Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-040
Drug-Coated Balloon Versus Drug-Eluting Stent Revascularization in the Treatment of De Novo Acute Myocardial Infarction
By Ae-Young Her, Yong Hoon Kim, Eun-Seok Shin
Presenter
Ae-Young Her
Authors
Ae-Young Her1, Yong Hoon Kim1, Eun-Seok Shin2
Affiliation
Kangwon National University, Korea (Republic of)1, Ulsan University Hospital, Korea (Republic of)2
View Study Report
TCTAP A-040
DES/BRS/DCB
Drug-Coated Balloon Versus Drug-Eluting Stent Revascularization in the Treatment of De Novo Acute Myocardial Infarction
Ae-Young Her1, Yong Hoon Kim1, Eun-Seok Shin2
Kangwon National University, Korea (Republic of)1, Ulsan University Hospital, Korea (Republic of)2
Background
BACKGROUND:
Methods
METHODS A total of 96 patients with de novoAMI successfully treated with DCB alone were retrospectively enrolled. Visualresidual stenosis ≤ 30% without flow-limiting dissection was considered asatisfactory pre-balloon angioplasty and followed by DCB treatment. We comparedit with 96 propensity-matched patients treated with second-generation drug-elutingstent (DES) from the PTRG-DES registry (n = 13,160 patients). Major adversecardiovascular events (MACE) comprised cardiac death, myocardial infarction,stroke, stent or target lesion thrombosis, target vessel revascularization, andmajor bleeding (Bleeding Academic Research Consortium bleeding type 3 orgreater) at 1 year.
Results
RESULTS Baseline clinical characteristicswere comparable between the groups. The mean device diameter was larger in DESgroup (2.7 ± 0.3 mm vs. 3.1 ± 0.4 mm, P < 0.001). No abrupt vessel closurerequiring treatment occurred after treatment with DCB. The MACE was comparablein both groups (6.2% in DCB group vs. 7.3% in DES group, P = 0.301) at 1-yearfollow-up.
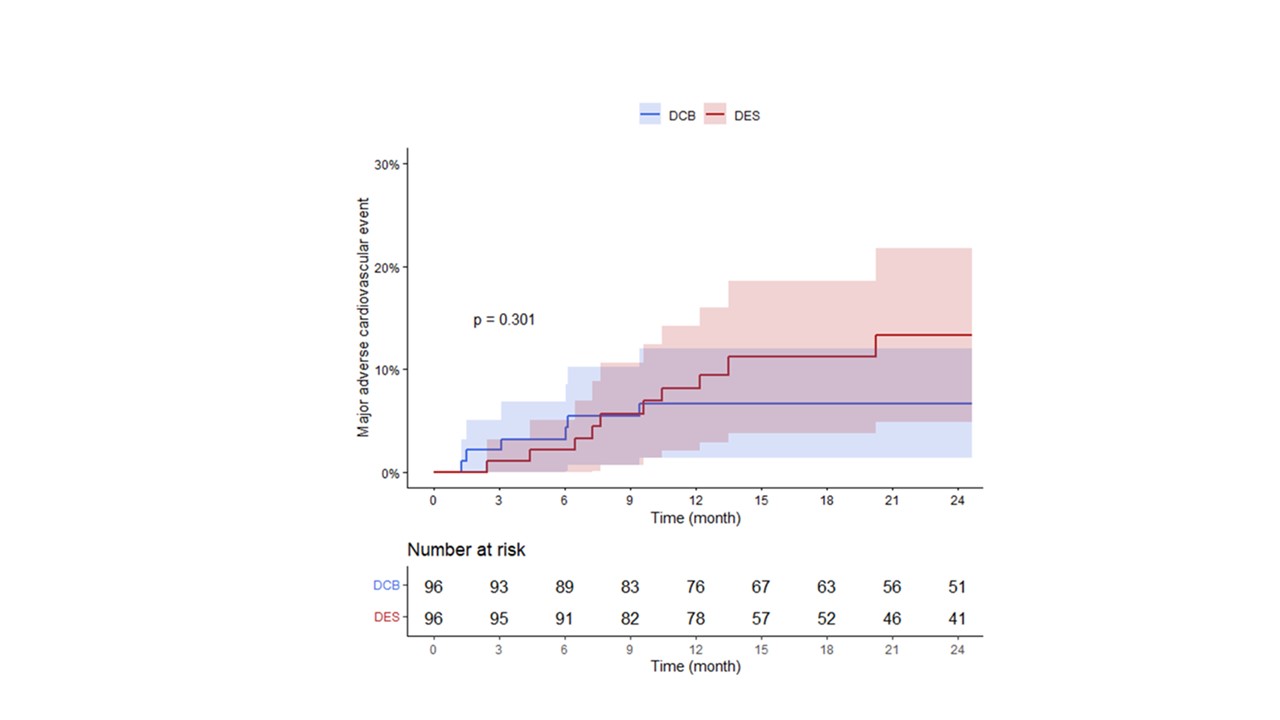

Conclusion
CONCLUSIONS In de novo AMI patients,DCB-only treatment approach had comparable clinical outcomes at 1-yearfollow-up. DCB-only treatment may be a safe and effective alternative to DES incarefully selected patients who had satisfactory pre-dilation results.


