Lots of interesting abstracts and cases were submitted for TCTAP 2025. Below are the accepted ones after a thorough review by our official reviewers. Don’t miss the opportunity to expand your knowledge and interact with authors as well as virtual participants by sharing your opinion in the comment section!
TCTAP A-023
Personalizing Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndrome: Clinical Utility of the HANC Score
By Chia-Chen Lee, Ting-Tse Lin, Kuan-Chih Huang, Yen-Hung Lin, Lian-Yu Lin
Presenter
Chia-Chen Lee
Authors
Chia-Chen Lee1, Ting-Tse Lin1, Kuan-Chih Huang1, Yen-Hung Lin1, Lian-Yu Lin1
Affiliation
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan1
View Study Report
TCTAP A-023
Clinical Trials & Science
Personalizing Antiplatelet Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndrome: Clinical Utility of the HANC Score
Chia-Chen Lee1, Ting-Tse Lin1, Kuan-Chih Huang1, Yen-Hung Lin1, Lian-Yu Lin1
National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan1
Background
High on-treatment platelet reactivity (HPR) to clopidogrel is prevalent among Asian populations. Prior research demonstrated that the HANC score—comprising hemoglobin < 13 g/dL for men and < 12 g/dL for women (H), age ≥ 65 years (A), non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (N), and chronic kidney disease defined by estimated glomerular filtration rate < 60 mL/min (C)—is predictive of HPR in Eastern patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) when ≥ 2 points. This study assessed whether a HANC score ≥ 2 also correlates with poorer clinical outcomes in patients treated with clopidogrel.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the National Taiwan University Hospital-integrated Medical Database, evaluating patients with ACS prescribed clopidogrel based on their HANC score. The primary composite outcome included the incidence of cardiac death, target lesion revascularization, or stroke at one-year follow-up, analyzed with multivariable Cox regression.
Results
From 2009 to 2016, 2,537 patients (78.9% male; mean age, 64.2 ± 13.9 years) met inclusion criteria. Of these, 55.8% had a HANC score ≥ 2, with 1,070 (75.6%) receiving clopidogrel and 345 (24.4%) on non-clopidogrel regimens. The primary outcome among patients with a HANC score ≥ 2 occurred in 35.1% (376/1,070) of clopidogrel group, compared to 26.7% (92/354) in the non-clopidogrel group (hazard ratio 0.77; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.61–0.97; p=0.027). Patients with a HANC score < 2 showed no significant difference in primary outcomes (hazard ratio 1.19; 95% CI, 0.92–1.55; p=0.190). For secondary outcomes, target lesion revascularization (TLR) occurred in 27.2% of clopidogrel patients and 19.7% of non-clopidogrel patients (hazard ratio 0.72; 95% CI, 0.56–0.94; p=0.017). Predictor of TLR in patients with HANC score ≥ 2 included absence of coronary stenting.
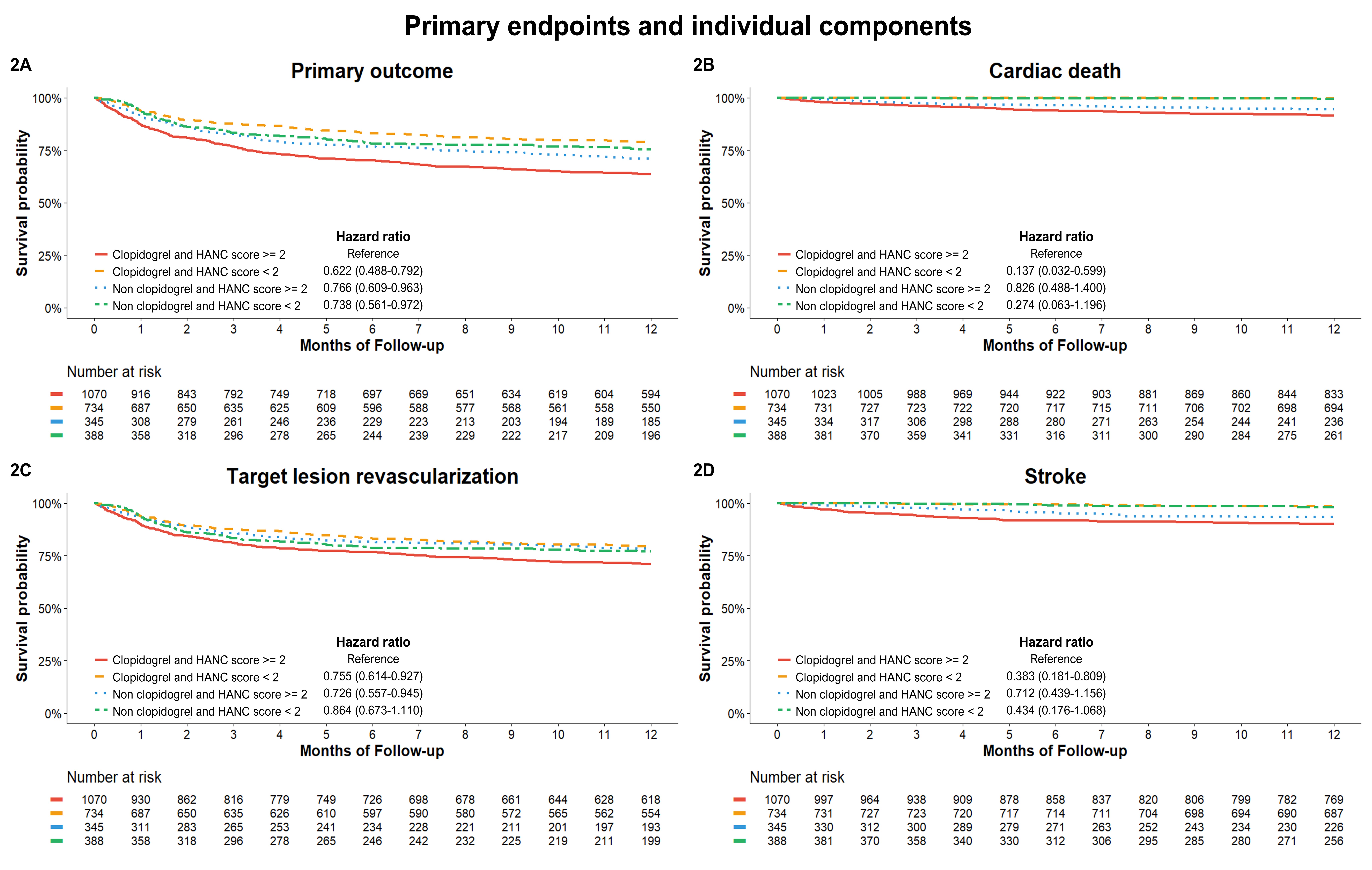
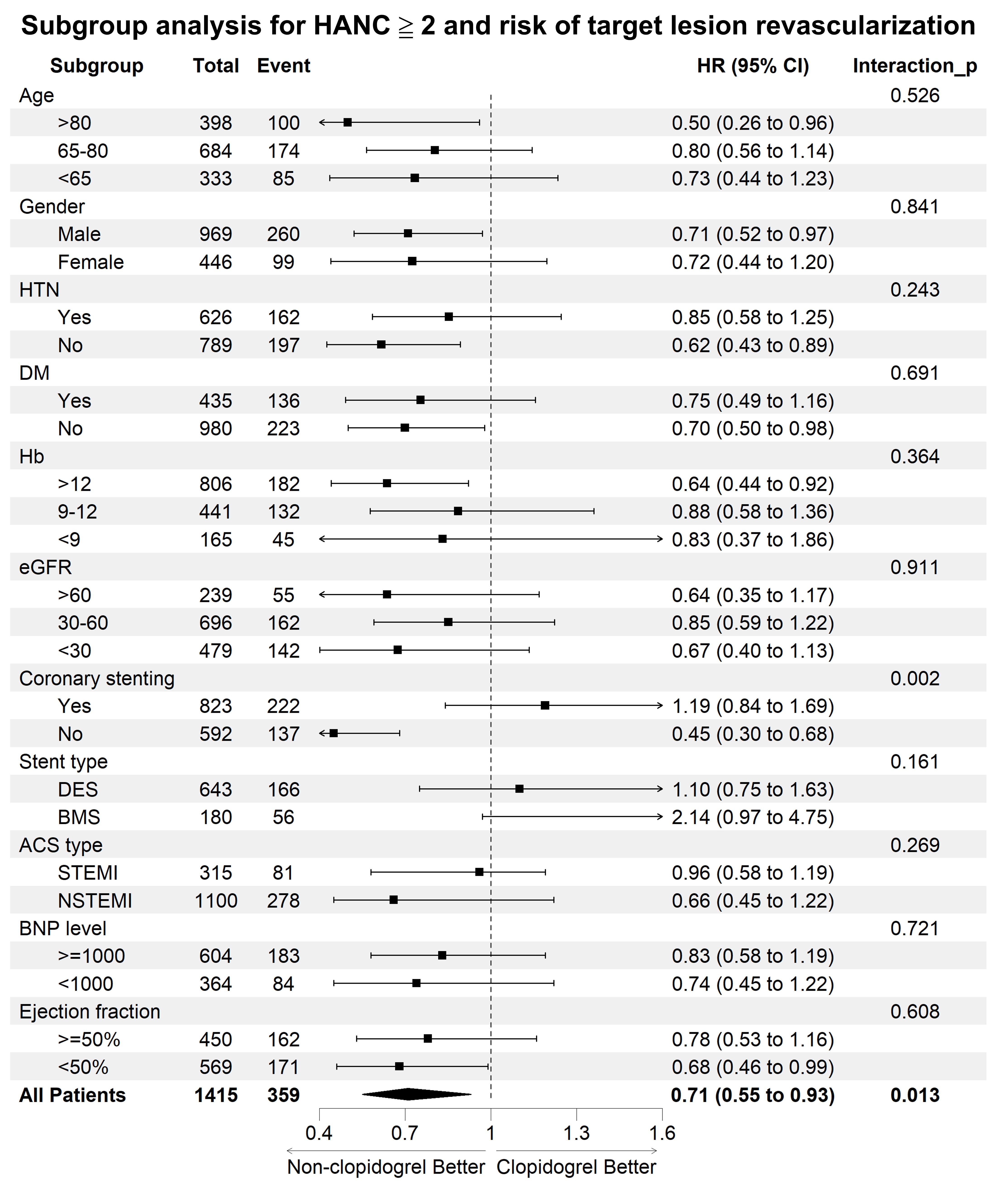


Conclusion
A HANC score ≥ 2 is associated with an increased risk of clopidogrel resistance and target lesion revascularization among ACS patients, underscoring its potential utility in optimizing antiplatelet therapy for this population.


