Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-030
Development and Validation of a Global Scoring System for Predicting Technical Success of Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Interventions: The Taiwan Research Initiative on Coronary Total Occlusion (TRIO) Score
By Cheng-Wei Lien, Khaled Saber Qayed, Chih-Fan Yeh, Hsien-Li Kao, Ching-Chang Huang
Presenter
Cheng-Wei Lien
Authors
Cheng-Wei Lien1, Khaled Saber Qayed2, Chih-Fan Yeh1, Hsien-Li Kao1, Ching-Chang Huang1
Affiliation
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan1, Assiut University, Egypt2
View Study Report
TCTAP A-030
CTO
Development and Validation of a Global Scoring System for Predicting Technical Success of Chronic Total Occlusion Percutaneous Coronary Interventions: The Taiwan Research Initiative on Coronary Total Occlusion (TRIO) Score
Cheng-Wei Lien1, Khaled Saber Qayed2, Chih-Fan Yeh1, Hsien-Li Kao1, Ching-Chang Huang1
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan1, Assiut University, Egypt2
Background
Chronic total occlusion (CTO) percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is regarded as one of the most challenging procedures in the field of interventional cardiology. Predicting technical success of CTO PCI was valuable for clinical decision making and procedural planning. Therefore, global scoring systems based on patient and lesion characteristics were needed. Yet, current scoring systems lacked comprehensive evaluation of collateral channels (CC). This study aimed to develop a scoring system incorporating CC features based on The Taiwan Research Initiative on Coronary Total occlusion (TRIO) database.
Methods
We evaluated clinical and angiographic parameters in 698 CTO PCIs between January 2016 and July 2023 from National Taiwan University Hospital (NTUH). Potential predictive parameters significantly associated with technical success were adopted from univariate logistic regression analysis. Selected factors were concurrently entered into a multivariate model. Variables with strong association with technical success in multivariable analysis were used to establish a nomogram as a scoring system, which would be validated in the TRIO database. The TRIO database included 1541 patients receiving CTO PCI between January 2016 and September 2024 from three tertiary centers including NTUH, Linkou Chang-Gung Memorial Hospital (CGMH) and Taipei Veterans General Hospital (TVGH).
Results
We identified six predictors of technical failure and collectedly forming the nomogram (Female, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery bypass graft history, low CC score, moderate/severe bending, and blunt/stumpless/unidentified CTO entry shape). Absence of each parameter was assigned points according to their odd ratio in multivariable analysis. The TRIO score (from 0 to 425 points) demonstrated good predictive value of technical success in both derivation and validation cohort (all p<0.01). The discriminatory capacity was strong in the derivation cohort (Receiver-operator characteristic curves [ROC] area 0.772 in NTUH dataset) and modest in the validation cohort (ROC area 0.606 in CGMH dataset and ROC area 0.570 in TVGH dataset).
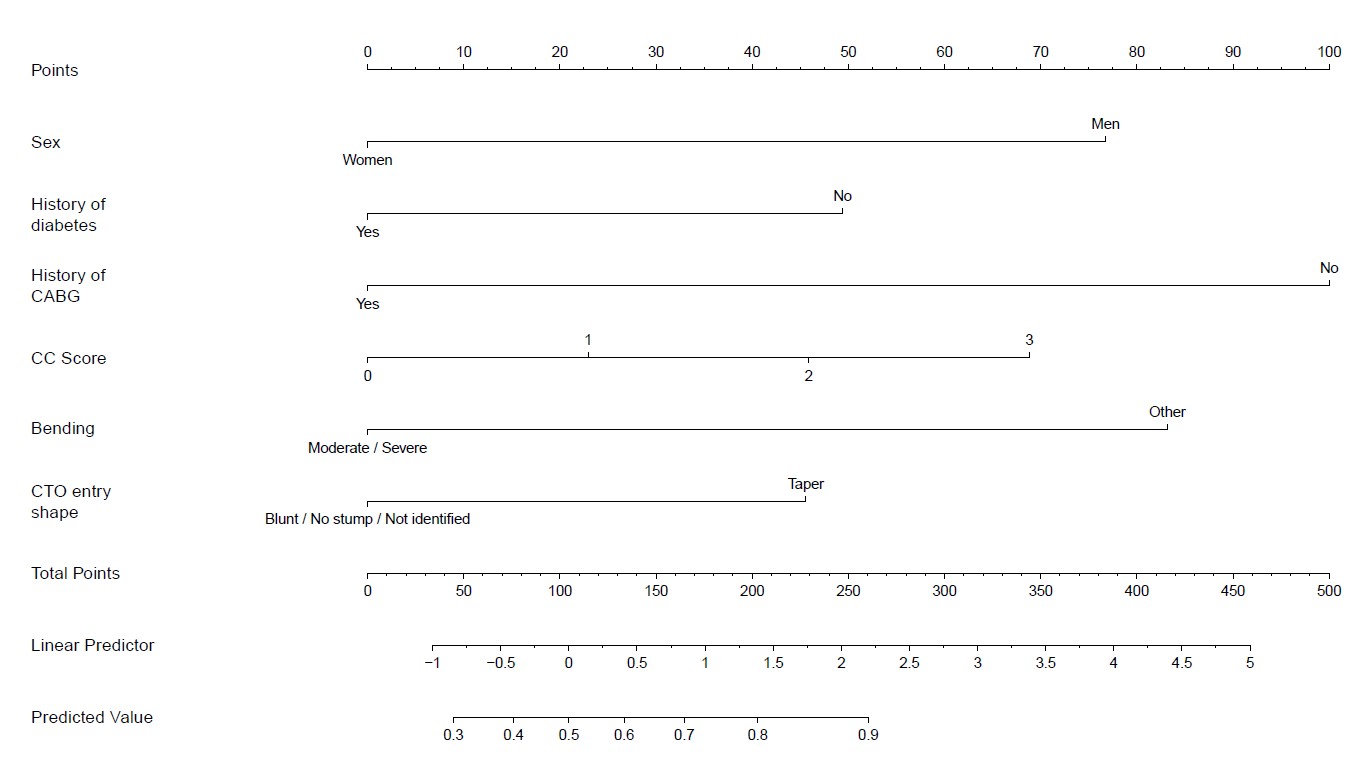
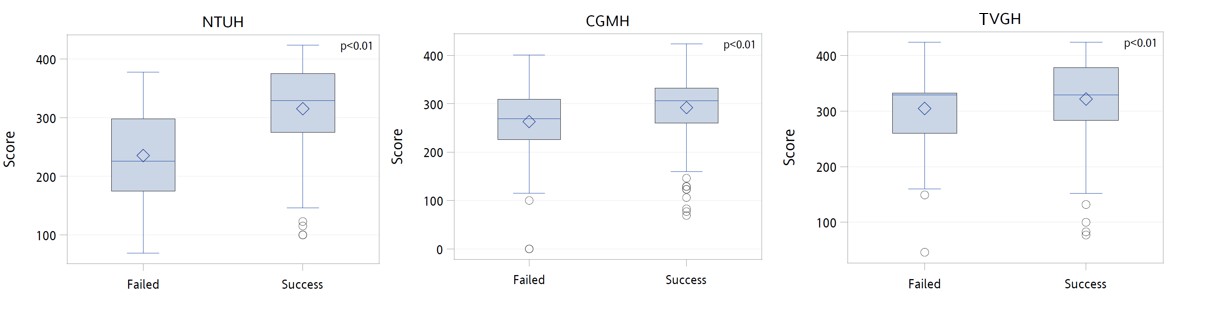
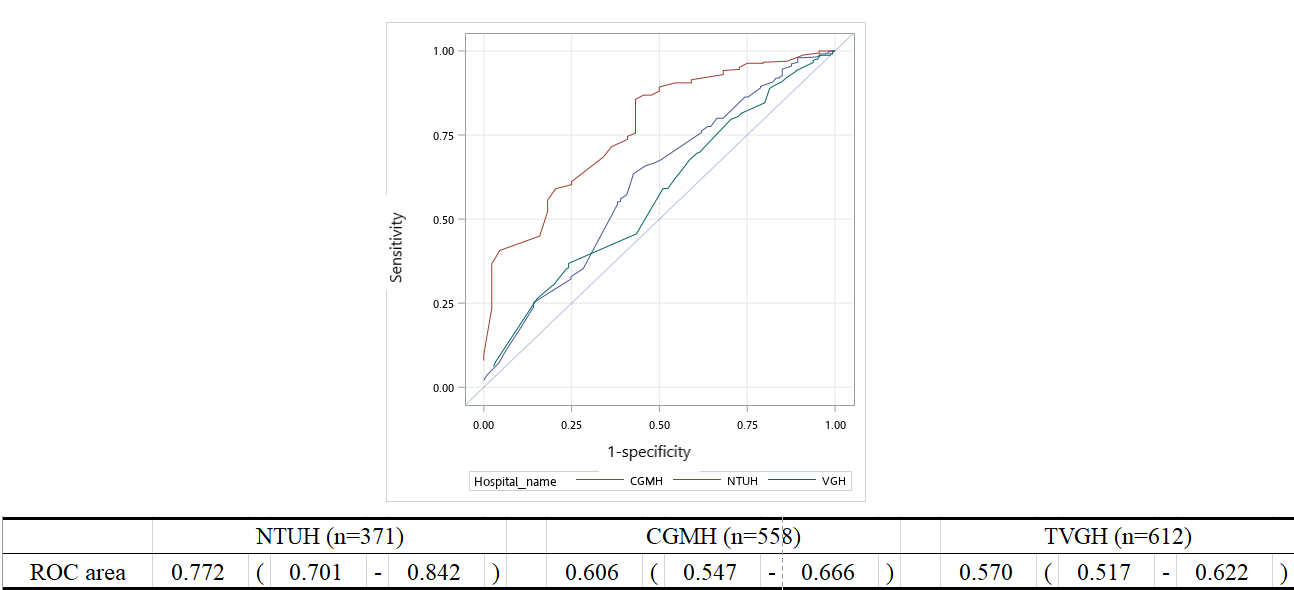



Conclusion
The TRIO (Taiwan Research Initiative on Coronary Total occlusion) score, which incorporates patient, CTO body and CC features, is a global scoring system for predicting technical success in CTO PCI.


