subgroups. Within the diabetic subgroup with reassessments, restenosis was found to be associated with ISR lesions, prior PCI and the use of antihypertensives.
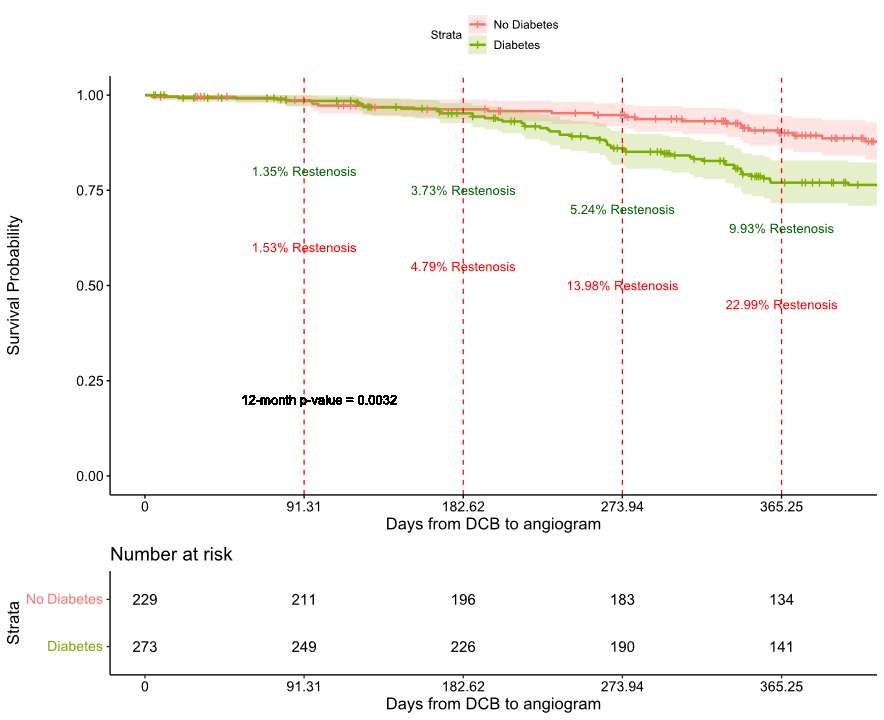

Conclusion
This real-world study demonstrated favorable clinical outcomes of DCB treatment in patients with IHD. However, diabetic patients experienced higher restenosis rates, particularly in ISR lesions, those with prior PCI, and those using antihypertensives. These findings highlight the potential of DCBs as a viable strategy for managing high-risk diabetic populations with complex lesions.


